J1939 is a high-level communication protocol commonly used in heavy-duty vehicles for efficient data exchange over CAN networks, while ISO 9141 is an older, slower protocol primarily utilized in OBD-II diagnostics for passenger cars. Discover the key differences and applications of these protocols to understand which best suits Your vehicle communication needs.
Table of Comparison
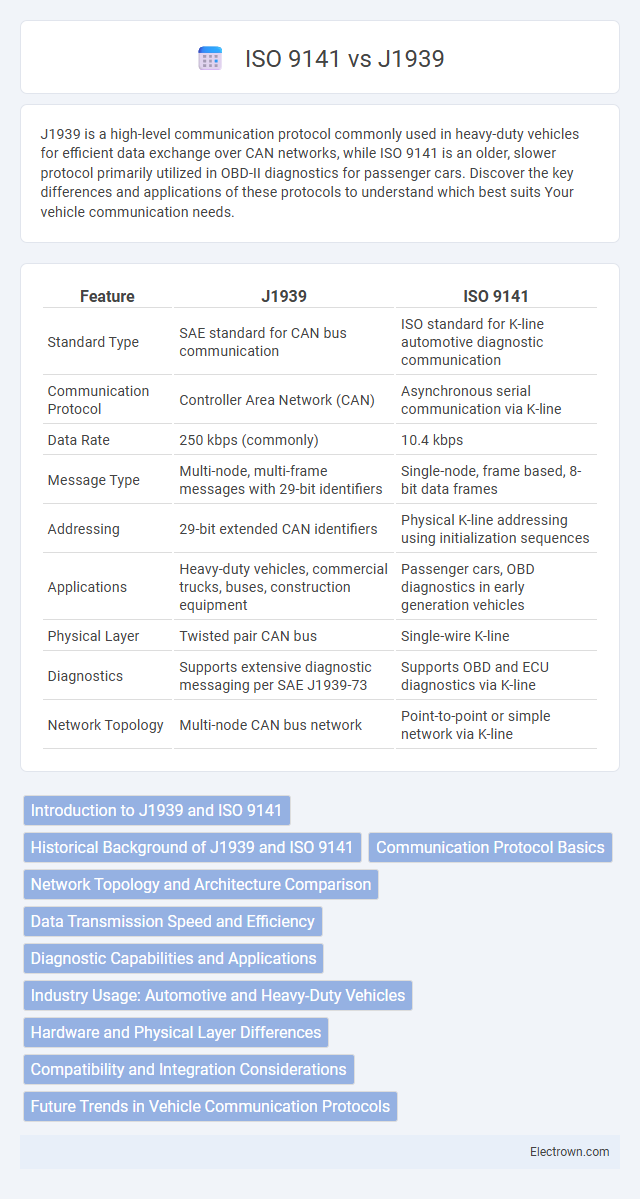
| Feature | J1939 | ISO 9141 |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Type | SAE standard for CAN bus communication | ISO standard for K-line automotive diagnostic communication |
| Communication Protocol | Controller Area Network (CAN) | Asynchronous serial communication via K-line |
| Data Rate | 250 kbps (commonly) | 10.4 kbps |
| Message Type | Multi-node, multi-frame messages with 29-bit identifiers | Single-node, frame based, 8-bit data frames |
| Addressing | 29-bit extended CAN identifiers | Physical K-line addressing using initialization sequences |
| Applications | Heavy-duty vehicles, commercial trucks, buses, construction equipment | Passenger cars, OBD diagnostics in early generation vehicles |
| Physical Layer | Twisted pair CAN bus | Single-wire K-line |
| Diagnostics | Supports extensive diagnostic messaging per SAE J1939-73 | Supports OBD and ECU diagnostics via K-line |
| Network Topology | Multi-node CAN bus network | Point-to-point or simple network via K-line |
Introduction to J1939 and ISO 9141
J1939 is a SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standard designed for heavy-duty vehicles, utilizing the CAN (Controller Area Network) protocol to support complex diagnostic and communication needs in commercial transportation. ISO 9141 is an older OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) protocol primarily used in light-duty vehicles and passenger cars, relying on a slower serial communication method for emission control diagnostics. J1939 offers faster data rates and more robust network management compared to the simpler, less scalable ISO 9141, making it more suitable for modern vehicle communication systems.
Historical Background of J1939 and ISO 9141
J1939 was developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers in the 1990s to create a standardized communication protocol for heavy-duty vehicles, specifically targeting data exchange on Controller Area Networks (CAN) within commercial trucks and buses. ISO 9141 originated in the 1980s as part of the standards for onboard diagnostics in light and medium vehicles, using a slower, serial communication method mainly adopted by European and Asian automakers. Your understanding of these protocols highlights how J1939 supports more complex, high-speed communication for modern trucks, while ISO 9141 caters to earlier generation vehicle diagnostics with simpler data transmission needs.
Communication Protocol Basics
J1939 is a high-level communication protocol primarily used in heavy-duty vehicles, relying on the CAN bus with 29-bit identifiers to facilitate complex data exchange at speeds up to 500 kbps. ISO 9141 operates on a single-wire K-line, using a slower, asynchronous serial communication method, typically at 10.4 kbps, suited for older vehicle diagnostics. The key difference lies in J1939's multi-node, broadcast system designed for real-time control and diagnostics, while ISO 9141 supports primarily point-to-point communication for engine management and emission testing.
Network Topology and Architecture Comparison
J1939 utilizes a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus topology with a multi-drop architecture, enabling multiple electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate efficiently over a single twisted-pair cable, ideal for complex vehicle systems. ISO 9141 employs a single-wire or dual-wire serial communication with a master-slave architecture, primarily supporting point-to-point and simple network configurations. The J1939 network supports higher data rates up to 1 Mbps and robust error handling, whereas ISO 9141 operates at lower speeds around 10.4 kbps, limiting its scalability for modern vehicle diagnostics.
Data Transmission Speed and Efficiency
J1939 supports data transmission speeds up to 250 kbps using the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol, providing efficient multi-node communication for heavy-duty vehicles. ISO 9141 operates at much lower speeds around 10.4 kbps, limiting its efficiency in modern automotive diagnostics and control systems. The higher speed and robust error detection of J1939 enable faster, more reliable data exchange compared to the slower, simpler ISO 9141 protocol.
Diagnostic Capabilities and Applications
J1939 offers advanced diagnostic capabilities with extensive parameter group numbers (PGNs) and support for real-time engine and vehicle data monitoring, making it ideal for heavy-duty commercial vehicles and off-road machinery. ISO 9141, primarily used in light-duty vehicles, provides basic diagnostic access through standardized Readiness Codes and simple diagnostic trouble code (DTC) retrieval but lacks the comprehensive data structure found in J1939. J1939's robust communication protocol supports more complex fault detection and system integration, enhancing predictive maintenance and fleet management applications.
Industry Usage: Automotive and Heavy-Duty Vehicles
J1939 is widely used in heavy-duty vehicles and commercial trucks for its robust CAN-based communication protocol, enabling real-time diagnostics and control. ISO 9141 is primarily found in passenger cars, especially in older vehicles for OBD-II diagnostics, with slower data transmission compared to J1939. The preference for J1939 in heavy-duty applications stems from its higher data transfer rates and ability to support complex vehicle networks.
Hardware and Physical Layer Differences
J1939 uses a Controller Area Network (CAN) physical layer, relying on twisted pair wiring and differential signaling to ensure robust communication in heavy-duty vehicles. ISO 9141 employs a single-wire K-line interface, which limits speed and is more susceptible to electrical noise compared to the CAN bus. Your choice between these protocols affects the complexity, reliability, and speed of data transmission hardware in automotive systems.
Compatibility and Integration Considerations
J1939 and ISO 9141 differ significantly in compatibility and integration, with J1939 designed for heavy-duty vehicle networks utilizing CAN protocol, while ISO 9141 is tailored for light-duty vehicles using a single-wire K-line communication. Integration of J1939 involves compatibility with advanced CAN-based systems, enabling robust multi-node communication and diagnostics, whereas ISO 9141 integration requires simpler diagnostic tools focused on OBD-II protocols in older vehicles. Your choice depends on vehicle type and network complexity, as J1939 supports more sophisticated data exchange across multiple ECUs compared to the more basic, slower ISO 9141 standard.
Future Trends in Vehicle Communication Protocols
Future trends in vehicle communication protocols emphasize the expansion of J1939 due to its robust support for high-speed data exchange and extensive use in commercial vehicles, enabling enhanced diagnostics and telemetry. ISO 9141, primarily designed for older passenger vehicles with lower data rate requirements, faces obsolescence as industry demand shifts towards more scalable and interoperable standards like J1939 and CAN FD. Integration of J1939 with emerging Ethernet-based protocols promises greater bandwidth and real-time data processing, essential for autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
J1939 vs ISO 9141 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com