Baseband transmits digital signals over a single channel without modulation, making it ideal for short-distance communication like within local area networks, while broadband uses multiple channels by modulating signals for simultaneous data transmission over longer distances such as cable internet. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right communication method for your network needs; explore the rest of the article to dive deeper into baseband and broadband technologies.
Table of Comparison
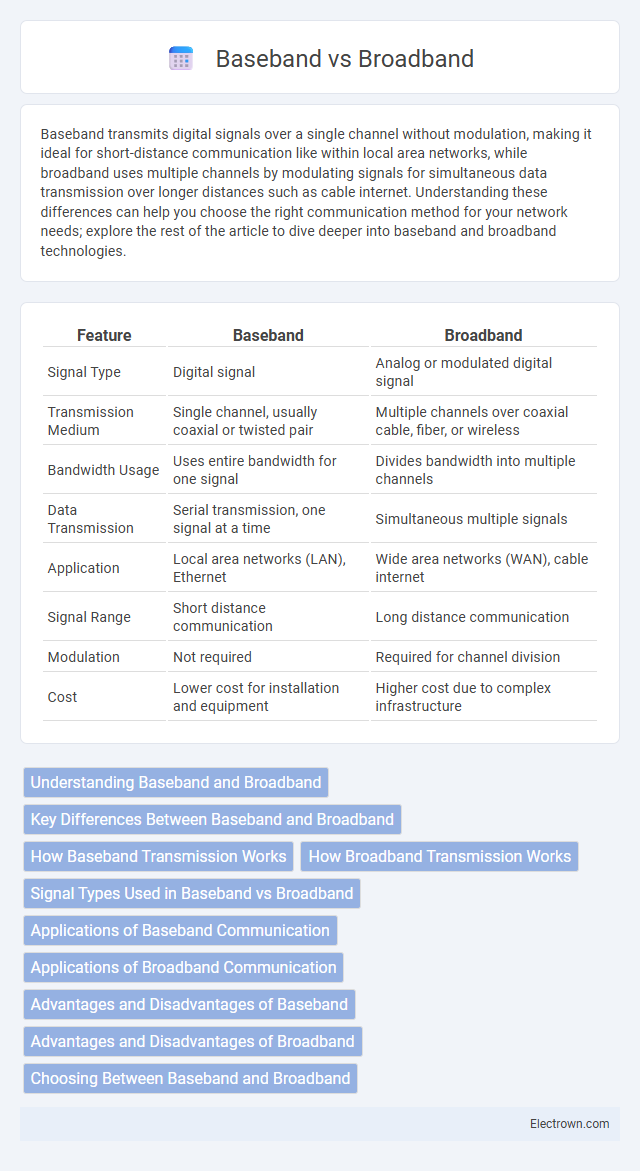
| Feature | Baseband | Broadband |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Digital signal | Analog or modulated digital signal |
| Transmission Medium | Single channel, usually coaxial or twisted pair | Multiple channels over coaxial cable, fiber, or wireless |
| Bandwidth Usage | Uses entire bandwidth for one signal | Divides bandwidth into multiple channels |
| Data Transmission | Serial transmission, one signal at a time | Simultaneous multiple signals |
| Application | Local area networks (LAN), Ethernet | Wide area networks (WAN), cable internet |
| Signal Range | Short distance communication | Long distance communication |
| Modulation | Not required | Required for channel division |
| Cost | Lower cost for installation and equipment | Higher cost due to complex infrastructure |
Understanding Baseband and Broadband
Baseband communication transmits digital signals over a single channel using the entire bandwidth, ideal for short-distance or point-to-point connections such as Ethernet networks. Broadband communication divides the bandwidth into multiple channels, enabling simultaneous data transmission over different frequencies, commonly used in cable internet and television systems. Understanding the difference between baseband and broadband is crucial for selecting the appropriate transmission method based on network requirements and distance.
Key Differences Between Baseband and Broadband
Baseband transmission uses a single signal over a single channel, making it ideal for shorter distances and simpler network designs, while broadband transmission divides the bandwidth into multiple channels, allowing simultaneous data streams over long distances. Baseband networks typically employ digital signals, whereas broadband supports both analog and digital signals, enhancing versatility in communication. Your choice between baseband and broadband depends on factors like required data rate, distance, and network complexity.
How Baseband Transmission Works
Baseband transmission works by sending a single data signal directly over the communication medium without modulation, utilizing the entire bandwidth for one channel at a time. It typically transmits digital signals as square waves, with data encoded into discrete voltage pulses, allowing for high-speed, short-distance communication on local area networks (LANs) such as Ethernet. Your network devices use baseband transmission to achieve precise timing and synchronization, optimizing data integrity within confined environments.
How Broadband Transmission Works
Broadband transmission works by dividing the communication channel into multiple frequency bands, allowing simultaneous transmission of several signals without interference. By using modulation techniques such as Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM), broadband enables high-speed data transfer over various media like coaxial cables, fiber optics, or wireless networks. Your internet experience benefits from broadband's ability to carry diverse types of data streams concurrently, supporting activities like streaming, gaming, and large file downloads efficiently.
Signal Types Used in Baseband vs Broadband
Baseband communication uses digital signals that transmit data over a single channel without modulation, supporting binary or discrete signal types directly on the physical medium. Broadband communication employs analog signals or modulated digital signals, allowing multiple frequency channels to coexist for simultaneous data transmission. Signal types in baseband are typically unmodulated digital pulses, while broadband relies on frequency division multiplexing to handle modulated sinusoidal waveforms across different bands.
Applications of Baseband Communication
Baseband communication is primarily used in digital data transmission applications such as local area networks (LANs), Ethernet, and USB connections, where signals are sent over a single channel without modulation. This technique suits short-distance communication within buildings or campuses, offering high data transfer rates and minimal interference. Your systems can benefit from baseband communication when reliable, direct digital signaling is essential for efficient and secure data exchange.
Applications of Broadband Communication
Broadband communication is widely used in internet services, enabling high-speed data transfer for online gaming, streaming, and video conferencing. It supports multiple devices simultaneously in residential and commercial networks, enhancing connectivity and user experience. Broadband's capacity for continuous data transmission makes it essential for smart homes, IoT applications, and telemedicine.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Baseband
Baseband communication offers the advantage of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reduced interference due to its use of a single channel for data transmission, making it suitable for short-distance, high-speed networking like Ethernet. However, its limited range and inability to support multiple simultaneous signals restrict its use to local area networks and constrain scalability in larger, more complex communication systems. The exclusive use of one signaling method also reduces flexibility compared to broadband, which can carry multiple frequency channels simultaneously.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Broadband
Broadband offers high-speed internet access with a wide bandwidth, enabling simultaneous data transmission and supporting multiple devices, which is ideal for streaming, gaming, and large file downloads. Its primary disadvantage includes potential security vulnerabilities due to persistent connectivity and fluctuating speeds caused by network congestion. Broadband's always-on nature provides convenience but can lead to higher costs and increased exposure to cyber threats compared to baseband connections.
Choosing Between Baseband and Broadband
Choosing between baseband and broadband depends on your network requirements and environment. Baseband transmits digital signals over a single channel, ideal for short-range and less complex setups, while broadband supports multiple channels and is better suited for long-distance communication and high data traffic. Your choice should consider factors like bandwidth needs, interference tolerance, and infrastructure complexity.
Baseband vs Broadband Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com