RS-485 supports longer cable lengths and multiple devices on a single bus, offering superior noise immunity and data transmission over RS-232, which is limited to point-to-point communication and shorter distances. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these interfaces impact Your specific communication needs.
Table of Comparison
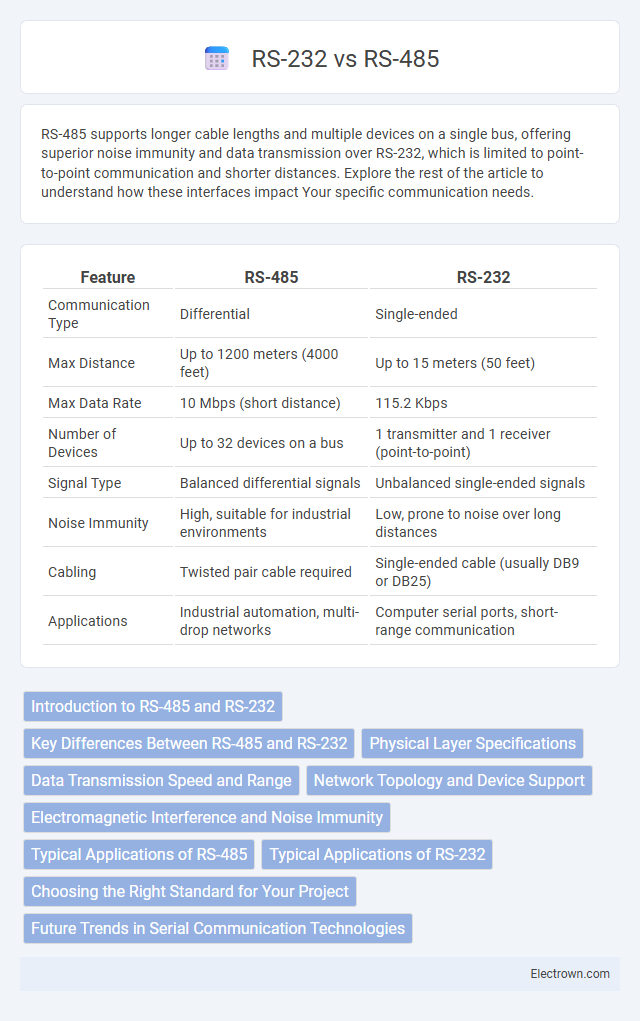
| Feature | RS-485 | RS-232 |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Differential | Single-ended |
| Max Distance | Up to 1200 meters (4000 feet) | Up to 15 meters (50 feet) |
| Max Data Rate | 10 Mbps (short distance) | 115.2 Kbps |
| Number of Devices | Up to 32 devices on a bus | 1 transmitter and 1 receiver (point-to-point) |
| Signal Type | Balanced differential signals | Unbalanced single-ended signals |
| Noise Immunity | High, suitable for industrial environments | Low, prone to noise over long distances |
| Cabling | Twisted pair cable required | Single-ended cable (usually DB9 or DB25) |
| Applications | Industrial automation, multi-drop networks | Computer serial ports, short-range communication |
Introduction to RS-485 and RS-232
RS-485 and RS-232 are widely used serial communication standards designed for different applications and environments. RS-232 supports point-to-point communication with a maximum cable length of 15 meters, ideal for simple, low-speed data exchange between devices. RS-485, on the other hand, allows multi-point communication over longer distances up to 1,200 meters, making it suitable for industrial networks and robust data transmission in noisy environments.
Key Differences Between RS-485 and RS-232
RS-485 supports multi-point communications with up to 32 devices on a single bus, while RS-232 is designed for point-to-point connections between two devices. The RS-485 standard allows for longer cable lengths up to 1,200 meters and higher data rates of up to 10 Mbps, compared to RS-232's maximum cable length of 15 meters and data rate of 115.2 kbps. If your setup requires robust, long-distance communication in industrial environments, RS-485 is the superior choice over RS-232.
Physical Layer Specifications
RS-485 supports differential signaling on a twisted pair cable, enabling transmission distances up to 1,200 meters and multiple devices on a single bus with up to 32 drivers and 32 receivers. RS-232 uses single-ended signaling with a maximum cable length of 15 meters and supports point-to-point communication between one transmitter and receiver. Your choice depends on the required communication distance, noise immunity, and network topology, with RS-485 being superior for long-distance and multi-drop networks.
Data Transmission Speed and Range
RS-485 supports data transmission speeds up to 10 Mbps over short distances, maintaining reliable communication up to 4000 feet (1200 meters), making it ideal for long-distance and industrial applications. RS-232 typically offers speeds up to 115.2 Kbps with a maximum cable length of 50 feet (15 meters), limiting its use to shorter, point-to-point connections. The differential signaling in RS-485 reduces noise and allows for higher speeds and extended range compared to the single-ended RS-232 standard.
Network Topology and Device Support
RS-485 supports multi-point network topology, allowing up to 32 devices on a single bus, ideal for complex industrial communication systems. RS-232 uses a point-to-point topology, typically connecting only two devices, limiting its scalability in networked environments. The differential signaling in RS-485 enhances noise immunity, making it suitable for long-distance and multi-device setups compared to the single-ended RS-232.
Electromagnetic Interference and Noise Immunity
RS-485 offers superior electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance compared to RS-232 due to its differential signaling, which effectively cancels out noise and ensures reliable data transmission in electrically noisy environments. RS-485's twisted-pair cables further enhance noise immunity, making it ideal for industrial applications where EMI is prevalent. In contrast, RS-232 uses single-ended signaling, which is more susceptible to noise and EMI, limiting its performance over longer distances and in high-interference settings.
Typical Applications of RS-485
RS-485 is commonly used in industrial automation, building management systems, and remote sensor networks due to its robust differential signaling and ability to support long-distance communication up to 1,200 meters. Its multi-drop capabilities enable multiple devices to share a single communication line, making it ideal for control systems and data acquisition in harsh electrical environments. Typical applications also include Modbus networks, motor controllers, and HVAC systems where reliable, noise-resistant serial data transmission is critical.
Typical Applications of RS-232
RS-232 is commonly used in serial communication for short-distance data exchange, such as connecting computers to peripherals like modems, printers, and industrial instrumentation. Its point-to-point architecture supports low-speed communication up to 50 feet, ideal for legacy systems and simple serial interfaces. RS-232 remains prevalent in embedded systems, barcode scanners, and laboratory instruments due to its straightforward implementation and compatibility with standard COM ports.
Choosing the Right Standard for Your Project
Choosing the right communication standard depends on your project's distance and speed requirements. RS-485 supports longer cable lengths up to 1,200 meters and higher data rates, making it ideal for industrial and multi-drop networks, while RS-232 is suited for short-distance, point-to-point connections up to 15 meters. Evaluate the environment, noise immunity, and number of devices to determine whether RS-485's differential signaling or RS-232's single-ended transmission best fits your application.
Future Trends in Serial Communication Technologies
RS-485 is gaining prominence in industrial automation due to its robust multi-drop communication and longer cable length capabilities compared to RS-232, which remains limited to short-distance, point-to-point connections. Emerging serial communication technologies emphasize enhanced data rates, noise immunity, and network scalability, with RS-485 often integrated into IoT and smart grid applications because of its differential signaling and support for multiple devices on a single bus. Innovations like enhanced protocol standards and integration with wireless modules indicate a future where RS-485 evolves alongside Ethernet and USB for hybrid serial communication systems.
RS-485 vs RS-232 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com