DSD (Direct Stream Digital) and PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) are two distinct audio encoding formats, with DSD offering a higher resolution through a 1-bit sigma-delta modulation process, while PCM relies on sampling the audio signal at discrete intervals and representing it with multi-bit values. Understanding the differences in sound quality and compatibility between DSD and PCM can help you choose the best format for your audio needs--explore further to learn more about their unique advantages.
Table of Comparison
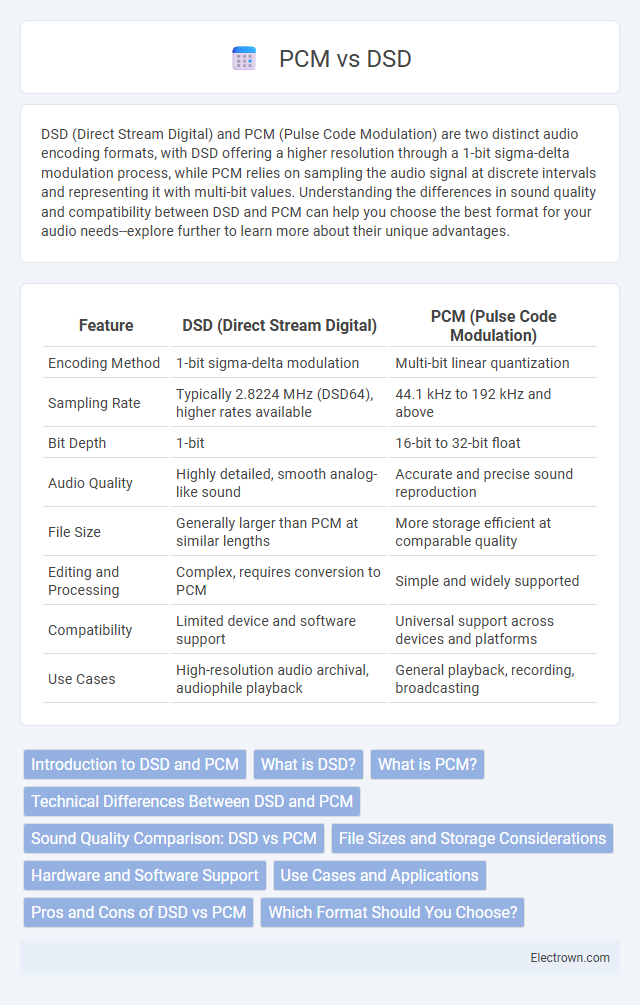
| Feature | DSD (Direct Stream Digital) | PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) |
|---|---|---|
| Encoding Method | 1-bit sigma-delta modulation | Multi-bit linear quantization |
| Sampling Rate | Typically 2.8224 MHz (DSD64), higher rates available | 44.1 kHz to 192 kHz and above |
| Bit Depth | 1-bit | 16-bit to 32-bit float |
| Audio Quality | Highly detailed, smooth analog-like sound | Accurate and precise sound reproduction |
| File Size | Generally larger than PCM at similar lengths | More storage efficient at comparable quality |
| Editing and Processing | Complex, requires conversion to PCM | Simple and widely supported |
| Compatibility | Limited device and software support | Universal support across devices and platforms |
| Use Cases | High-resolution audio archival, audiophile playback | General playback, recording, broadcasting |
Introduction to DSD and PCM
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) and PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) are two primary audio encoding formats used in digital sound reproduction. DSD captures audio as a 1-bit stream sampled at an extremely high rate, often 2.8224 MHz, preserving more of the original analog waveform's details. PCM represents audio by sampling the amplitude at discrete intervals with multiple bits per sample, commonly at rates like 44.1 kHz or 96 kHz, providing precise amplitude resolution for Your digital audio needs.
What is DSD?
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) is a high-resolution audio format that captures sound using a 1-bit sigma-delta modulation process at an ultra-high sampling rate, typically 2.8224 MHz. Unlike PCM (Pulse Code Modulation), which uses multi-bit samples at lower frequencies, DSD preserves more of the original analog waveform's detail, resulting in a warmer and more natural sound reproduction. Your choice of DSD playback can significantly enhance audio fidelity, especially in high-end audiophile systems.
What is PCM?
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a digital audio encoding method that represents analog signals through a series of binary numbers, capturing the amplitude of sound waves at uniform time intervals. PCM is the standard format for digital audio in CDs, DVDs, and many streaming platforms because it offers high fidelity and compatibility across devices. Understanding PCM is essential for comparing it with DSD, as it provides a foundation for how digital audio is sampled and processed in modern playback systems.
Technical Differences Between DSD and PCM
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) encodes audio using a 1-bit sigma-delta modulation at extremely high sampling rates, typically 2.8224 MHz or higher, enabling a continuous bitstream representation of sound with minimal digital filtering. PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) utilizes multi-bit sampling, commonly at 44.1 kHz or 96 kHz with 16-bit or 24-bit depths, capturing discrete amplitude values for each sample. The primary technical difference lies in DSD's single-bit, high-frequency modulation versus PCM's multi-bit, lower-frequency sampling, affecting noise shaping, dynamic range, and the digital-to-analog conversion process.
Sound Quality Comparison: DSD vs PCM
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) offers a natural, smooth sound characterized by its high sampling rate and 1-bit encoding, which captures audio with minimal digital artifacts, making it favored for audiophile-grade recordings. PCM (Pulse Code Modulation), with its multi-bit encoding and widespread use in digital audio, delivers precise and detailed sound, especially at higher bit depths and sampling frequencies like 24-bit/192kHz. Your choice between DSD and PCM sound quality depends on your playback system's compatibility and personal audio preferences, as both formats excel in different sonic nuances.
File Sizes and Storage Considerations
DSD files typically require significantly more storage space than PCM files due to their high bit rates and direct stream encoding, which captures audio with greater detail. PCM formats, like FLAC or WAV, compress audio data more efficiently, resulting in smaller file sizes that are easier to manage on your storage devices. Understanding these differences helps you optimize your audio library by balancing sound quality with available storage capacity.
Hardware and Software Support
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) is supported by a limited range of hardware devices such as high-end digital audio players, DACs, and specialized sound cards that can natively decode DSD streams. PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) enjoys widespread hardware compatibility across nearly all digital audio devices, including CD players, smartphones, and computers, due to its long-standing industry standard status. Software support for PCM is extensive, embedded in virtually all audio playback and editing programs, while DSD requires specific software capable of native or DoP (DSD over PCM) decoding, limiting its accessibility in consumer audio applications.
Use Cases and Applications
DSD excels in high-fidelity audio playback for audiophiles and professional studio mastering due to its continuous waveform representation, providing a more natural sound reproduction especially for classical and jazz music. PCM dominates in digital audio recording, editing, and streaming platforms because of its widespread compatibility, ease of processing, and support in consumer electronics like smartphones and home theater systems. Your choice between DSD and PCM depends on whether your priority lies in ultimate audio purity or practical versatility across various digital media workflows.
Pros and Cons of DSD vs PCM
DSD offers a more natural sound quality with smoother waveforms due to its 1-bit sigma-delta modulation, excelling in capturing analog nuances but demands higher storage and processing power. PCM provides greater flexibility with standardized bit depths and sampling rates, delivering precise digital representation and widespread hardware compatibility, though it may introduce quantization noise and requires complex filtering. The choice between DSD and PCM depends on the priority of audio fidelity versus practicality in encoding and playback capabilities.
Which Format Should You Choose?
Choosing between DSD and PCM depends on your audio equipment and listening preferences. DSD offers a more natural, analog-like sound ideal for audiophiles with compatible DACs and playback systems. PCM is widely supported, versatile, and provides excellent sound quality, making it suitable for general use and digital music production.
dsd vs pcm Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com