Bit depth and sample rate are crucial audio parameters where bit depth determines the dynamic range and sound resolution by defining the number of bits per sample, while sample rate controls the frequency range by measuring how many samples per second are taken from an audio signal. Understanding these differences can help you optimize sound quality for various audio applications, so dive into the full article to learn more about their impact on your audio experience.
Table of Comparison
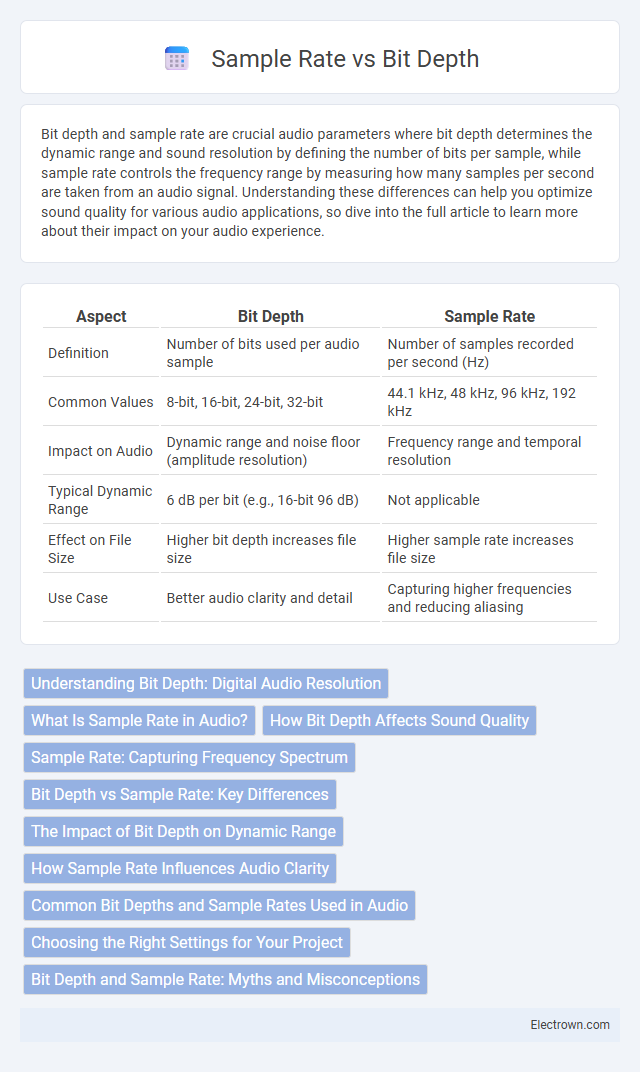
| Aspect | Bit Depth | Sample Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of bits used per audio sample | Number of samples recorded per second (Hz) |
| Common Values | 8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit, 32-bit | 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz, 96 kHz, 192 kHz |
| Impact on Audio | Dynamic range and noise floor (amplitude resolution) | Frequency range and temporal resolution |
| Typical Dynamic Range | 6 dB per bit (e.g., 16-bit 96 dB) | Not applicable |
| Effect on File Size | Higher bit depth increases file size | Higher sample rate increases file size |
| Use Case | Better audio clarity and detail | Capturing higher frequencies and reducing aliasing |
Understanding Bit Depth: Digital Audio Resolution
Bit depth determines the digital audio resolution by specifying the number of bits used to represent each audio sample, directly affecting the dynamic range and noise floor of your recordings. Higher bit depths, such as 24-bit, provide greater detail and lower quantization noise compared to 16-bit, resulting in more accurate sound reproduction. Understanding bit depth helps optimize your audio quality by balancing file size and fidelity alongside sample rate considerations.
What Is Sample Rate in Audio?
Sample rate in audio refers to the number of samples of audio carried per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). It determines the audio's frequency range and fidelity, with common sample rates including 44.1 kHz for CDs and 96 kHz for professional audio recordings. Higher sample rates capture more audio detail, enabling better reproduction of sound but also requiring more storage space.
How Bit Depth Affects Sound Quality
Bit depth directly impacts sound quality by determining the dynamic range and resolution of audio recordings, with higher bit depths reducing quantization noise and allowing for more precise representation of amplitude variations. Common bit depths like 16-bit provide adequate quality for CDs, while 24-bit is preferred in professional audio for capturing greater detail and headroom. Increasing bit depth enhances the clarity and depth of sound, especially in quiet passages and complex audio material.
Sample Rate: Capturing Frequency Spectrum
Sample rate defines how many times per second an audio signal is measured, directly affecting the accuracy of capturing the frequency spectrum up to half the sample rate, known as the Nyquist frequency. Higher sample rates, such as 96 kHz or 192 kHz, enable the recording of ultrasonic frequencies beyond human hearing, allowing for more precise representation of the original sound wave and reducing aliasing artifacts. Bit depth influences dynamic range and noise floor, but the sample rate primarily determines the fidelity of frequency content in digital audio capture.
Bit Depth vs Sample Rate: Key Differences
Bit depth determines the dynamic range and resolution of audio signals by specifying the number of bits used per sample, directly affecting the sound's detail and noise floor. Sample rate defines the number of samples captured per second, influencing the frequency range and overall audio clarity. Understanding the key differences between bit depth and sample rate helps you optimize recording quality for your specific audio needs.
The Impact of Bit Depth on Dynamic Range
Bit depth directly influences the dynamic range of an audio recording, determining how accurately your device can capture the quietest and loudest sounds without distortion. Higher bit depths, such as 24-bit, provide a wider dynamic range up to 144 dB, enabling more detailed sound reproduction with less noise compared to 16-bit's 96 dB range. This expanded range is crucial for preserving audio fidelity in professional music production, film scoring, and high-resolution sound formats.
How Sample Rate Influences Audio Clarity
Sample rate defines how many times per second audio is captured, directly affecting the frequency range your recording can reproduce. Higher sample rates capture more sound detail, improving audio clarity and reducing aliasing artifacts. Your audio's fidelity depends on balancing sample rate with bit depth to ensure precise sound representation and dynamic range.
Common Bit Depths and Sample Rates Used in Audio
Common bit depths in audio range from 16-bit, used in CDs, to 24-bit, prevalent in professional recording and mixing for higher dynamic range. Sample rates frequently include 44.1 kHz, standard for CD audio, and 48 kHz, widely utilized in video production, with higher rates like 96 kHz and 192 kHz employed for high-resolution audio to capture more detail. Choosing appropriate bit depth and sample rate depends on the intended application, balancing file size and audio fidelity.
Choosing the Right Settings for Your Project
Choosing the right bit depth and sample rate depends on the project's purpose and desired audio quality. Higher bit depths such as 24-bit provide greater dynamic range and lower noise floor, ideal for professional music production, while 16-bit is sufficient for standard CD-quality audio. Sample rates like 44.1 kHz are standard for music, whereas 48 kHz or higher are preferred for video post-production to ensure synchronization and detailed audio fidelity.
Bit Depth and Sample Rate: Myths and Misconceptions
Bit depth determines the dynamic range and noise floor of digital audio, while sample rate affects the frequency range captured during recording. Common myths confuse higher sample rates with improved audio quality, though human hearing typically cannot discern frequencies beyond 20 kHz, making standard rates like 44.1 kHz sufficient. Misunderstandings about bit depth often overlook that increased bit depth reduces quantization noise but does not inherently enhance perceived sound clarity beyond certain levels such as 16-bit CD quality.
bit depth vs sample rate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com