Litz cable, composed of multiple insulated strands woven together, reduces skin effect and is ideal for high-frequency applications, while solid core cable, with a single solid conductor, offers lower resistance and durability for low-frequency or DC uses. Explore the rest of this article to understand which cable suits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
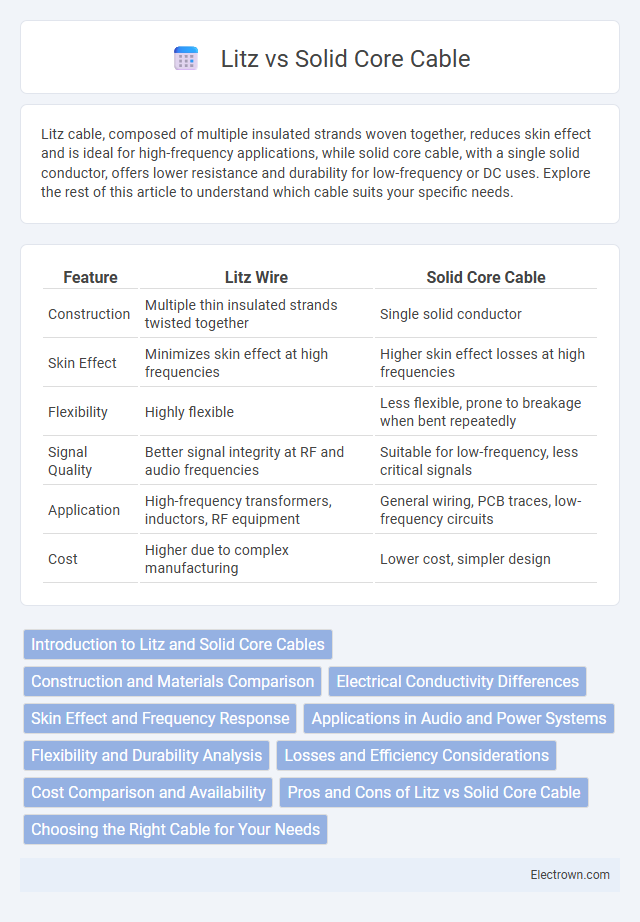
| Feature | Litz Wire | Solid Core Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Multiple thin insulated strands twisted together | Single solid conductor |
| Skin Effect | Minimizes skin effect at high frequencies | Higher skin effect losses at high frequencies |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible | Less flexible, prone to breakage when bent repeatedly |
| Signal Quality | Better signal integrity at RF and audio frequencies | Suitable for low-frequency, less critical signals |
| Application | High-frequency transformers, inductors, RF equipment | General wiring, PCB traces, low-frequency circuits |
| Cost | Higher due to complex manufacturing | Lower cost, simpler design |
Introduction to Litz and Solid Core Cables
Litz cables consist of multiple thin, insulated strands twisted or woven together to minimize skin effect and proximity effect losses at high frequencies. Solid core cables are made of a single, solid conductor that provides lower resistance and durability at lower frequencies but suffers from higher AC losses in high-frequency applications. Choosing between Litz and solid core cables depends on frequency range and application-specific power efficiency requirements.
Construction and Materials Comparison
Litz wire consists of multiple thin, individually insulated strands woven together to minimize skin effect and proximity losses, enhancing high-frequency performance. Solid core cable is made from a single, solid conductor, typically copper or aluminum, providing lower resistance at low frequencies but suffering from greater skin effect losses at high frequencies. The choice of litz wire versus solid core cable depends on frequency range, with litz preferred for RF applications due to its reduced AC resistance and solid core favored for DC or low-frequency power delivery.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Litz cable improves electrical conductivity by reducing the skin effect and proximity effect in high-frequency applications, allowing more efficient current flow compared to solid core cable. Solid core cables have a single, solid conductor that experiences increased resistance at higher frequencies due to current crowding on the surface. Your choice between litz and solid core cables should consider the application frequency, as litz cable offers superior conductivity for RF and audio frequencies, while solid core cables perform well for low-frequency and DC uses.
Skin Effect and Frequency Response
Litz cable is specifically designed to counteract the skin effect by using multiple thin, insulated strands twisted together, allowing high-frequency signals to penetrate deeper and reducing signal loss compared to solid core cable. Solid core cables experience significant signal attenuation at higher frequencies due to the skin effect, where current tends to flow only on the conductor's surface, increasing resistance. This fundamental difference results in litz cables offering superior frequency response and reduced power losses in high-frequency applications such as RF circuits and audio devices.
Applications in Audio and Power Systems
Litz wire minimizes skin effect losses, making it ideal for high-frequency audio signal transmission and RF power applications, where maintaining signal integrity is crucial. Solid core cables provide lower resistance and better durability, preferred in low-frequency power delivery and fixed wiring systems due to their robustness and cost-effectiveness. In audio systems, litz wire enhances clarity in headphones and speaker coils by reducing distortion, while solid core excels in delivering stable power in amplifiers and home electrical circuits.
Flexibility and Durability Analysis
Litz wire offers superior flexibility compared to solid core cable, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent bending or movement without risk of internal damage. Solid core cables provide enhanced durability under static conditions due to their single solid conductor that resists wear from abrasion and environmental factors. Your choice should prioritize flexibility for dynamic use or solid core for long-term, stationary durability.
Losses and Efficiency Considerations
Litz wire significantly reduces skin effect and proximity effect losses in high-frequency applications compared to solid core cables, resulting in improved efficiency. Solid core cables exhibit higher AC resistance at elevated frequencies, causing increased power dissipation and heat generation. Using litz wire enhances signal integrity and energy transfer by minimizing eddy current losses and maintaining lower effective resistance in RF circuits.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Litz wire typically costs more than solid core cable due to its intricate construction of multiple insulated strands, making it a premium choice for reducing high-frequency losses. Solid core cables are more widely available and generally less expensive, making them a practical option for budget-conscious projects or standard low-frequency applications. Your choice depends on balancing performance needs with cost and availability constraints.
Pros and Cons of Litz vs Solid Core Cable
Litz cable offers superior performance in high-frequency applications by reducing skin effect and proximity losses, making it ideal for RF circuits and transformers, but it tends to be more expensive and less durable than solid core cable. Solid core cable provides greater mechanical strength, easier soldering, and better signal integrity at low frequencies, though it suffers from higher AC resistance and losses in high-frequency environments. Your choice depends on balancing frequency performance needs against cost and mechanical robustness.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs
Litz cable, composed of multiple insulated strands woven together, minimizes skin effect and is ideal for high-frequency applications such as RF circuits and transformers. Solid core cable offers superior durability and lower resistance for low-frequency or power transmission, making it suitable for audio cables and general wiring. Selecting the right cable depends on the operating frequency, flexibility requirements, and electrical characteristics needed for optimal performance.
litz vs solid core cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com