Headroom refers to the maximum voltage a circuit can handle without distortion, while slew rate measures how quickly an amplifier can change its output voltage over time. Understanding the relationship between headroom and slew rate is crucial for optimizing your audio or signal processing equipment performance; read on to explore their differences and impact.
Table of Comparison
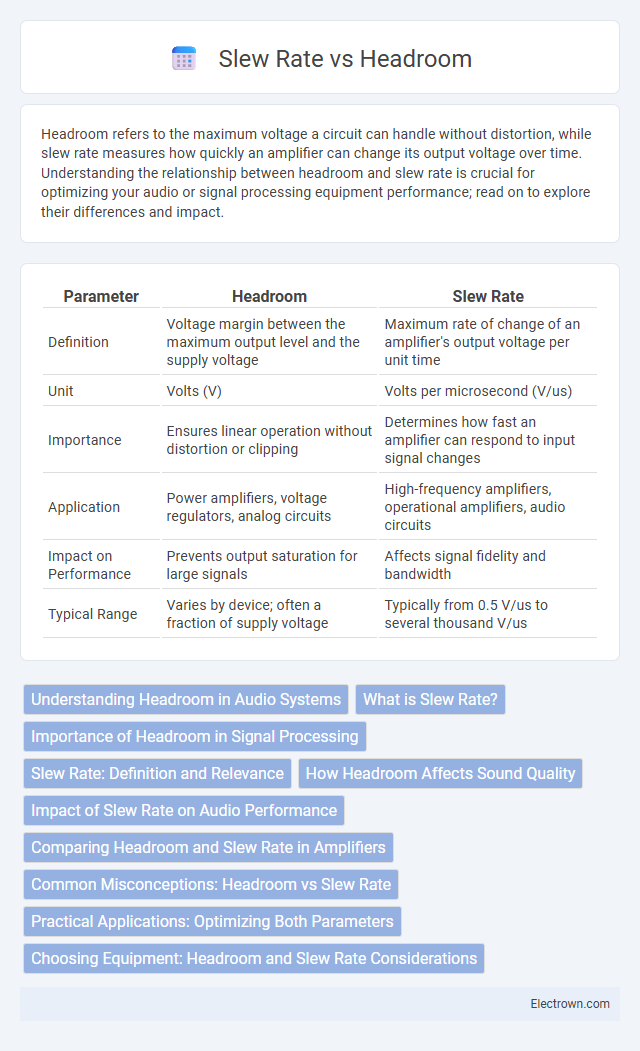
| Parameter | Headroom | Slew Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voltage margin between the maximum output level and the supply voltage | Maximum rate of change of an amplifier's output voltage per unit time |
| Unit | Volts (V) | Volts per microsecond (V/us) |
| Importance | Ensures linear operation without distortion or clipping | Determines how fast an amplifier can respond to input signal changes |
| Application | Power amplifiers, voltage regulators, analog circuits | High-frequency amplifiers, operational amplifiers, audio circuits |
| Impact on Performance | Prevents output saturation for large signals | Affects signal fidelity and bandwidth |
| Typical Range | Varies by device; often a fraction of supply voltage | Typically from 0.5 V/us to several thousand V/us |
Understanding Headroom in Audio Systems
Headroom in audio systems refers to the difference between the nominal operating level and the maximum level a system can handle without distortion. It allows your audio signals to accommodate sudden transients or peaks without clipping, maintaining sound quality and dynamic range. While slew rate measures how quickly an amplifier can respond to rapid changes in voltage, proper headroom ensures these peaks can be captured cleanly within the system's limits.
What is Slew Rate?
Slew rate refers to the maximum rate of change of an amplifier's output voltage per unit time, typically measured in volts per microsecond (V/us). It determines how quickly an amplifier can respond to rapid changes in the input signal, impacting signal fidelity and distortion at high frequencies. Understanding slew rate is essential for optimizing your audio system's performance and ensuring accurate reproduction of fast transient sounds.
Importance of Headroom in Signal Processing
Headroom in signal processing ensures Your audio signals maintain clarity by preventing distortion when unexpected peaks occur. It provides the necessary margin between the signal's maximum level and the system's limit, allowing the slew rate to handle rapid voltage changes effectively. Proper headroom management optimizes dynamic range, enhancing overall sound quality and system performance.
Slew Rate: Definition and Relevance
Slew rate is the maximum rate of change of an amplifier's output voltage per unit time, typically measured in volts per microsecond (V/us). It determines how quickly an amplifier can respond to rapid changes in the input signal, directly affecting the fidelity of high-frequency or transient signals. In audio and high-speed applications, an insufficient slew rate can cause distortion and limit the effective headroom by preventing the output from accurately following the input waveform.
How Headroom Affects Sound Quality
Headroom significantly impacts sound quality by providing extra dynamic range, preventing distortion when audio signals peak. A higher headroom ensures your audio maintains clarity and fullness, even during sudden loud passages. This buffer allows the slew rate to respond accurately, preserving the integrity of fast transient sounds.
Impact of Slew Rate on Audio Performance
Slew rate directly influences audio performance by determining how quickly an amplifier can respond to rapid changes in input signal, affecting the accuracy and clarity of high-frequency sounds. Insufficient slew rate causes distortion known as slew rate-induced distortion (SRID), which can degrade transient response and reduce the fidelity of dynamic audio signals. Higher slew rates ensure cleaner reproduction of sharp audio transients and preserve headroom by preventing clipping during complex, fast-changing sound passages.
Comparing Headroom and Slew Rate in Amplifiers
Headroom in amplifiers refers to the margin between the maximum output voltage and the signal amplitude before distortion occurs, crucial for maintaining clean audio signals. Slew rate defines the maximum rate at which an amplifier can change its output voltage, impacting its ability to accurately reproduce fast transient signals. Comparing headroom and slew rate reveals that while headroom ensures distortion-free operation under high signal peaks, slew rate limits the amplifier's speed in tracking rapid voltage changes, both essential for high-fidelity audio performance.
Common Misconceptions: Headroom vs Slew Rate
Headroom and slew rate are often confused but represent distinct concepts in audio and electronics. Headroom refers to the margin between the normal operating level and the maximum level a system can handle without distortion, while slew rate measures how quickly an amplifier can respond to rapid changes in the input signal. Understanding that increased headroom does not necessarily improve slew rate helps you optimize your audio system's performance accurately.
Practical Applications: Optimizing Both Parameters
Optimizing both headroom and slew rate is crucial in high-fidelity audio amplifiers to ensure clear signal reproduction without clipping or distortion. Engineers balance sufficient headroom to accommodate transient signal peaks while maintaining a high slew rate for rapid voltage changes, critical in fast transient responses and accurate waveform tracking. Practical applications include professional audio equipment and high-speed data converters where optimizing these parameters enhances overall system performance and sound quality.
Choosing Equipment: Headroom and Slew Rate Considerations
When choosing audio equipment, understanding headroom and slew rate is essential to ensure high-fidelity sound reproduction. Headroom provides the margin needed to prevent audio clipping during dynamic peaks, while slew rate measures how quickly an amplifier can respond to rapid changes in the input signal, impacting clarity and detail. Selecting gear with adequate headroom and a high slew rate protects Your audio signal from distortion and preserves the integrity of your sound.
Headroom vs slew rate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com