Single supply op amps operate with a single positive voltage source, making them ideal for battery-powered or low-voltage applications, while dual supply op amps use both positive and negative voltage sources, allowing for better handling of AC signals and improved signal swings. Explore the rest of the article to understand which configuration best suits Your electronic design needs.
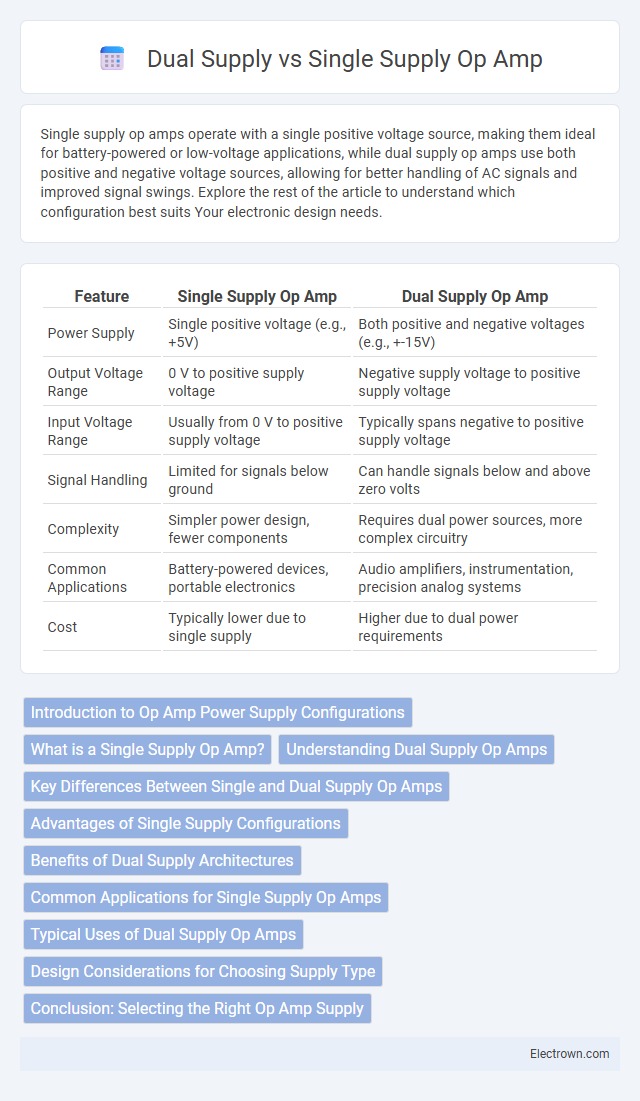
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single Supply Op Amp | Dual Supply Op Amp |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Single positive voltage (e.g., +5V) | Both positive and negative voltages (e.g., +-15V) |
| Output Voltage Range | 0 V to positive supply voltage | Negative supply voltage to positive supply voltage |
| Input Voltage Range | Usually from 0 V to positive supply voltage | Typically spans negative to positive supply voltage |
| Signal Handling | Limited for signals below ground | Can handle signals below and above zero volts |
| Complexity | Simpler power design, fewer components | Requires dual power sources, more complex circuitry |
| Common Applications | Battery-powered devices, portable electronics | Audio amplifiers, instrumentation, precision analog systems |
| Cost | Typically lower due to single supply | Higher due to dual power requirements |
Introduction to Op Amp Power Supply Configurations
Operational amplifiers (op amps) can be powered using either single supply or dual supply configurations, each impacting circuit design and performance. Single supply op amps operate from a positive voltage and ground, simplifying power requirements but requiring level shifting for signals near ground. Dual supply op amps use symmetric positive and negative voltages, enabling input and output signals to swing around zero volts, improving linearity and dynamic range for analog applications.
What is a Single Supply Op Amp?
A single supply op amp operates using one positive voltage source and ground, allowing the device to amplify signals when only a single positive power rail is available. This type of amplifier is commonly used in battery-powered or low-voltage applications where dual power supplies are impractical. Single supply op amps require specific input and output voltage ranges to function correctly within the limited voltage swing compared to dual supply configurations.
Understanding Dual Supply Op Amps
Dual supply op amps operate with two voltage sources, typically positive and negative rails (e.g., +-15V), enabling the output to swing both above and below ground level. This configuration simplifies signal processing for AC signals and allows symmetric voltage swings, reducing distortion and cliping issues in analog circuits. Dual supply op amps are ideal for applications requiring true zero-voltage reference points, such as audio amplification and analog computation.
Key Differences Between Single and Dual Supply Op Amps
Single supply op amps operate with a single positive voltage rail and ground, simplifying power design but requiring level shifting for signals near ground, whereas dual supply op amps use both positive and negative voltage rails, enabling direct amplification of AC signals centered around zero volts. Single supply designs are ideal for battery-powered or low-voltage applications, offering reduced complexity and lower cost, while dual supply op amps provide better signal range and linearity for applications demanding symmetrical voltage swings. Your choice depends on voltage availability, signal type, and circuit complexity, influencing performance and power consumption in precision analog systems.
Advantages of Single Supply Configurations
Single supply operational amplifiers simplify power management by requiring only one voltage source, which reduces design complexity and cost. They enable more compact and energy-efficient circuits, particularly beneficial in battery-powered and portable devices. Improved compatibility with digital circuits operating at low voltages enhances overall system integration and performance.
Benefits of Dual Supply Architectures
Dual supply operational amplifiers provide symmetrical positive and negative voltage rails, enabling the output to swing both above and below ground, which is essential for accurate AC signal amplification and improved linearity. This architecture enhances dynamic range and reduces distortion, making it ideal for analog signal processing in audio, instrumentation, and sensor applications. Dual supply designs also simplify biasing and improve common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), resulting in better noise performance and stability compared to single supply configurations.
Common Applications for Single Supply Op Amps
Single supply op amps are commonly used in battery-powered devices, portable instrumentation, and sensor signal conditioning where a single voltage source simplifies power design. They excel in low-voltage applications such as consumer electronics, medical devices, and automotive sensors, offering ease of integration and reduced component count. Your choice of a single supply op amp ensures efficient operation in systems with limited power availability and space constraints.
Typical Uses of Dual Supply Op Amps
Dual supply op amps are commonly used in analog signal processing applications requiring both positive and negative voltage swings, such as audio amplification, instrumentation amplifiers, and active filters. They are essential in systems where the input signal fluctuates around zero volts, enabling accurate amplification without distortion. Typical uses include precision sensor signal conditioning, analog computation circuits, and waveform generation in laboratory equipment.
Design Considerations for Choosing Supply Type
When selecting between single supply and dual supply op amps, consider the circuit's voltage range and output swing requirements, as single supply op amps operate from one positive voltage relative to ground, limiting output to a positive voltage range. Dual supply op amps provide both positive and negative voltages, enabling signals to swing bipolar around zero volts, which is essential for AC signal amplification and applications requiring symmetric voltage swings. Your choice depends on factors such as power availability, signal characteristics, and the need for simplicity in design versus precision in handling bipolar inputs.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Op Amp Supply
Choosing between single supply and dual supply op amps depends on the application's voltage requirements and signal range. Single supply op amps simplify design and power consumption by operating from one positive voltage and ground, ideal for battery-powered devices. Dual supply op amps offer greater signal swing and better handling of AC signals by providing positive and negative voltages, essential for analog audio and signal processing circuits.
single supply vs dual supply op amp Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com