TOSLINK and coaxial cables both transmit digital audio signals but differ in medium and susceptibility to interference, with TOSLINK using optical fiber for reduced electrical noise and coaxial relying on copper cables for potentially higher bandwidth. Explore how choosing the right connection can enhance Your audio experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
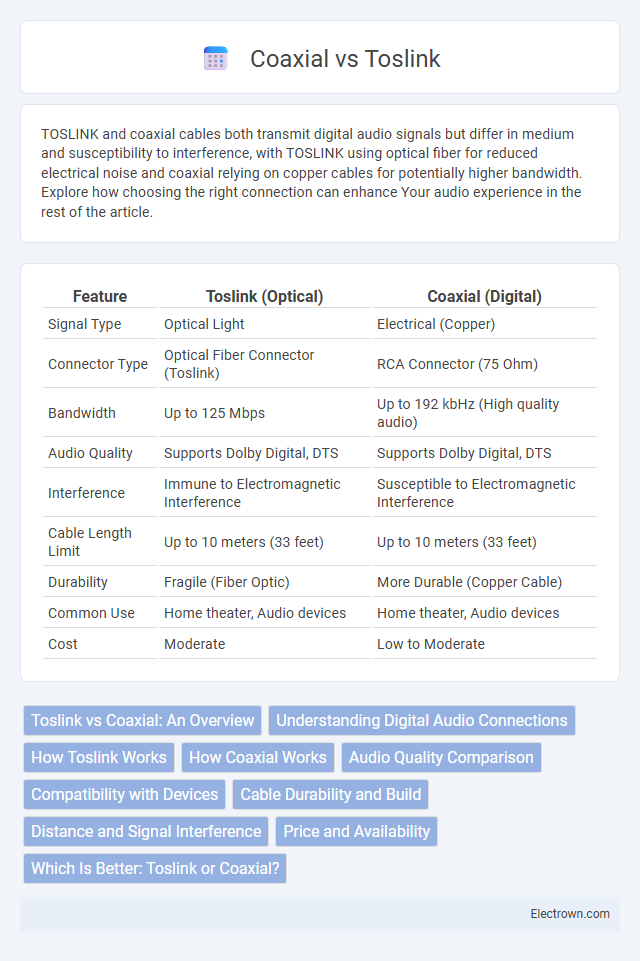
| Feature | Toslink (Optical) | Coaxial (Digital) |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Optical Light | Electrical (Copper) |
| Connector Type | Optical Fiber Connector (Toslink) | RCA Connector (75 Ohm) |
| Bandwidth | Up to 125 Mbps | Up to 192 kbHz (High quality audio) |
| Audio Quality | Supports Dolby Digital, DTS | Supports Dolby Digital, DTS |
| Interference | Immune to Electromagnetic Interference | Susceptible to Electromagnetic Interference |
| Cable Length Limit | Up to 10 meters (33 feet) | Up to 10 meters (33 feet) |
| Durability | Fragile (Fiber Optic) | More Durable (Copper Cable) |
| Common Use | Home theater, Audio devices | Home theater, Audio devices |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
Toslink vs Coaxial: An Overview
Toslink and coaxial cables are popular digital audio connections used in home theater and audio systems, with Toslink using optical fiber to transmit audio signals as pulses of light, providing electrical isolation and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Coaxial cables use a single copper conductor with a shield, offering slightly higher bandwidth and supporting longer cable runs without signal degradation. Your choice between Toslink vs coaxial depends on your system's compatibility, desired audio quality, and installation environment.
Understanding Digital Audio Connections
TOSLINK and coaxial cables both transmit digital audio signals but differ in signal type and susceptibility to interference. TOSLINK uses optical fiber to send light pulses, providing electrical isolation and eliminating ground loop issues, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments. Coaxial cables transmit electrical signals via a copper conductor, offering higher bandwidth and longer cable runs but with potential electromagnetic interference risk.
How Toslink Works
Toslink uses optical fiber cables to transmit digital audio signals through pulses of light, ensuring immunity to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation. This method converts electrical signals into light, which is then decoded by the receiving device into audio data, supporting formats like PCM and Dolby Digital. Compared to coaxial cables that transmit electrical signals over copper, Toslink provides a cleaner transmission, especially beneficial in setups prone to electrical noise.
How Coaxial Works
Coaxial digital audio transmits signals using electrical pulses through a single copper cable with 75-ohm impedance, minimizing signal loss and interference over longer distances. It carries S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format) data, ensuring compatibility with most home theater and audio equipment. The cable's shielding and precise impedance improve sound quality by maintaining signal integrity compared to other digital connections.
Audio Quality Comparison
TOSLINK and coaxial cables transmit digital audio signals with minimal interference, but coaxial often delivers slightly better audio quality due to its higher bandwidth and lower jitter. TOSLINK uses optical fibers immune to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for setups prone to electrical noise, while coaxial's copper construction can provide a more stable signal over shorter distances. Your choice should depend on your audio system's compatibility and the specific environment to ensure optimal sound performance.
Compatibility with Devices
Toslink and coaxial cables offer distinct compatibility depending on your audio equipment, with Toslink widely supported by modern TVs, game consoles, and soundbars due to its optical digital signal transmission. Coaxial cables, using electrical signals, are commonly compatible with older audio receivers, DVD players, and some high-end DACs, ensuring a reliable connection for devices lacking optical inputs. Choosing between Toslink and coaxial depends on your device's input options and the quality of digital audio connection you require.
Cable Durability and Build
Toslink cables utilize optical fiber made from plastic or glass, providing excellent resistance to electromagnetic interference but making them more susceptible to physical damage like bending or crushing. Coaxial cables feature a robust copper core surrounded by insulation, shielding, and a protective jacket, resulting in superior durability and flexibility for various installation environments. The build quality of coaxial cables generally supports longer lifespans in harsh conditions compared to Toslink's delicate optical fibers.
Distance and Signal Interference
TOSLINK optical cables transmit digital audio signals using light, making them resistant to electromagnetic interference and ideal for longer distances up to 10 meters without signal degradation. Coaxial cables, which use electrical signals, can support longer runs of up to 20 meters but are more susceptible to noise and interference from nearby electronic devices. Your choice between TOSLINK and coaxial should consider the distance of your setup and the potential for signal interference in your environment.
Price and Availability
Toslink cables are generally more affordable and widely available in various lengths and qualities, making them a cost-effective choice for most audio setups. Coaxial cables tend to be slightly more expensive but offer better durability and shielding, which can justify the higher price for certain uses. Your decision may depend on budget constraints and the specific equipment compatibility in your audio system.
Which Is Better: Toslink or Coaxial?
Toslink uses optical fiber to transmit digital audio signals, providing strong resistance to electromagnetic interference and ensuring clear sound quality in most home audio setups. Coaxial cables utilize electrical pulses through copper wiring, offering slightly better bandwidth and potentially superior performance for high-resolution audio formats. The choice depends on specific system compatibility, but coaxial often edges out Toslink in delivering higher fidelity due to less signal degradation over distance.
toslink vs coaxial Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com