Symmetric power supplies provide equal positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground, ensuring stable operation in audio and operational amplifier circuits, while asymmetric power supplies offer a single voltage rail and ground, commonly used in simpler electronic devices. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right power supply for your specific application; read on to explore the advantages and ideal use cases for each type.
Table of Comparison
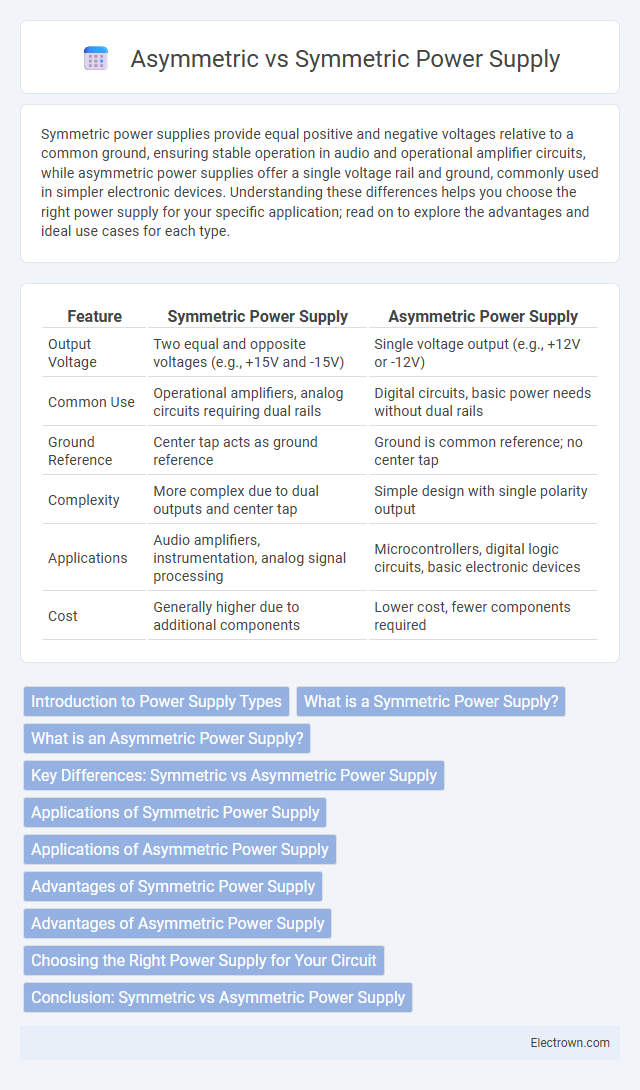
| Feature | Symmetric Power Supply | Asymmetric Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Output Voltage | Two equal and opposite voltages (e.g., +15V and -15V) | Single voltage output (e.g., +12V or -12V) |
| Common Use | Operational amplifiers, analog circuits requiring dual rails | Digital circuits, basic power needs without dual rails |
| Ground Reference | Center tap acts as ground reference | Ground is common reference; no center tap |
| Complexity | More complex due to dual outputs and center tap | Simple design with single polarity output |
| Applications | Audio amplifiers, instrumentation, analog signal processing | Microcontrollers, digital logic circuits, basic electronic devices |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additional components | Lower cost, fewer components required |
Introduction to Power Supply Types
Symmetric and asymmetric power supplies differ primarily in voltage output configurations, with symmetric power supplies providing equal positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground, ideal for operational amplifiers and audio equipment requiring balanced signals. Asymmetric power supplies offer a single polarity output, typically positive voltage referenced to ground, commonly used in digital circuits and microcontrollers. Understanding these differences helps you select the appropriate power supply based on your electronic device's voltage and grounding requirements.
What is a Symmetric Power Supply?
A symmetric power supply provides equal positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground, essential for powering operational amplifiers and analog circuits requiring balanced voltage rails. This type of power supply ensures voltage stability and minimizes noise, improving circuit performance in audio and signal processing applications. Your choice of a symmetric power supply can enhance the efficiency and reliability of devices needing dual voltage levels.
What is an Asymmetric Power Supply?
An asymmetric power supply delivers unequal or single-sided voltage levels, typically providing a positive voltage with a ground reference without a complementary negative voltage. It is commonly used in circuits where only a single polarity is required, such as in simple DC power applications or digital electronics. Compared to symmetric power supplies, which provide equal positive and negative voltages around a common ground, asymmetric power supplies are simpler and more cost-effective but may limit the design flexibility in analog and audio circuits.
Key Differences: Symmetric vs Asymmetric Power Supply
Symmetric power supplies provide equal positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground, essential for balanced analog circuits and operational amplifiers requiring dual polarity. Asymmetric power supplies deliver a single voltage level referenced to ground, commonly used in digital and simple electronic devices where only one polarity is necessary. Understanding whether Your application demands balanced voltages or a single rail can guide the optimal choice between symmetric and asymmetric power supplies.
Applications of Symmetric Power Supply
Symmetric power supplies provide dual voltages (positive and negative) essential for powering operational amplifiers, analog circuits, and audio equipment, ensuring signal integrity and reduced noise. These power supplies are commonly used in instrumentation systems, data acquisition devices, and telecommunications where balanced voltage rails enhance circuit stability. Their ability to deliver consistent bipolar voltages makes them ideal for applications requiring precise analog signal processing and linear amplification.
Applications of Asymmetric Power Supply
Asymmetric power supplies are widely used in applications where different voltage levels are required, such as in battery chargers, LED drivers, and audio amplifiers. These supplies provide a positive voltage output relative to ground, simplifying circuit design and reducing cost for devices that do not need dual polarity voltages. Asymmetric power supplies are ideal for low-power electronics, portable devices, and systems with single-ended signal processing.
Advantages of Symmetric Power Supply
Symmetric power supplies provide equal positive and negative voltages relative to a common ground, ensuring stable operation for analog circuits like operational amplifiers and audio equipment. These power supplies reduce noise and distortion by maintaining balanced voltage rails, which enhances signal integrity and performance in precision applications. Their design simplifies power regulation and improves the linearity of electrical components, making them ideal for sensitive, low-voltage electronic devices.
Advantages of Asymmetric Power Supply
Asymmetric power supplies simplify circuit design by providing a single voltage rail and ground reference, reducing component count and cost. These power supplies are often more efficient for applications requiring only one polarity, such as digital circuits or single-ended amplifiers. Their compact size and ease of integration make them ideal for battery-powered and portable devices.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Circuit
Selecting the right power supply for your circuit depends on the voltage and current requirements, as well as the type of components used. Symmetric power supplies provide equal positive and negative voltages around a common ground, ideal for operational amplifiers and analog circuits requiring dual rails. Asymmetric power supplies offer a single voltage output relative to ground, better suited for digital circuits and systems with unipolar voltage needs.
Conclusion: Symmetric vs Asymmetric Power Supply
Symmetric power supplies provide balanced positive and negative voltage outputs relative to a common ground, ideal for operational amplifiers and audio equipment requiring stable dual rails. Asymmetric power supplies offer a single voltage output and ground, suitable for circuits with unipolar voltage requirements and simpler designs. Choosing between symmetric and asymmetric power supplies depends on the application's voltage needs, signal type, and overall complexity.
symmetric vs asymmetric power supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com