Twisted pair cable offers cost-effective, flexible wiring ideal for short to medium distances, while coaxial cable provides superior shielding and bandwidth suited for longer distances and high-frequency signals. Discover which cable type best fits Your networking needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
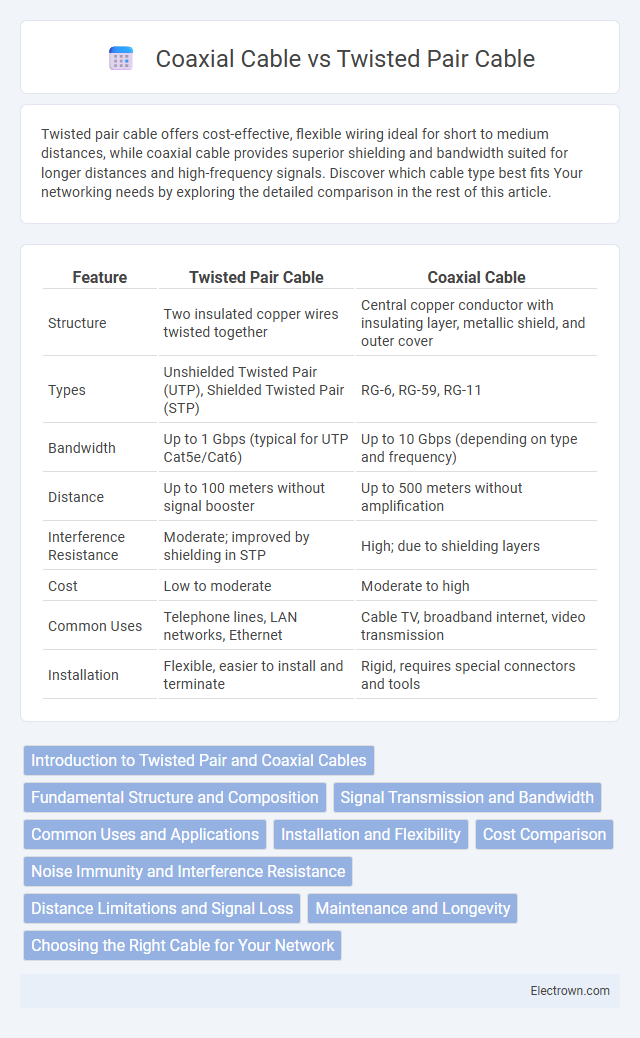
| Feature | Twisted Pair Cable | Coaxial Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two insulated copper wires twisted together | Central copper conductor with insulating layer, metallic shield, and outer cover |
| Types | Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP), Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) | RG-6, RG-59, RG-11 |
| Bandwidth | Up to 1 Gbps (typical for UTP Cat5e/Cat6) | Up to 10 Gbps (depending on type and frequency) |
| Distance | Up to 100 meters without signal booster | Up to 500 meters without amplification |
| Interference Resistance | Moderate; improved by shielding in STP | High; due to shielding layers |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Common Uses | Telephone lines, LAN networks, Ethernet | Cable TV, broadband internet, video transmission |
| Installation | Flexible, easier to install and terminate | Rigid, requires special connectors and tools |
Introduction to Twisted Pair and Coaxial Cables
Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, widely used in telephone and Ethernet networks. Coaxial cables feature a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and a metallic shield, designed to carry high-frequency signals with low signal loss, commonly found in cable television and internet connections. Understanding your network requirements helps determine whether twisted pair or coaxial cable best suits your connectivity needs.
Fundamental Structure and Composition
Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, commonly used in telephone and Ethernet networks. Coaxial cables feature a central copper conductor surrounded by an insulating dielectric layer, a metallic shield, and an outer protective sheath, enabling higher bandwidth and better resistance to signal degradation. The fundamental structural differences determine their respective performance in signal transmission and applications across communication systems.
Signal Transmission and Bandwidth
Twisted pair cables use differential signaling to reduce electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for short to medium distance data transmission with bandwidths typically up to 1 Gbps in standard Ethernet applications. Coaxial cables feature a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator and a metallic shield, offering superior protection against signal loss and electromagnetic interference, enabling higher bandwidths up to 10 Gbps or more over longer distances. The choice between twisted pair and coaxial cables depends largely on the required transmission distance, bandwidth needs, and environmental interference.
Common Uses and Applications
Twisted pair cable is widely used in local area networks (LANs), telephone systems, and Ethernet connections due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Coaxial cable is commonly employed for cable television distribution, broadband internet, and radio frequency transmission because of its superior shielding and higher bandwidth capacity. Your choice depends on the specific requirements of signal quality, distance, and environmental interference in your network infrastructure.
Installation and Flexibility
Twisted pair cables offer easier installation and greater flexibility due to their lightweight and smaller diameter, allowing them to be routed through tight spaces and around corners with minimal effort. Coaxial cables, being thicker and less pliable, require more careful handling and specialized connectors but provide better shielding against electromagnetic interference. Your choice depends on the environment and ease of cable management needed for your network setup.
Cost Comparison
Twisted pair cable generally offers a lower cost per meter compared to coaxial cable, making it a budget-friendly option for most networking setups. Coaxial cable, while more expensive due to its thicker insulation and shielding, provides better resistance to electromagnetic interference and supports higher bandwidth over longer distances. Your choice between the two should consider both initial budget constraints and long-term performance needs to optimize cost-efficiency.
Noise Immunity and Interference Resistance
Twisted pair cables offer moderate noise immunity by using paired wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for short to medium distance data transmission. Coaxial cables provide superior interference resistance due to their single copper conductor enclosed by a grounded shielding layer, effectively blocking external noise and crosstalk. For your network setup, choosing coaxial cable can enhance signal integrity in environments with high electromagnetic interference, while twisted pair cables remain cost-effective for less noisy conditions.
Distance Limitations and Signal Loss
Twisted pair cable typically supports shorter distance transmissions, generally up to 100 meters for Ethernet, due to higher susceptibility to electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation. Coaxial cable offers longer distance capabilities, often exceeding 500 meters, with improved shielding that reduces signal loss and maintains better signal integrity over extended runs. Understanding these distance limitations and signal loss characteristics helps you select the appropriate cable type for your network infrastructure needs.
Maintenance and Longevity
Twisted pair cables generally require more frequent maintenance due to their susceptibility to electromagnetic interference and physical damage, affecting their longevity in harsh environments. Coaxial cables offer superior durability and longer lifespan with better shielding against interference, making them ideal for stable, long-term installations. Your choice between these cables should consider the specific maintenance demands and expected durability based on the operational setting.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Network
When selecting the right cable for your network, twisted pair cables like Cat5e and Cat6 offer cost-effective solutions with excellent flexibility and support for high-speed data transmission up to 10 Gbps over short distances. Coaxial cables provide superior shielding against electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for environments requiring stable signal quality over longer distances, such as in broadband internet or cable TV networks. Assessing factors like network speed requirements, installation environment, and budget will help determine whether twisted pair or coaxial cable best suits your connectivity needs.
Twisted Pair Cable vs Coaxial Cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com