Li-ion batteries offer high energy density and long cycle life, making them ideal for smartphones and laptops, while Li-polymer batteries provide greater flexibility in shape and lighter weight, suited for wearable devices and drones. Discover the detailed differences to determine which battery technology best suits Your needs.
Table of Comparison
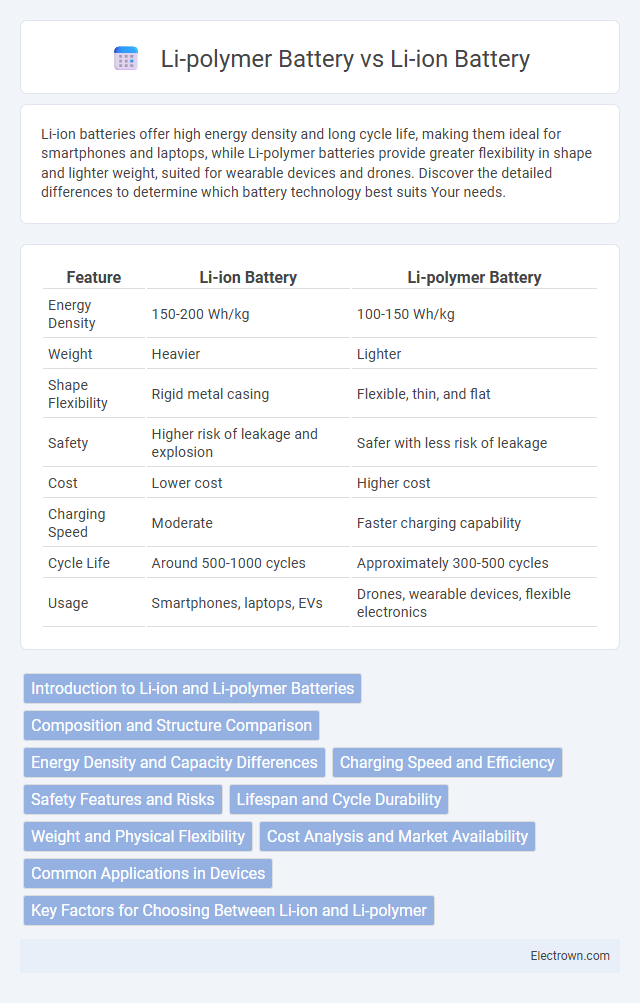
| Feature | Li-ion Battery | Li-polymer Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150-200 Wh/kg | 100-150 Wh/kg |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Shape Flexibility | Rigid metal casing | Flexible, thin, and flat |
| Safety | Higher risk of leakage and explosion | Safer with less risk of leakage |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Charging Speed | Moderate | Faster charging capability |
| Cycle Life | Around 500-1000 cycles | Approximately 300-500 cycles |
| Usage | Smartphones, laptops, EVs | Drones, wearable devices, flexible electronics |
Introduction to Li-ion and Li-polymer Batteries
Li-ion batteries feature liquid electrolytes, offering high energy density and long cycle life, making them ideal for smartphones and laptops. Li-polymer batteries use a solid or gel-like polymer electrolyte, resulting in lighter weight and flexible shapes suitable for wearable devices and drones. Both technologies provide rechargeable power solutions but differ in safety, form factor, and energy storage efficiency.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Li-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte and cylindrical or prismatic cells, offering high energy density with rigid metal casings, while Li-polymer batteries utilize a solid or gel-like polymer electrolyte enabling flexible, lightweight pouch cells. The polymer electrolyte in Li-polymer batteries enhances safety by reducing leakage risks and allows for diverse form factors suited to compact devices. Your choice depends on balancing the need for energy density, shape flexibility, and safety in your specific application.
Energy Density and Capacity Differences
Li-ion batteries typically offer higher energy density, ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, providing more capacity for longer usage in compact devices. Li-polymer batteries, while having slightly lower energy density around 100 to 200 Wh/kg, excel in flexible design and lighter weight, which benefits slim and custom-shaped gadgets. Understanding these differences helps you choose the optimal battery type to match your device's power and form factor requirements.
Charging Speed and Efficiency
Li-ion batteries generally offer faster charging speeds compared to Li-polymer batteries due to their higher energy density and stable electrochemical properties, allowing more rapid energy absorption. However, Li-polymer batteries provide better charging efficiency with less heat generation and reduced risk of swelling, enhancing longevity and safety during charging cycles. When optimizing your device's charging performance, understanding these differences can help in choosing the most suitable battery type for your needs.
Safety Features and Risks
Li-ion batteries offer high energy density but carry risks of overheating and potential thermal runaway if damaged or improperly charged, requiring built-in safety circuits to protect Your devices. Li-polymer batteries use a gel-like electrolyte, reducing leakage risks and enhancing safety with more flexible shapes and lower chances of swelling or rupture. Both technologies include protective features such as overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit prevention to minimize safety hazards.
Lifespan and Cycle Durability
Li-ion batteries typically offer a lifespan of 500 to 1,000 charge cycles, maintaining around 80% capacity before degradation significantly impacts performance. Li-polymer batteries generally exhibit similar cycle durability, but their flexible form factor allows for slimmer designs without compromising longevity. Both battery types benefit from optimized charge and discharge practices to maximize lifespan and cycle efficiency in various electronic applications.
Weight and Physical Flexibility
Li-ion batteries generally have a higher energy density but are heavier compared to Li-polymer batteries, which offer a lighter overall weight ideal for portable devices. Li-polymer batteries feature flexible, thin, and customizable shapes due to their gel-like electrolyte, providing superior physical flexibility over the rigid, cylindrical or prismatic Li-ion cells. This flexibility enables Li-polymer batteries to fit into unconventional and compact designs, making them preferred for modern smartphones, wearables, and drones.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Li-ion batteries generally offer a lower cost per watt-hour compared to Li-polymer batteries, making them a more budget-friendly option for mass-market applications. Li-polymer batteries, while typically more expensive due to their flexible packaging and lighter weight, are increasingly available in consumer electronics where space and weight are critical. Your choice depends on balancing upfront cost savings with specific device requirements and availability in your target market.
Common Applications in Devices
Li-ion batteries are commonly found in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long cycle life. Li-polymer batteries, favored for their flexible shapes and lightweight design, are used in wearable devices, drones, and tablets where form factor and safety are critical. Your choice between these battery types depends on the device's size constraints and performance requirements.
Key Factors for Choosing Between Li-ion and Li-polymer
Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer cycle life, making them ideal for devices requiring extended usage and compact design. Li-polymer batteries provide greater flexibility in shape and safety due to their solid electrolyte, which reduces the risk of leakage or explosion. Cost, application-specific size constraints, and weight are critical factors when deciding between Li-ion and Li-polymer battery technologies.
Li-ion vs Li-polymer Battery Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com