Software DSP offers flexibility and ease of updates by running digital signal processing algorithms on general-purpose processors, while hardware DSP provides faster, dedicated processing power optimized for real-time performance. Explore the article to understand which DSP approach best suits Your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
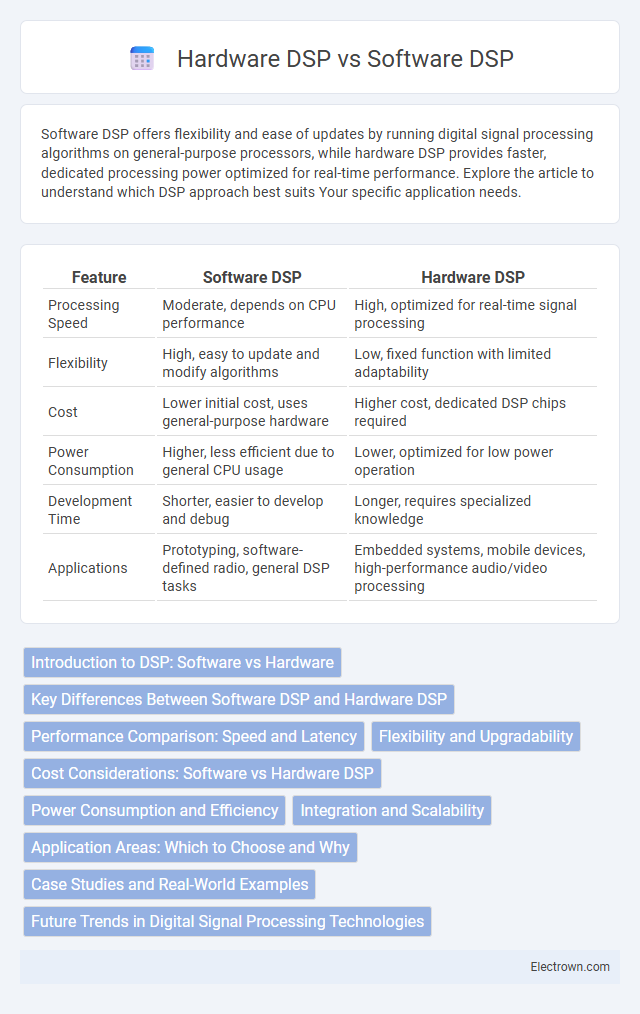
| Feature | Software DSP | Hardware DSP |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Speed | Moderate, depends on CPU performance | High, optimized for real-time signal processing |
| Flexibility | High, easy to update and modify algorithms | Low, fixed function with limited adaptability |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, uses general-purpose hardware | Higher cost, dedicated DSP chips required |
| Power Consumption | Higher, less efficient due to general CPU usage | Lower, optimized for low power operation |
| Development Time | Shorter, easier to develop and debug | Longer, requires specialized knowledge |
| Applications | Prototyping, software-defined radio, general DSP tasks | Embedded systems, mobile devices, high-performance audio/video processing |
Introduction to DSP: Software vs Hardware
Software DSP offers flexibility and ease of updates by processing digital signals through programmable processors, making it ideal for complex algorithms and rapid development cycles. Hardware DSP provides dedicated, high-speed performance through specialized integrated circuits designed for low-latency and power-efficient real-time signal processing. Comparing software DSP and hardware DSP highlights trade-offs in adaptability, cost, and processing speed critical for applications like telecommunications and audio processing.
Key Differences Between Software DSP and Hardware DSP
Software DSP processes digital signals using general-purpose processors or specialized software environments, offering flexibility and ease of updates for your audio or communication applications. Hardware DSP relies on dedicated integrated circuits designed for high-speed, low-latency signal processing, delivering superior real-time performance and energy efficiency. Key differences include adaptability, processing power, and cost, with software DSP favoring versatility and hardware DSP excelling in speed and dedicated tasks.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Latency
Hardware DSPs typically offer superior speed and lower latency due to dedicated processing units optimized for real-time signal processing tasks, enabling faster execution of complex algorithms. Software DSPs run on general-purpose processors, which may introduce higher latency and slower processing speeds, especially under heavy multitasking conditions. Your choice between software and hardware DSP should consider specific performance requirements, balancing flexibility against the need for rapid, low-latency signal processing.
Flexibility and Upgradability
Software DSP offers superior flexibility and upgradability by allowing algorithms to be easily modified or replaced through software updates without changing physical components. Hardware DSPs, while providing high-speed processing and efficiency, are less adaptable since their functionality is fixed by integrated circuits and require redesign or hardware replacement for upgrades. The ability of software DSPs to accommodate evolving standards and new features makes them ideal for dynamic environments requiring frequent enhancements.
Cost Considerations: Software vs Hardware DSP
Software DSP offers lower initial costs due to the use of general-purpose processors and flexible development environments, making it ideal for prototyping and low to medium volume production. Hardware DSP, while involving higher upfront expenses for dedicated DSP chips and custom hardware design, delivers superior performance and efficiency in high-volume or real-time processing applications. The total cost of ownership favors software DSP for adaptability and updates, whereas hardware DSP incurs added costs from manufacturing, power consumption, and specialized development.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Software DSP leverages general-purpose processors, resulting in higher power consumption due to less specialized instruction execution and overhead. Hardware DSP, designed with dedicated processing units and optimized architectures, achieves superior power efficiency and faster real-time signal processing. Embedded hardware DSP solutions typically deliver better performance per watt, making them ideal for battery-powered and energy-sensitive applications.
Integration and Scalability
Software DSP offers seamless integration with existing digital systems and provides unparalleled scalability by allowing easy updates and expansions through code modifications. Hardware DSP, while delivering high performance through dedicated processing units, often faces limitations in scalability due to fixed resources and more complex integration requirements. Choosing the right DSP depends on your application's need for flexible integration and future scalability demands.
Application Areas: Which to Choose and Why
Software DSP excels in applications requiring flexibility and quick updates, such as audio processing, telecommunications, and adaptive filtering. Hardware DSP is preferred in real-time, high-performance scenarios like radar systems, medical imaging, and automotive control due to lower latency and power efficiency. Choosing between software and hardware DSP depends on the need for customization, processing speed, and energy constraints specific to the application.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Software DSP offers flexibility in applications like smartphone audio processing and adaptive noise cancellation, demonstrated by Qualcomm's Snapdragon processors optimizing sound quality through programmable algorithms. Hardware DSP excels in high-performance scenarios such as automotive radar systems and medical imaging equipment, where fixed-function chips from Texas Instruments provide low-latency and energy-efficient signal processing. Your choice between software and hardware DSP depends on whether customizable updates or specialized, real-time processing is prioritized in the deployment environment.
Future Trends in Digital Signal Processing Technologies
Software DSP offers unmatched flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, driving innovation in AI integration and adaptive algorithms. Hardware DSP continues advancing with specialized architectures like FPGA and ASIC, optimizing power efficiency and real-time processing for 5G and IoT applications. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid approaches combining software adaptability with hardware acceleration to meet the demands of next-generation communication and multimedia systems.
software dsp vs hardware dsp Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com