Active volume control uses electronic components to amplify or attenuate audio signals, providing precise adjustments and improved sound quality, while passive volume control relies on simple resistive components without amplification, often resulting in signal loss. Understanding the differences can help you choose the best option for your audio setup; read on to explore the advantages and limitations of each method.
Table of Comparison
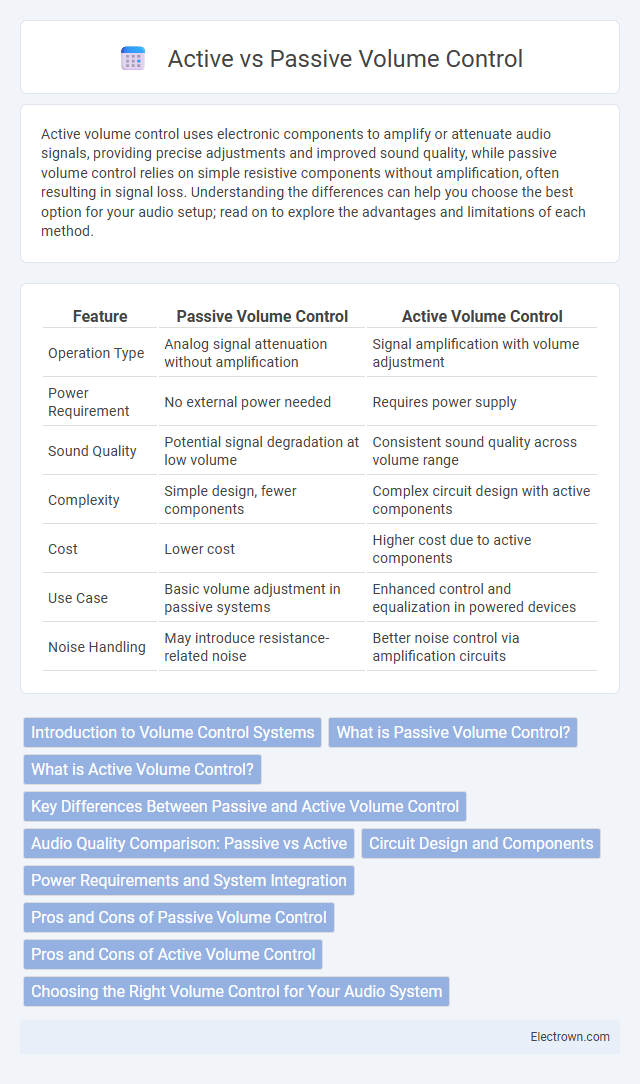
| Feature | Passive Volume Control | Active Volume Control |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Type | Analog signal attenuation without amplification | Signal amplification with volume adjustment |
| Power Requirement | No external power needed | Requires power supply |
| Sound Quality | Potential signal degradation at low volume | Consistent sound quality across volume range |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | Complex circuit design with active components |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to active components |
| Use Case | Basic volume adjustment in passive systems | Enhanced control and equalization in powered devices |
| Noise Handling | May introduce resistance-related noise | Better noise control via amplification circuits |
Introduction to Volume Control Systems
Volume control systems regulate the audio output level in sound devices, with passive and active types serving distinct functions. Passive volume control relies on simple hardware components like resistors to adjust volume without additional power, resulting in lower noise but limited amplification capabilities. Active volume control uses powered electronic circuits to amplify and finely tune audio signals, offering greater precision and flexibility for Your sound management needs.
What is Passive Volume Control?
Passive volume control adjusts the audio signal level without using any amplification, relying solely on resistive components such as potentiometers to reduce signal strength. This method preserves the original audio quality by avoiding active circuitry that can introduce noise or distortion, making it ideal for audiophiles seeking a pure sound experience. Your choice of passive volume control impacts the clarity and fidelity of the audio output, especially in high-end stereo systems where signal integrity is critical.
What is Active Volume Control?
Active volume control uses electronic components like amplifiers to adjust audio signals, providing precise and consistent sound level management. It requires a power source to operate and can improve audio quality by minimizing signal loss and distortion. Understanding active volume control helps you achieve better sound customization and overall listening experience.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Volume Control
Passive volume control uses a simple potentiometer to adjust signal level without additional amplification, limiting its ability to boost or drive long cable runs. Active volume control integrates built-in amplification, allowing precise volume adjustments and maintaining signal integrity even with longer cables or complex audio setups. Key differences include power necessity, signal gain capability, and overall audio quality impact, with active controls offering more flexibility and improved performance.
Audio Quality Comparison: Passive vs Active
Active volume control generally provides superior audio quality by offering built-in amplification and precise adjustment, minimizing signal loss and interference compared to passive volume control. Passive volume control, relying on simple resistive attenuation without additional power, can introduce signal degradation and noise, especially in low-level signals or complex audio setups. High-fidelity audio systems often favor active control for its enhanced clarity, dynamic range, and reduced distortion.
Circuit Design and Components
Passive volume control circuits rely on simple components such as resistors and potentiometers, providing signal attenuation without requiring a power source, resulting in minimal noise but potential signal loss. Active volume control designs use operational amplifiers or transistor-based circuits to amplify and control the audio signal, offering better impedance matching and consistent sound quality at various volume levels. Your choice between passive and active volume control impacts the complexity, component count, and overall audio fidelity of your system.
Power Requirements and System Integration
Passive volume control requires no additional power as it relies solely on resistive networks, making it ideal for simple system integration without extra power supplies or complex circuitry. Active volume control needs an external power source to operate internal amplifiers or digital processors, allowing for more precise volume adjustments and tone shaping but increasing system complexity. Choosing between passive and active volume control impacts your device's power budget and integration flexibility, especially in compact or battery-powered audio systems.
Pros and Cons of Passive Volume Control
Passive volume control offers simplicity and reliability by using a physical attenuator without requiring power, ensuring minimal signal coloration and enhanced audio purity. However, it can suffer from impedance mismatch issues that may reduce signal strength and affect sound quality, especially with low-output sources. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize straightforward, noise-free operation or require greater amplification flexibility and precision.
Pros and Cons of Active Volume Control
Active volume control offers precise sound adjustment through built-in amplification, enhancing audio quality and signal strength for various audio devices. However, it requires external power, increasing complexity and potential noise interference compared to passive systems. While providing superior control and flexibility, active volume control may introduce additional costs and maintenance needs due to its electronic components.
Choosing the Right Volume Control for Your Audio System
Choosing the right volume control for your audio system depends on your setup and listening preferences. Active volume controls offer amplification and tone shaping, enhancing audio clarity and allowing for precise adjustments, while passive volume controls provide a straightforward signal attenuation without power, preserving signal purity and simplicity. Your choice impacts sound quality, convenience, and compatibility with components like preamps or amplifiers.
passive vs active volume control Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com