Low-pass filters allow frequencies below a certain cutoff point to pass through while attenuating higher frequencies, making them ideal for reducing noise and smoothing signals. High-pass filters, in contrast, block low frequencies and let higher frequencies through, which is useful for removing baseline drift and enhancing signal details--discover how choosing the right filter impacts your audio or signal processing needs further in the article.
Table of Comparison
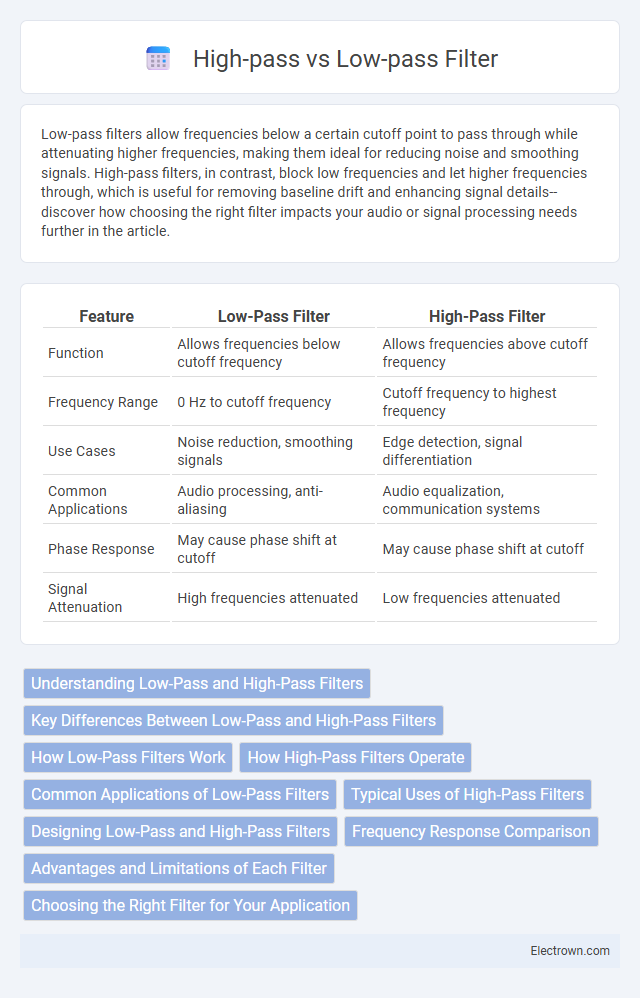
| Feature | Low-Pass Filter | High-Pass Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Allows frequencies below cutoff frequency | Allows frequencies above cutoff frequency |
| Frequency Range | 0 Hz to cutoff frequency | Cutoff frequency to highest frequency |
| Use Cases | Noise reduction, smoothing signals | Edge detection, signal differentiation |
| Common Applications | Audio processing, anti-aliasing | Audio equalization, communication systems |
| Phase Response | May cause phase shift at cutoff | May cause phase shift at cutoff |
| Signal Attenuation | High frequencies attenuated | Low frequencies attenuated |
Understanding Low-Pass and High-Pass Filters
Low-pass filters allow frequencies below a specific cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, making them essential in audio processing and noise reduction. High-pass filters, conversely, permit frequencies above the cutoff frequency to pass, effectively removing low-frequency noise and rumble. Both filters are fundamental in signal processing, enabling precise control over frequency content in applications like communication systems and electronic circuits.
Key Differences Between Low-Pass and High-Pass Filters
Low-pass filters allow frequencies below a specific cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, making them ideal for noise reduction and smoothing signals. High-pass filters, in contrast, permit frequencies above a certain cutoff frequency to pass, effectively removing low-frequency noise and enhancing signal details like edges. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate filter for applications such as audio processing, communication systems, or image enhancement.
How Low-Pass Filters Work
Low-pass filters allow signals with frequencies below a certain cutoff point to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, effectively smoothing out rapid changes in the signal. They are commonly used in audio processing to reduce high-frequency noise and in electronics to prevent aliasing. Your understanding of low-pass filters helps in designing systems that require clean, stable signals without high-frequency interference.
How High-Pass Filters Operate
High-pass filters operate by allowing frequencies higher than a specific cutoff frequency to pass through while attenuating frequencies below that threshold. This is achieved using components like capacitors or inductors that block low-frequency signals and permit high-frequency signals, making them essential in applications such as audio processing and communication systems. Understanding how your high-pass filter functions ensures optimal signal clarity by removing unwanted low-frequency noise.
Common Applications of Low-Pass Filters
Low-pass filters are widely used in audio processing to remove high-frequency noise and preserve the desired low-frequency signals, enhancing sound quality in music and communications. They play a crucial role in image processing for smoothing and reducing sharp transitions, which helps in noise reduction and edge detection tasks. In electronics, low-pass filters protect circuits by blocking unwanted high-frequency signals, ensuring stable and accurate performance of devices like power supplies and radio receivers.
Typical Uses of High-Pass Filters
High-pass filters are typically used to eliminate low-frequency noise or rumble in audio signals, making them essential for improving sound clarity in music production and broadcasting. They are also employed in image processing to enhance edges and fine details by blocking low-frequency background information. Your audio or image system benefits significantly from high-pass filters when you need to isolate and preserve high-frequency components for better quality and precision.
Designing Low-Pass and High-Pass Filters
Designing low-pass and high-pass filters requires selecting the appropriate cutoff frequency to control the bandwidth of the signal passing through the filter. Low-pass filters allow frequencies below the cutoff point to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, ideal for smoothing signals or removing noise. High-pass filters block frequencies below the cutoff, enhancing signal clarity by removing unwanted low-frequency components from your audio or data.
Frequency Response Comparison
Low-pass filters allow frequencies below a cutoff point to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, resulting in a smooth frequency response ideal for noise reduction and signal smoothing. High-pass filters, on the other hand, permit frequencies above the cutoff point and reduce lower-frequency signals, making them effective for eliminating DC offsets and enhancing high-frequency details. Your choice depends on whether you need to preserve low-frequency content or emphasize high-frequency components in your signal processing.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Filter
Low-pass filters excel in removing high-frequency noise, improving signal clarity in audio processing and sensor data, but they can cause signal distortion by attenuating desired high-frequency components. High-pass filters effectively eliminate low-frequency interference and baseline drift, enhancing signal detection of rapid changes, though they may introduce phase shifts and reduce signal strength for lower frequency elements. Both filters require careful cutoff frequency selection to balance signal preservation with noise reduction, tailored to specific application needs.
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate filter depends on the frequency range you want to preserve or eliminate; low-pass filters allow signals below a cutoff frequency to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, ideal for reducing noise or smoothing signals. High-pass filters block frequencies below a set threshold, making them suitable for applications requiring the removal of low-frequency interference or DC offset. Understanding the signal characteristics and target frequency spectrum is crucial for optimizing filter performance in audio processing, communications, or signal conditioning tasks.
low-pass vs high-pass filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com