I2S and USB audio serve different purposes in digital sound transmission, with I2S primarily used for direct inter-chip communication in audio devices, ensuring low-latency and high-quality signal transfer, while USB audio is designed for general-purpose connectivity, offering compatibility with a wide range of devices and higher convenience. Explore the rest of the article to understand which interface best suits Your audio implementation needs.
Table of Comparison
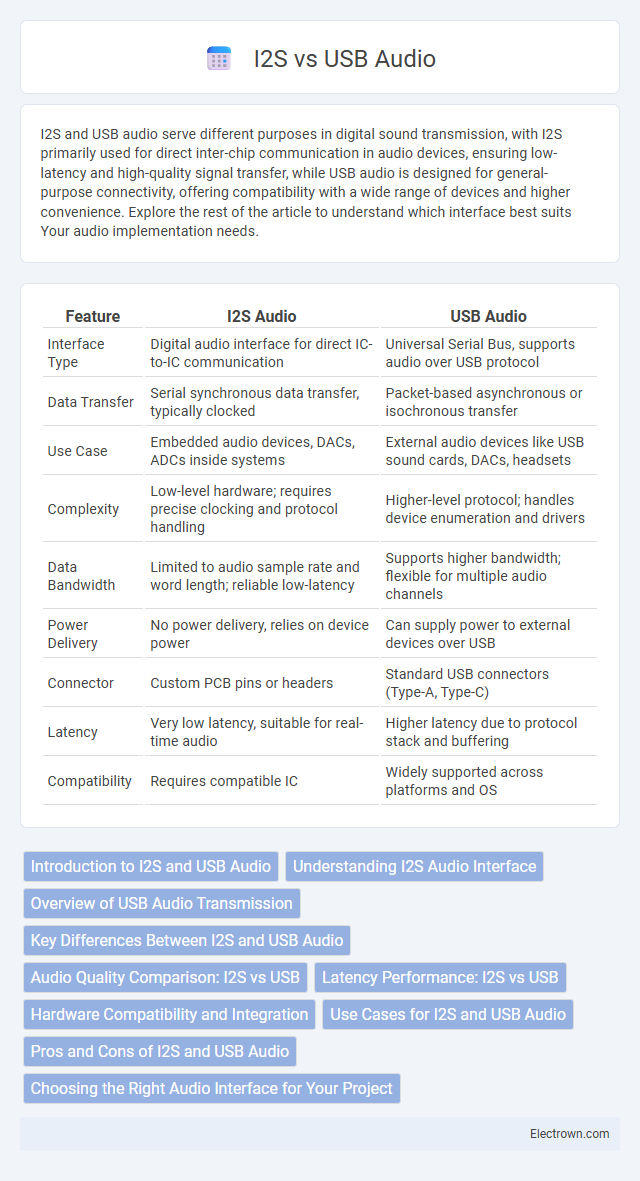
| Feature | I2S Audio | USB Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Interface Type | Digital audio interface for direct IC-to-IC communication | Universal Serial Bus, supports audio over USB protocol |
| Data Transfer | Serial synchronous data transfer, typically clocked | Packet-based asynchronous or isochronous transfer |
| Use Case | Embedded audio devices, DACs, ADCs inside systems | External audio devices like USB sound cards, DACs, headsets |
| Complexity | Low-level hardware; requires precise clocking and protocol handling | Higher-level protocol; handles device enumeration and drivers |
| Data Bandwidth | Limited to audio sample rate and word length; reliable low-latency | Supports higher bandwidth; flexible for multiple audio channels |
| Power Delivery | No power delivery, relies on device power | Can supply power to external devices over USB |
| Connector | Custom PCB pins or headers | Standard USB connectors (Type-A, Type-C) |
| Latency | Very low latency, suitable for real-time audio | Higher latency due to protocol stack and buffering |
| Compatibility | Requires compatible IC | Widely supported across platforms and OS |
Introduction to I2S and USB Audio
I2S (Inter-IC Sound) is a serial bus interface standard used primarily for connecting digital audio devices within a system, enabling direct transfer of PCM audio data with low latency and minimal processing overhead. USB audio, on the other hand, utilizes the Universal Serial Bus protocol to transmit audio data between computers and external devices, supporting higher compatibility and complex audio formats but often introducing higher latency due to data packetization and processing. Both interfaces serve distinct purposes: I2S excels in embedded audio applications with direct hardware integration, while USB audio offers versatility and ease of use for consumer and professional audio peripherals.
Understanding I2S Audio Interface
I2S (Inter-IC Sound) is a specialized digital audio interface designed for high-fidelity, low-latency audio data transfer between integrated circuits, making it ideal for direct communication between audio processors and DACs. Unlike USB audio, which transmits data packets over a general-purpose bus and requires more complex drivers, I2S offers a simpler, synchronous clocked interface that preserves audio integrity by minimizing jitter and noise. Your choice between I2S and USB audio interfaces depends on the application's need for audio quality, latency, and system complexity, with I2S often preferred in embedded audio systems for precise, real-time sound processing.
Overview of USB Audio Transmission
USB audio transmission delivers digital sound data through Universal Serial Bus connections, supporting high-resolution formats and plug-and-play compatibility with various devices. Unlike I2S, which is a dedicated serial bus designed specifically for audio data between integrated circuits, USB manages audio alongside other data types, making it more versatile but potentially introducing latency. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize direct, low-latency audio interfacing (I2S) or flexible device connectivity and ease of use (USB).
Key Differences Between I2S and USB Audio
I2S (Inter-IC Sound) is a hardware-level digital audio interface used for direct communication between audio components, offering low latency and high fidelity by transmitting raw audio data without encoding. USB audio functions as a multimedia protocol enabling audio transfer between devices over USB ports, incorporating digital audio formats with higher compatibility but added processing overhead. Key differences include I2S's direct point-to-point connection suited for embedded systems, contrasted with USB audio's broader device support and plug-and-play capability ideal for consumer electronics.
Audio Quality Comparison: I2S vs USB
I2S (Inter-IC Sound) delivers superior audio quality by transmitting unprocessed digital audio data directly between components, minimizing jitter and signal interference. USB audio, while versatile and widely compatible, often involves additional processing and buffering that can introduce latency and potential noise, affecting the purity of the sound. Audio engineers prefer I2S for high-fidelity applications due to its direct, low-latency data path that preserves audio integrity better than USB interfaces.
Latency Performance: I2S vs USB
I2S audio interface offers significantly lower latency compared to USB audio due to its direct, synchronous data transfer between the audio codec and processor, minimizing buffering delays. USB audio, while flexible and widely compatible, involves more complex protocol layers and host-based processing, which inherently increases latency. In real-time audio applications like digital mixing and live sound, I2S provides superior timing precision and reduced jitter, making it the ideal choice for latency-sensitive performance.
Hardware Compatibility and Integration
I2S audio interfaces provide direct communication with digital-to-analog converters (DACs) and microcontrollers, making them highly compatible with embedded systems and custom hardware designs. USB audio interfaces are broadly supported across consumer devices, offering plug-and-play functionality with computers and smartphones but often require external DACs or adapters for integration with specialized hardware. Hardware integration via I2S is ideal for low-latency and synchronized audio data transfer, whereas USB prioritizes ease of use and widespread compatibility over direct hardware control.
Use Cases for I2S and USB Audio
I2S audio interfaces excel in embedded systems and microcontroller projects where low-latency, high-fidelity digital audio data transfer between ICs is critical, such as in DSP modules, audio codecs, and custom audio hardware. USB audio interfaces are ideal for connecting external audio devices like DACs, headphones, and microphones to computers and smartphones, offering plug-and-play convenience and standardized communication for streaming high-resolution audio. I2S is best suited for internal device communication, while USB audio supports a broad range of consumer and professional audio applications requiring compatibility and ease of use.
Pros and Cons of I2S and USB Audio
I2S offers low-latency, high-fidelity audio transmission directly between digital audio components, minimizing interference and preserving signal integrity, but requires precise hardware synchronization and limited device compatibility. USB audio provides broad compatibility with most computers and devices, supports plug-and-play convenience, and enables power delivery, though it may introduce higher latency and potential signal degradation due to protocol overhead. Choosing between I2S and USB audio depends on the specific use case, balancing sound quality needs against ease of integration and device support.
Choosing the Right Audio Interface for Your Project
Choosing between I2S and USB audio interfaces depends on your project's requirements for latency, complexity, and compatibility. I2S offers low-latency, direct digital audio data transfer primarily used in embedded systems and microcontrollers, making it ideal for hardware-level audio processing. USB audio interfaces provide broader compatibility with computers and external devices, supporting higher bit rates and plug-and-play functionality, which suits desktop and consumer applications.
i2s vs usb audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com