PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) converts analog signals into digital form by sampling and quantizing them, while DM (Delta Modulation) encodes the difference between successive samples, offering simpler implementation but potentially lower fidelity. Explore the article to understand how each method impacts audio quality and application efficiency for your digital communication needs.
Table of Comparison
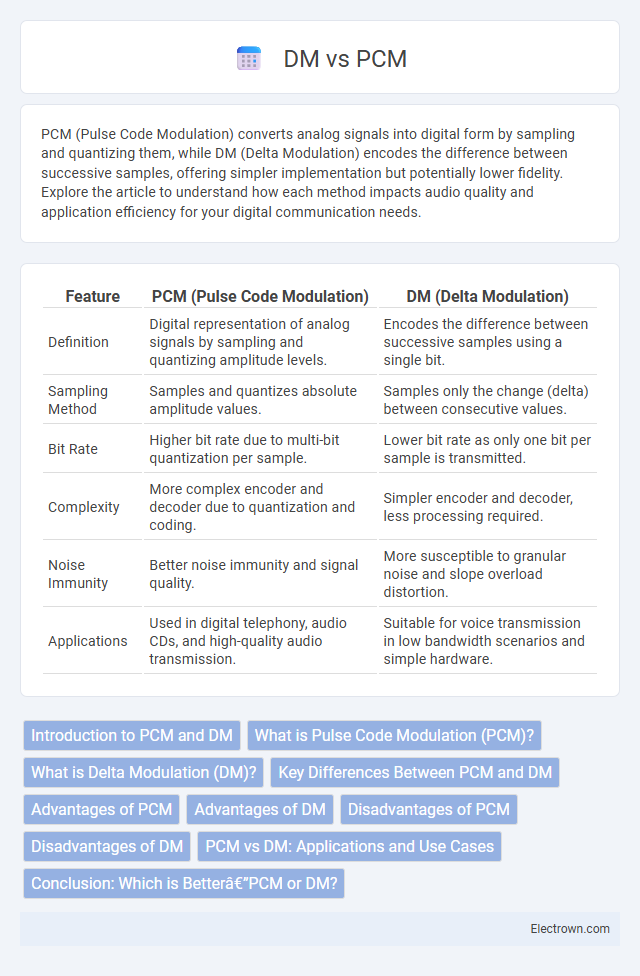
| Feature | PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) | DM (Delta Modulation) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital representation of analog signals by sampling and quantizing amplitude levels. | Encodes the difference between successive samples using a single bit. |
| Sampling Method | Samples and quantizes absolute amplitude values. | Samples only the change (delta) between consecutive values. |
| Bit Rate | Higher bit rate due to multi-bit quantization per sample. | Lower bit rate as only one bit per sample is transmitted. |
| Complexity | More complex encoder and decoder due to quantization and coding. | Simpler encoder and decoder, less processing required. |
| Noise Immunity | Better noise immunity and signal quality. | More susceptible to granular noise and slope overload distortion. |
| Applications | Used in digital telephony, audio CDs, and high-quality audio transmission. | Suitable for voice transmission in low bandwidth scenarios and simple hardware. |
Introduction to PCM and DM
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a digital representation of analog signals where the amplitude of the analog signal is sampled at uniform intervals and quantized into a series of coded pulses. Delta Modulation (DM) simplifies PCM by encoding the difference between successive samples rather than absolute values, enabling reduced bit rates for transmission. PCM offers higher accuracy with increased bandwidth usage, while DM provides a more bandwidth-efficient alternative with lower complexity but increased quantization noise.
What is Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)?
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a digital representation technique where analog signals are sampled at uniform intervals and quantized into discrete numerical values. PCM converts continuous audio or voice signals into binary form, enabling efficient transmission and storage without significant loss of quality. Your audio devices rely on PCM to ensure clear, high-fidelity sound reproduction in telephony, digital audio, and broadcasting systems.
What is Delta Modulation (DM)?
Delta Modulation (DM) is a simplified form of analog-to-digital signal conversion that encodes the difference between consecutive samples rather than absolute signal levels. Unlike Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), which uses multiple bits per sample to represent amplitude values, DM uses a single bit to indicate whether the signal is increasing or decreasing, resulting in lower complexity and bandwidth usage. This makes DM suitable for low-bit-rate applications, though it may suffer from granular noise and slope overload distortion compared to PCM.
Key Differences Between PCM and DM
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) converts analog signals into a digital bitstream by sampling amplitude values, while Delta Modulation (DM) encodes the difference between successive samples, focusing on signal changes rather than absolute values. PCM offers higher accuracy and better noise immunity at the cost of increased bandwidth, whereas DM requires less data transmission but may suffer from slope overload and granular noise in rapidly changing signals. Your choice depends on application needs: PCM suits high-fidelity audio and data transmission, while DM is efficient for simpler, low-bandwidth scenarios.
Advantages of PCM
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) offers superior noise immunity and higher signal fidelity compared to Delta Modulation (DM) due to its multi-bit encoding process, which reduces quantization errors. PCM's robust digital representation facilitates easier integration with modern digital communication systems and supports advanced error detection and correction techniques. Your choice of PCM ensures enhanced audio quality and reliable data transmission, especially in environments with significant interference.
Advantages of DM
Differential Manchester (DM) encoding offers superior synchronization benefits compared to Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) by embedding clock information within the signal transitions, which reduces timing errors during data transmission. DM's differential nature also enhances noise immunity, making it more resilient to signal degradation over long distances or in electrically noisy environments. If You require reliable data integrity and efficient synchronization for your communication systems, DM is often the preferred choice over PCM.
Disadvantages of PCM
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) suffers from higher bandwidth requirements compared to Delta Modulation (DM), leading to increased transmission costs. PCM systems are more complex and require precise synchronization to prevent signal distortion and data loss. Furthermore, PCM's quantization process introduces quantization noise, which can degrade signal quality if not adequately managed through higher bit rates or advanced filtering techniques.
Disadvantages of DM
Delta Modulation (DM) suffers from granular noise and slope overload distortion due to its single-bit quantization, limiting its performance in high-frequency or rapidly changing signals. Its low resolution causes significant quantization errors compared to Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), which employs multi-bit encoding for higher fidelity. Furthermore, DM requires precise step size adjustment to balance noise and distortion, complicating implementation compared to PCM's more robust and scalable design.
PCM vs DM: Applications and Use Cases
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is widely used in traditional telephony, audio recording, and digital audio applications due to its straightforward encoding and high fidelity. Delta Modulation (DM) excels in low-bandwidth scenarios such as voice transmission over constrained communication channels and real-time telemetry, offering reduced complexity and data rate. PCM is preferred for high-quality sound reproduction, while DM suits applications requiring simpler, low-latency digital encoding.
Conclusion: Which is Better—PCM or DM?
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) offers superior noise immunity and fidelity for high-quality digital audio transmission, making it ideal for professional audio and communication systems. DM (Delta Modulation) requires lower bandwidth and simpler hardware, which suits applications with limited resources or where moderate audio quality is acceptable. The choice between PCM and DM depends on specific needs: PCM excels in accuracy and clarity, while DM is better for cost-effective, bandwidth-efficient scenarios.
PCM vs DM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com