24bit audio offers a dynamic range suitable for professional recordings, capturing more detail and subtlety than standard 16bit files, while 32bit audio provides an even greater range and headroom, reducing distortion during mixing and processing. Discover how choosing between 24bit and 32bit audio can impact Your sound quality and workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
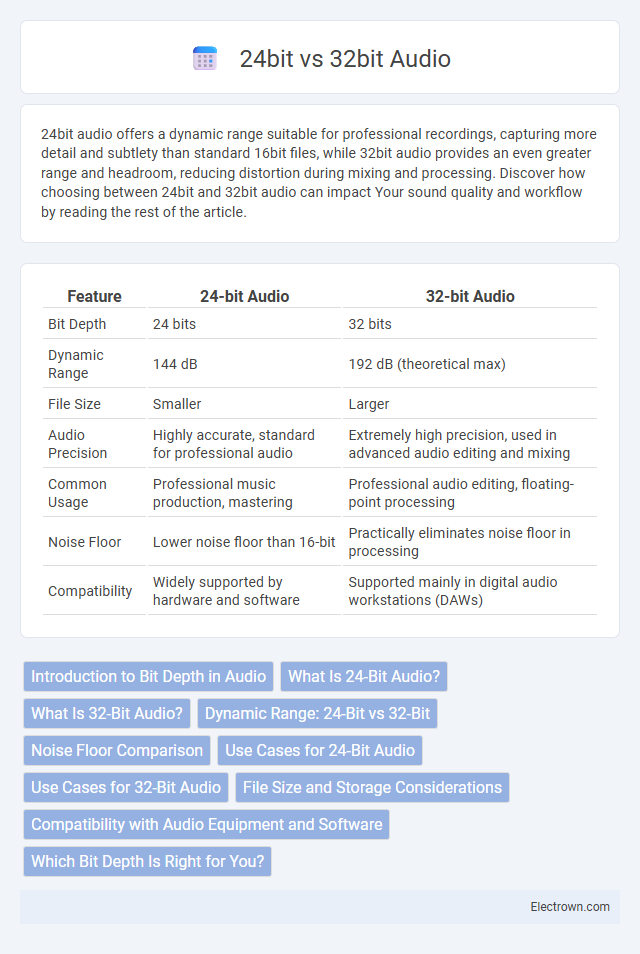
| Feature | 24-bit Audio | 32-bit Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Bit Depth | 24 bits | 32 bits |
| Dynamic Range | 144 dB | 192 dB (theoretical max) |
| File Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Audio Precision | Highly accurate, standard for professional audio | Extremely high precision, used in advanced audio editing and mixing |
| Common Usage | Professional music production, mastering | Professional audio editing, floating-point processing |
| Noise Floor | Lower noise floor than 16-bit | Practically eliminates noise floor in processing |
| Compatibility | Widely supported by hardware and software | Supported mainly in digital audio workstations (DAWs) |
Introduction to Bit Depth in Audio
Bit depth in audio determines the dynamic range and resolution of sound recordings, with 24-bit audio offering 16,777,216 possible amplitude levels compared to 32-bit's 4,294,967,296 levels, allowing for finer detail and less noise. While 24-bit is standard in professional audio production due to its balance of quality and file size, 32-bit audio provides an extended headroom mainly used in high-end editing and mastering workflows. Your choice between 24-bit and 32-bit audio affects the precision of sound capture and the potential for post-production adjustments without quality loss.
What Is 24-Bit Audio?
24-bit audio refers to sound recording and playback formats that use 24 bits of data per sample, enabling a greater dynamic range compared to 16-bit or 32-bit formats. This increased bit depth allows for capturing finer details and more accurate sound representation by providing up to 144 dB of dynamic range, which significantly reduces noise and distortion in recordings. Understanding 24-bit audio helps you appreciate the difference in audio quality, especially in professional music production and high-fidelity listening scenarios.
What Is 32-Bit Audio?
32-bit audio refers to digital sound files that use a 32-bit depth for each audio sample, allowing for a significantly larger dynamic range and more precise audio representation compared to 24-bit audio. This increased bit depth results in reduced quantization noise and greater headroom, making 32-bit audio ideal for professional recording, mixing, and mastering processes where preserving maximum audio fidelity is critical. While 32-bit audio files offer superior sound quality and editing flexibility, playback benefits are limited without compatible hardware and software that can process the higher bit depth effectively.
Dynamic Range: 24-Bit vs 32-Bit
The dynamic range of 24-bit audio is approximately 144 dB, providing a vast spectrum between the quietest and loudest sounds, ideal for high-resolution audio recording and playback. In contrast, 32-bit float audio offers an effectively unlimited dynamic range by allowing headroom beyond 24-bit limitations via floating-point encoding, reducing distortion and clipping during processing. While 32-bit does not inherently improve playback quality, its expanded dynamic range greatly benefits mixing, mastering, and post-production workflows.
Noise Floor Comparison
A 32-bit audio system offers a significantly lower noise floor compared to 24-bit audio, providing greater dynamic range and more precise sound reproduction. While 24-bit audio has a theoretical dynamic range of 144 dB, 32-bit float extends this range, effectively eliminating quantization noise and preserving audio quality during processing and mixing. Your recordings benefit from cleaner, more detailed sound with fewer artifacts, especially in highly dynamic or complex audio environments.
Use Cases for 24-Bit Audio
24-bit audio is commonly used in professional music production, recording studios, and mastering due to its higher dynamic range of 144 dB, which captures more detail and reduces noise compared to 16-bit audio. It is ideal for preserving audio quality during mixing and post-production processes, allowing engineers to work with greater precision and headroom. Audiophiles and high-resolution audio enthusiasts also prefer 24-bit formats for superior sound clarity and depth in playback systems.
Use Cases for 32-Bit Audio
32-bit audio offers superior dynamic range and headroom, making it ideal for professional sound engineers working on high-fidelity music production, film scoring, or audio mastering. Your audio projects benefit from the increased precision when mixing and editing complex sound layers, reducing the risk of clipping and distortion. This format is essential for environments demanding meticulous audio quality, such as studio recordings and post-production workflows.
File Size and Storage Considerations
24bit audio files typically consume less storage space compared to 32bit files, making them more efficient for managing large music libraries. The extra 8 bits in 32bit audio provide greater dynamic range, but this comes at the cost of significantly larger file sizes. Your choice between 24bit and 32bit should balance the need for audio quality with available storage capacity to optimize performance and space.
Compatibility with Audio Equipment and Software
24bit audio is widely compatible with most consumer audio equipment and software, offering a good balance between sound quality and file size. 32bit audio, often associated with professional applications, provides greater dynamic range but may not be fully supported by all playback devices or editing software. Understanding Your audio setup ensures optimal compatibility when choosing between 24bit and 32bit formats.
Which Bit Depth Is Right for You?
Choosing between 24bit and 32bit audio depends on your recording needs and playback environment. 24bit audio provides a dynamic range of 144 dB, which is sufficient for most professional music production and ensures high-fidelity sound quality. If you require greater headroom for extensive audio processing or mastering, 32bit float offers up to 1528 dB dynamic range and prevents clipping, making it ideal for complex projects and preserving your audio's integrity.
24bit vs 32bit audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com