Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) divides a single communication channel into multiple time slots, allowing multiple signals to share the same transmission medium by transmitting in rapid succession, whereas Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) separates signals by allocating different frequency bands within the same channel. Understanding the key differences between TDM and FDM will help you choose the best multiplexing method for your communication system--read on to explore their advantages and applications.
Table of Comparison
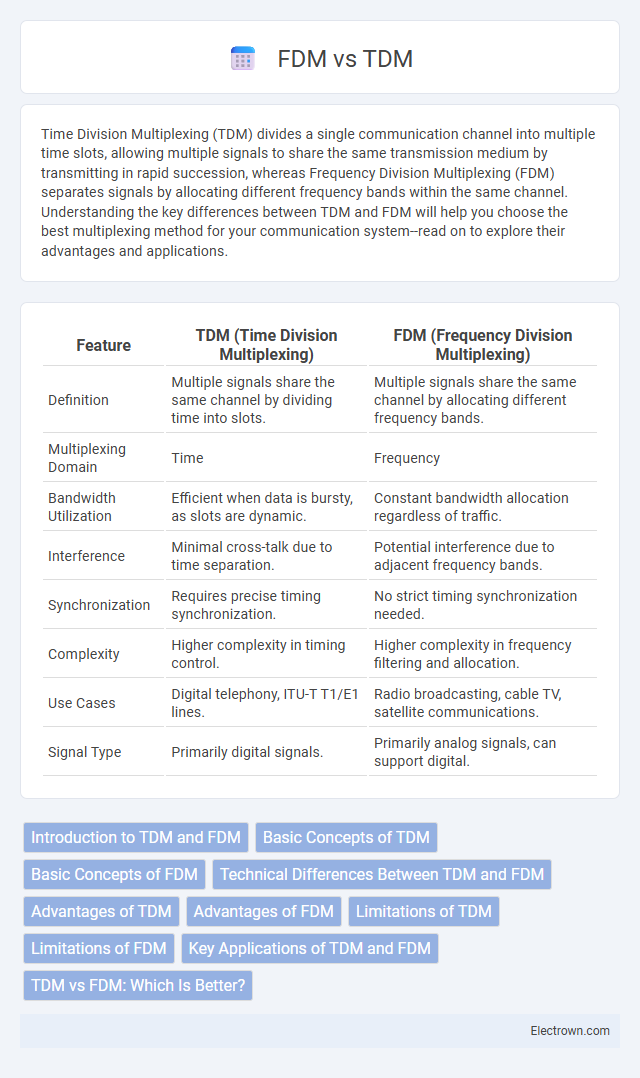
| Feature | TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) | FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple signals share the same channel by dividing time into slots. | Multiple signals share the same channel by allocating different frequency bands. |
| Multiplexing Domain | Time | Frequency |
| Bandwidth Utilization | Efficient when data is bursty, as slots are dynamic. | Constant bandwidth allocation regardless of traffic. |
| Interference | Minimal cross-talk due to time separation. | Potential interference due to adjacent frequency bands. |
| Synchronization | Requires precise timing synchronization. | No strict timing synchronization needed. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity in timing control. | Higher complexity in frequency filtering and allocation. |
| Use Cases | Digital telephony, ITU-T T1/E1 lines. | Radio broadcasting, cable TV, satellite communications. |
| Signal Type | Primarily digital signals. | Primarily analog signals, can support digital. |
Introduction to TDM and FDM
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) are key techniques for transmitting multiple signals over a single communication channel. TDM allocates distinct time slots to each signal, ensuring organized, sequential data transmission. FDM assigns separate frequency bands to different signals, enabling simultaneous transmission without interference.
Basic Concepts of TDM
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) divides a single communication channel into multiple time slots, each allocated to a different signal or user, allowing multiple data streams to share the same transmission medium efficiently. Each user transmits in rapid succession within their designated time slot, preventing overlap and interference. TDM is widely used in digital telephony and data networks to optimize bandwidth utilization by sequentially interleaving signals over a single communication path.
Basic Concepts of FDM
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) divides the available bandwidth into distinct frequency bands, each carrying a separate signal simultaneously. Each signal is modulated onto its unique carrier frequency, preventing overlap and interference between channels. Your communication system benefits from efficient utilization of the spectrum, supporting multiple transmissions concurrently within the same physical medium.
Technical Differences Between TDM and FDM
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) separates multiple signals by allocating distinct time slots for each within a single communication channel, enabling sequential data transmission. Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) divides the available bandwidth into multiple frequency bands, allowing simultaneous transmission of signals on different frequencies. TDM relies on precise timing synchronization, while FDM requires filters to isolate frequency bands and prevent interference.
Advantages of TDM
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) offers significant advantages over Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) by efficiently utilizing bandwidth through time slot allocation, which enables multiple signals to share the same frequency channel without interference. TDM supports higher data integrity and synchronization, making it ideal for digital communication systems where precise timing is critical. Its scalability and ease of integration with digital networks improve system flexibility and reduce the complexity of channel management compared to FDM.
Advantages of FDM
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) offers the advantage of simultaneous data transmission by allocating distinct frequency bands to each signal, which minimizes interference and ensures consistent bandwidth. Unlike Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), FDM supports continuous and real-time data flow, making it ideal for analog signals like radio and television broadcasting. Your network benefits from efficient spectrum utilization and improved signal clarity with FDM in high-frequency communication systems.
Limitations of TDM
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) faces limitations including limited time slot allocation, which reduces efficiency during low data traffic periods. Its fixed time intervals can cause synchronization issues and increased latency, especially in bursty or asynchronous data streams. Your network's performance may suffer if TDM is used in scenarios requiring dynamic bandwidth allocation or real-time data transmission.
Limitations of FDM
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) faces limitations such as limited bandwidth availability, which restricts the number of channels that can be simultaneously transmitted. Signal interference and crosstalk occur due to closely spaced frequency bands, reducing overall transmission quality. Furthermore, FDM requires complex filtering and guard bands, which increase system complexity and decrease spectral efficiency.
Key Applications of TDM and FDM
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) is primarily used in digital communication systems such as telephony and digital transmission where multiple signals share the same channel by allocating distinct time slots, making it ideal for synchronous data transmission. Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) finds its key applications in analog systems like radio and television broadcasting, where different signals are transmitted simultaneously over separate frequency bands, optimizing bandwidth usage in wireless communication. Understanding whether TDM or FDM best suits your network depends on the nature of your data and transmission requirements.
TDM vs FDM: Which Is Better?
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) and FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) serve different purposes depending on your communication needs. TDM offers higher efficiency in digital signal transmission by allocating time slots, while FDM is more suited for analog signals by dividing the frequency spectrum. Choosing between TDM vs FDM depends on factors like bandwidth availability, latency requirements, and signal type.
TDM vs FDM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com