ISDN offers faster digital data transmission compared to the analog signals used by PSTN, making it ideal for integrated voice, video, and data services. Explore the full article to understand how these technologies impact your communication infrastructure and which is best suited for your needs.
Table of Comparison
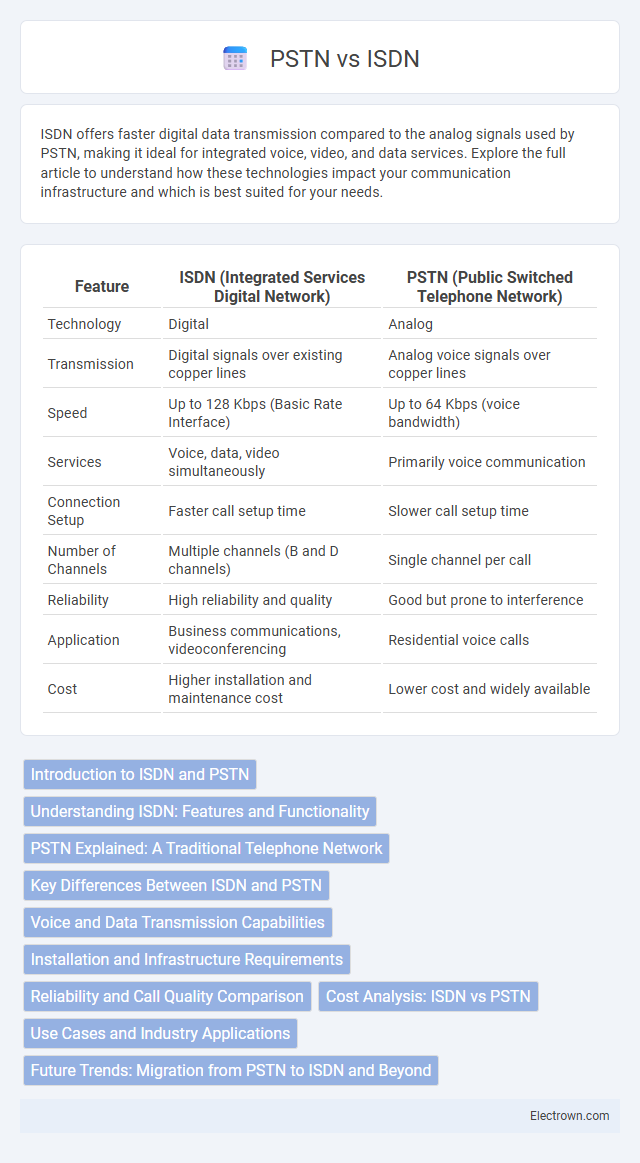
| Feature | ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) | PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Digital | Analog |
| Transmission | Digital signals over existing copper lines | Analog voice signals over copper lines |
| Speed | Up to 128 Kbps (Basic Rate Interface) | Up to 64 Kbps (voice bandwidth) |
| Services | Voice, data, video simultaneously | Primarily voice communication |
| Connection Setup | Faster call setup time | Slower call setup time |
| Number of Channels | Multiple channels (B and D channels) | Single channel per call |
| Reliability | High reliability and quality | Good but prone to interference |
| Application | Business communications, videoconferencing | Residential voice calls |
| Cost | Higher installation and maintenance cost | Lower cost and widely available |
Introduction to ISDN and PSTN
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) provides digital transmission of voice and data over traditional copper telephone lines, enabling faster and more reliable communication compared to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), which relies on analog signals for voice calls. PSTN represents the conventional circuit-switched telephony infrastructure that supports voice communication through analog signals, widely deployed for decades across global telephony networks. ISDN enhances basic telephony by allowing simultaneous digital voice, data, and video transmission, improving service capabilities beyond PSTN's analog limitations.
Understanding ISDN: Features and Functionality
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) offers digital transmission of voice, video, and data over traditional telephone lines, providing faster call setup and higher quality compared to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network). With ISDN, your communication benefits from simultaneous voice and data services, enabling features like multiple digital channels and integrated signaling. This enhanced functionality supports more efficient and versatile telecommunications for businesses and individuals alike.
PSTN Explained: A Traditional Telephone Network
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) is a global circuit-switched telephone network that connects landline phones using copper wires and analog signals. It relies on a system of switches and exchanges to establish dedicated voice communication paths between callers. PSTN's infrastructure supports reliable, low-latency voice transmission but is limited in data transfer capabilities compared to ISDN.
Key Differences Between ISDN and PSTN
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) transmits voice and data digitally over the same telephone lines, enabling faster and clearer communication, while PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) relies on analog signals for traditional voice calls. ISDN supports simultaneous multiple connections and services like video conferencing and data transfer, contrasting with PSTN's single-channel voice-only capacity. The digital architecture of ISDN offers improved call setup times and better line quality compared to the slower, less efficient analog PSTN system.
Voice and Data Transmission Capabilities
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) offers simultaneous voice and data transmission over a single line, enabling faster and clearer communication compared to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), which primarily supports analog voice signals with limited data transmission capabilities. ISDN's digital signals provide higher quality, faster call setup, and support for services like video conferencing and internet access. Your choice between ISDN and PSTN impacts communication efficiency, especially for businesses requiring reliable data and voice integration.
Installation and Infrastructure Requirements
ISDN requires digital-compatible infrastructure, including specialized terminal adapters and digital lines, enabling simultaneous voice and data transmission, while PSTN relies on traditional analog circuits with widespread copper wiring. ISDN installation involves configuring digital switches and network termination units, demanding more sophisticated setup compared to the simpler analog interfaces of PSTN. Consequently, ISDN supports advanced telephony features through dedicated digital lines, whereas PSTN offers basic voice services via established legacy infrastructure.
Reliability and Call Quality Comparison
ISDN offers higher reliability and superior call quality compared to PSTN due to its digital transmission, minimizing noise and signal degradation. PSTN relies on analog signals, which are more susceptible to interference and quality loss over long distances. For your communication needs, ISDN ensures clearer voice transmission and consistent connection stability, making it ideal for businesses requiring dependable phone services.
Cost Analysis: ISDN vs PSTN
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) typically incurs higher initial setup and monthly service costs compared to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), but offers faster data transmission and multiple simultaneous voice and data channels, enhancing efficiency for businesses. PSTN remains more cost-effective for basic voice communication needs due to its widespread infrastructure and lower maintenance expenses. Your choice between ISDN and PSTN should weigh the balance between upfront investment and the value gained from ISDN's advanced features.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) supports simultaneous voice, video, and data transmission, making it ideal for businesses requiring reliable, multi-channel communication such as call centers and video conferencing services. PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) primarily handles traditional voice calls and is widely used in residential telephony, emergency services, and basic corporate voice solutions. Industries like telecommunications, healthcare, and finance leverage ISDN for secure, high-quality connections, whereas PSTN remains prevalent in areas with limited broadband infrastructure and for standard voice communications.
Future Trends: Migration from PSTN to ISDN and Beyond
The migration from PSTN to ISDN is driven by the need for enhanced digital communication capabilities and higher data transmission speeds. ISDN supports integrated voice and data services, offering a more flexible and efficient infrastructure compared to traditional PSTN. Future trends point towards transitioning beyond ISDN to advanced IP-based networks like VoIP and fiber-optic technologies, enabling greater scalability, lower latency, and improved multimedia support.
ISDN vs PSTN Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com