Latency measures the delay between sending and receiving data, while jitter refers to the variation in that delay over time, impacting the stability of your network connection. Understanding the differences between latency and jitter is crucial for optimizing performance, so continue reading to explore their effects in detail.
Table of Comparison
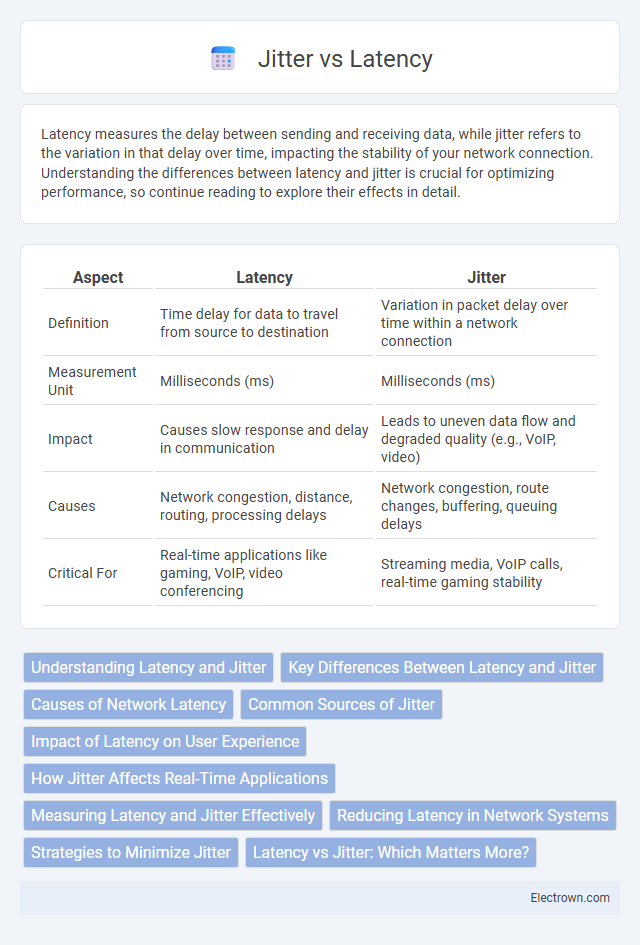
| Aspect | Latency | Jitter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time delay for data to travel from source to destination | Variation in packet delay over time within a network connection |
| Measurement Unit | Milliseconds (ms) | Milliseconds (ms) |
| Impact | Causes slow response and delay in communication | Leads to uneven data flow and degraded quality (e.g., VoIP, video) |
| Causes | Network congestion, distance, routing, processing delays | Network congestion, route changes, buffering, queuing delays |
| Critical For | Real-time applications like gaming, VoIP, video conferencing | Streaming media, VoIP calls, real-time gaming stability |
Understanding Latency and Jitter
Latency measures the time delay between data sending and receiving, directly affecting Your experience in real-time applications like gaming or video calls. Jitter refers to the variability in packet delay, causing irregular disruptions that can degrade call quality or streaming smoothness. Monitoring both latency and jitter is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring seamless digital communication.
Key Differences Between Latency and Jitter
Latency measures the fixed time delay for data packets to travel from source to destination, typically expressed in milliseconds. Jitter represents the variability or inconsistency in packet delay over time, impacting the smoothness of real-time communications like VoIP or gaming. While low latency ensures prompt data delivery, low jitter guarantees consistent timing, both critical for optimal network performance.
Causes of Network Latency
Causes of network latency include physical distance between devices, routing inefficiencies, and congestion on transmission paths. Delays can also arise from processing time at intermediate network devices, signal propagation speed limitations, and protocol overhead. Understanding these factors helps you optimize network performance and reduce latency impacts on applications.
Common Sources of Jitter
Common sources of jitter include network congestion, which causes packet delays and timing inconsistencies, and hardware issues such as faulty routers or switches that disrupt smooth data flow. Software processes like inefficient buffering or poor clock synchronization in devices also contribute to jitter by introducing irregular delays. Understanding these sources helps you optimize network performance and maintain consistent data transmission quality.
Impact of Latency on User Experience
High latency can cause noticeable delays in response times, significantly affecting Your real-time interactions such as video calls, online gaming, and live streaming. This lag disrupts the smooth delivery of content, leading to frustration and reduced satisfaction. Maintaining low latency is crucial to ensure a seamless and responsive user experience across digital applications.
How Jitter Affects Real-Time Applications
Jitter causes variations in packet delay, which disrupts the smooth delivery of data critical for real-time applications like VoIP and online gaming. High jitter results in choppy audio, video lag, and degraded user experience by interrupting the consistent flow of information. Your network performance can be significantly improved by implementing jitter buffers or prioritizing traffic to stabilize data transmission.
Measuring Latency and Jitter Effectively
Measuring latency requires capturing the time delay between a data packet's transmission and its arrival, often using tools like ping tests or network analyzers to quantify round-trip time accurately. Jitter measurement focuses on the variability in packet delay, which impacts real-time applications such as VoIP or online gaming, utilizing metrics like packet delay variation or statistical analysis of inter-arrival times. Your network monitoring should integrate continuous sampling and advanced analytics to differentiate between normal latency and jitter fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance and quality of service.
Reducing Latency in Network Systems
Reducing latency in network systems enhances real-time communication and application performance by minimizing the time data takes to travel from source to destination. Techniques such as optimizing routing paths, upgrading hardware to higher-speed interfaces, and implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies effectively lower latency. You can achieve smoother, faster network interactions by addressing latency without sacrificing stability.
Strategies to Minimize Jitter
To minimize jitter, prioritize implementing Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your network devices to ensure consistent packet delivery times. Deploy jitter buffers in real-time communication systems to smooth out packet arrival variations without adding excessive delay. Regularly monitor network performance and upgrade bandwidth or optimize routing paths to reduce congestion, which directly decreases jitter occurrences.
Latency vs Jitter: Which Matters More?
Latency measures the time it takes for data to travel from source to destination, directly affecting your experience in real-time applications like video calls or gaming. Jitter refers to the variation in latency over time, causing uneven data flow and potentially disrupting audio or video streams. While both impact performance, jitter often matters more in maintaining consistent quality, as high latency can be tolerated if steady, but unpredictable jitter leads to noticeable interruptions.
latency vs jitter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com