A half bridge rectifier converts AC to DC using two diodes and provides a pulsating DC output with lower efficiency and higher ripple compared to a full bridge rectifier, which uses four diodes to deliver a smoother DC output with better voltage utilization. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choice between these rectifiers impacts circuit performance and efficiency.
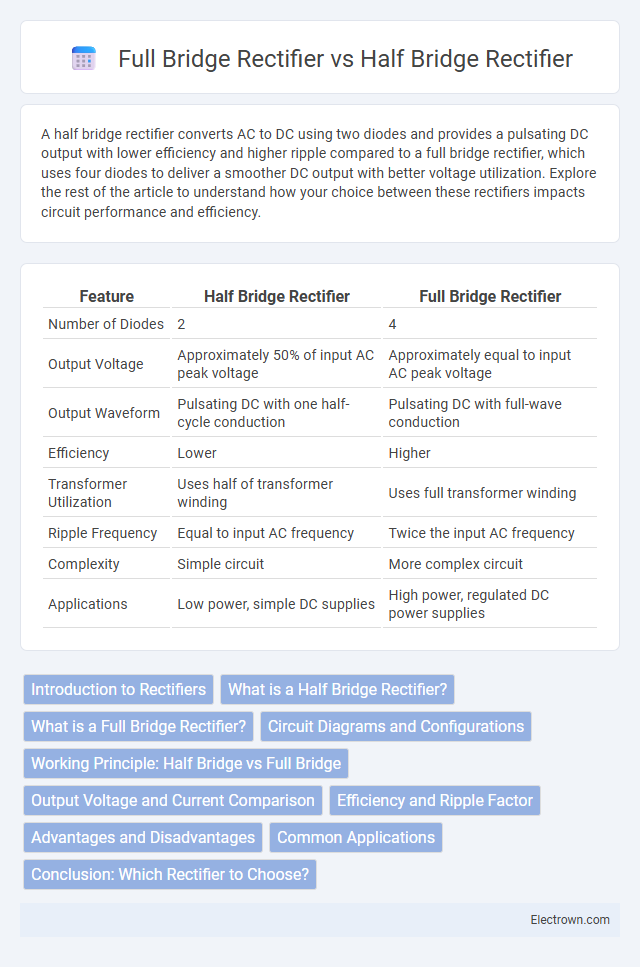
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Half Bridge Rectifier | Full Bridge Rectifier |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Diodes | 2 | 4 |
| Output Voltage | Approximately 50% of input AC peak voltage | Approximately equal to input AC peak voltage |
| Output Waveform | Pulsating DC with one half-cycle conduction | Pulsating DC with full-wave conduction |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Transformer Utilization | Uses half of transformer winding | Uses full transformer winding |
| Ripple Frequency | Equal to input AC frequency | Twice the input AC frequency |
| Complexity | Simple circuit | More complex circuit |
| Applications | Low power, simple DC supplies | High power, regulated DC power supplies |
Introduction to Rectifiers
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), essential for powering electronic devices. Your choice between a half bridge rectifier, which uses two diodes and provides a unidirectional output with lower component count, and a full bridge rectifier, employing four diodes for full-wave rectification, impacts efficiency and output smoothness. Full bridge rectifiers offer higher DC output voltage and better transformer utilization compared to half bridge rectifiers.
What is a Half Bridge Rectifier?
A half bridge rectifier is a type of AC to DC converter that uses two diodes and a center-tapped transformer to produce a pulsating DC output. It conducts current through each diode alternately during positive and negative half cycles of the input AC signal, resulting in reduced component count and cost compared to a full bridge rectifier. Half bridge rectifiers are commonly used in low-power applications where efficiency and simplicity are prioritized.
What is a Full Bridge Rectifier?
A full bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, enabling it to convert the entire AC input waveform into a pulsating DC output. Unlike a half bridge rectifier, which uses only two diodes and rectifies one half of the input AC signal, the full bridge rectifier utilizes both halves, resulting in higher efficiency and smoother DC output. Your choice of rectifier depends on the application's power requirements, with full bridge rectifiers commonly preferred for delivering full-wave rectification in power supplies.
Circuit Diagrams and Configurations
A half bridge rectifier configuration uses two diodes arranged in a simple series circuit with the load, allowing current flow during only one half of the AC cycle, and typically requires a center-tapped transformer. In contrast, a full bridge rectifier consists of four diodes configured in a bridge arrangement, enabling full-wave rectification by directing current through the load during both halves of the AC input cycle without needing a center-tapped transformer. The full bridge circuit diagram shows two diode pairs connected to each AC terminal with the load connected between the DC output terminals, offering higher efficiency and smoother DC output compared to the half bridge setup.
Working Principle: Half Bridge vs Full Bridge
A half bridge rectifier uses two diodes and a center-tapped transformer to convert AC to pulsating DC, conducting during alternate halves of the input waveform, thus producing a single polarity output. A full bridge rectifier employs four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing both halves of the AC input to be converted into pulsating DC without needing a center-tapped transformer. Your choice between half bridge and full bridge rectifiers impacts efficiency and transformer design, with the full bridge offering full-wave rectification and higher output voltage utilization.
Output Voltage and Current Comparison
A half bridge rectifier typically produces an output voltage that is approximately half of the input AC voltage peak, while a full bridge rectifier delivers an output voltage close to the full peak value of the input AC voltage. The current capacity of a full bridge rectifier is generally higher since it utilizes four diodes to conduct during both halves of the AC cycle, leading to a more continuous and higher output current. Your choice between these rectifiers should consider that a full bridge rectifier offers better voltage utilization and higher current output compared to a half bridge rectifier.
Efficiency and Ripple Factor
A full bridge rectifier offers higher efficiency compared to a half bridge rectifier by utilizing both halves of the AC input waveform, resulting in a greater DC output voltage. The ripple factor in a full bridge rectifier is lower, meaning the output is smoother and requires less filtering, which improves performance in power supply applications. Your choice between the two should consider the full bridge's superior efficiency and reduced ripple for more stable and reliable DC power.
Advantages and Disadvantages
A half bridge rectifier offers simplicity and requires fewer diodes, resulting in lower cost and reduced power losses, but it provides only half-wave rectification, leading to higher ripple current and lower efficiency. A full bridge rectifier utilizes four diodes to deliver full-wave rectification, producing smoother DC output with less ripple and higher efficiency, though it involves increased complexity, higher component count, and greater voltage drop across the diodes. The choice depends on the application's requirements for efficiency, cost, and output quality.
Common Applications
Half bridge rectifiers are commonly used in low-power applications such as signal demodulation and small power supplies where cost and simplicity are priorities. Full bridge rectifiers are preferred in higher power applications like DC motor drives, battery charging systems, and industrial power supplies because they provide a higher output voltage and better efficiency. Your choice depends on the power requirements and complexity of the electronic device being designed.
Conclusion: Which Rectifier to Choose?
A full bridge rectifier provides higher efficiency and better DC output voltage compared to a half bridge rectifier, making it ideal for applications requiring smoother power delivery. Half bridge rectifiers are simpler and cheaper but produce lower output voltage and more ripple, suitable for less demanding power supplies. You should choose a full bridge rectifier for improved performance in critical electronics, while a half bridge rectifier fits cost-sensitive, low-power applications.
half bridge rectifier vs full bridge rectifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com