RSSI measures the strength of a received signal, providing a numeric value that indicates how powerful the signal is at the receiver's location. Understanding the difference between RSSI and LQI can help you optimize wireless communication performance, so explore the rest of the article for a detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
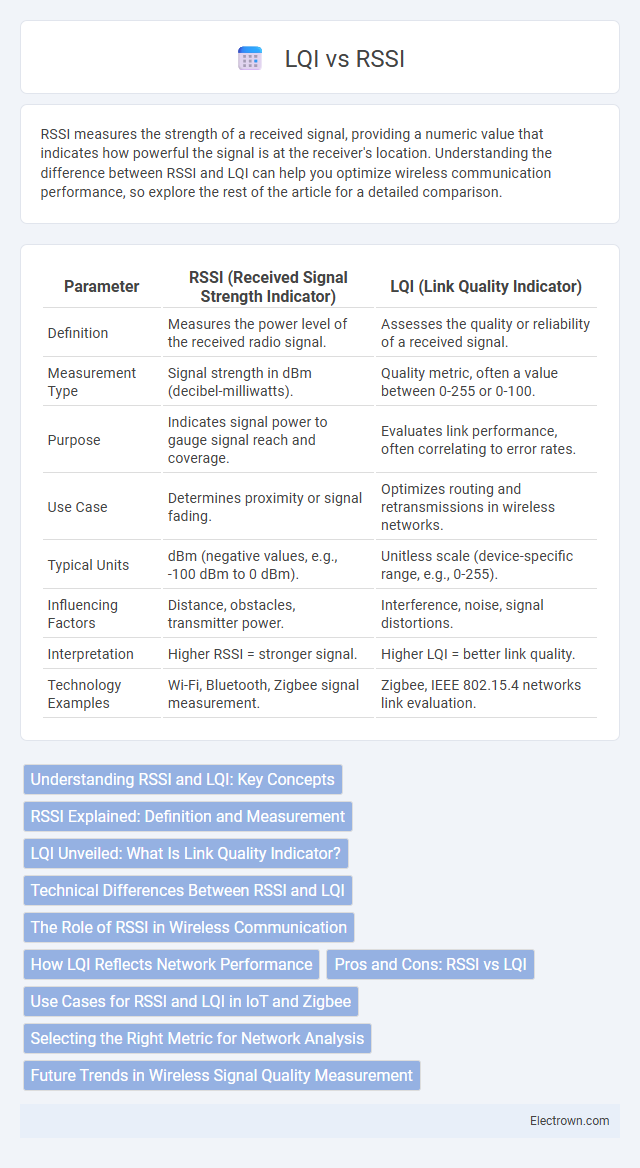
| Parameter | RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) | LQI (Link Quality Indicator) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the power level of the received radio signal. | Assesses the quality or reliability of a received signal. |
| Measurement Type | Signal strength in dBm (decibel-milliwatts). | Quality metric, often a value between 0-255 or 0-100. |
| Purpose | Indicates signal power to gauge signal reach and coverage. | Evaluates link performance, often correlating to error rates. |
| Use Case | Determines proximity or signal fading. | Optimizes routing and retransmissions in wireless networks. |
| Typical Units | dBm (negative values, e.g., -100 dBm to 0 dBm). | Unitless scale (device-specific range, e.g., 0-255). |
| Influencing Factors | Distance, obstacles, transmitter power. | Interference, noise, signal distortions. |
| Interpretation | Higher RSSI = stronger signal. | Higher LQI = better link quality. |
| Technology Examples | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee signal measurement. | Zigbee, IEEE 802.15.4 networks link evaluation. |
Understanding RSSI and LQI: Key Concepts
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received radio signal, providing an estimate of signal strength between devices. LQI (Link Quality Indicator) evaluates the quality and reliability of the received signal by analyzing factors like error rates and signal-to-noise ratio. Understanding both RSSI and LQI is crucial for optimizing wireless network performance and ensuring your communication link remains stable and efficient.
RSSI Explained: Definition and Measurement
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received radio signal, expressed in decibels (dBm), indicating the strength of the connection. It is commonly used to assess signal quality in wireless networks by evaluating the signal intensity from a specific transmitter, helping determine the range and reliability of communication. Your wireless device relies on accurate RSSI measurements to optimize network performance and maintain a stable connection.
LQI Unveiled: What Is Link Quality Indicator?
Link Quality Indicator (LQI) measures the quality of a received signal in wireless communication, providing a fine-grained assessment of link reliability beyond basic signal strength metrics like Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). Unlike RSSI, which quantifies the power level of the received signal, LQI evaluates the integrity and error rates within the transmission, offering a more accurate representation of communication health. LQI is crucial for optimizing network performance in protocols such as IEEE 802.15.4, where maintaining high link quality ensures efficient data transfer and reduced packet loss.
Technical Differences Between RSSI and LQI
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received radio signal, providing a quantitative value of signal strength in dBm, which helps assess link quality and range. LQI (Link Quality Indicator) evaluates the quality of a received packet based on error rates and signal-to-noise ratio, offering a qualitative metric for reliability and transmission integrity. While RSSI reflects raw signal power, LQI integrates error and noise metrics to better represent actual communication performance in wireless systems.
The Role of RSSI in Wireless Communication
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received radio signal, playing a crucial role in determining the quality and stability of wireless communication links. Unlike LQI (Link Quality Indicator), which evaluates the signal's quality through error rates, RSSI primarily reflects signal strength, helping optimize network performance and device connectivity. Understanding your RSSI values ensures better signal coverage and effective troubleshooting in wireless networks.
How LQI Reflects Network Performance
LQI (Link Quality Indicator) measures the quality of a wireless link by assessing factors such as signal-to-noise ratio and error rate, providing a holistic view of network performance beyond just signal strength. Unlike RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator), which solely indicates signal power, LQI reflects the reliability and stability of data transmission, directly impacting packet delivery success and communication efficiency. This makes LQI a crucial metric for optimizing and maintaining robust wireless networks, particularly in IoT and sensor applications.
Pros and Cons: RSSI vs LQI
RSSI measures signal strength, offering straightforward hardware implementation and immediate feedback but can be affected by noise and interference, reducing accuracy. LQI provides detailed link quality by analyzing signal modulation and errors, enhancing reliability in network decisions, though it requires more complex processing and may vary between devices. Choosing between RSSI and LQI depends on balancing simplicity and precision for specific wireless communication needs.
Use Cases for RSSI and LQI in IoT and Zigbee
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received signal, making it crucial for assessing link quality and range in IoT and Zigbee networks. LQI (Link Quality Indicator) evaluates the integrity and error rate of the received signal, providing insights into data reliability and network performance. You can use RSSI to optimize node placement for maximum coverage, while LQI helps ensure stable communication by monitoring link quality and minimizing packet loss.
Selecting the Right Metric for Network Analysis
Selecting the right metric for network analysis depends on the specific aspects of wireless communication being evaluated; RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of the received signal, providing insight into signal reach and strength. LQI (Link Quality Indicator) assesses the quality and reliability of the communication link, including factors like error rate and signal-to-noise ratio, making it more suitable for evaluating link stability and performance. For effective network troubleshooting and optimization, combining RSSI for signal coverage and LQI for link quality offers a comprehensive understanding of network health.
Future Trends in Wireless Signal Quality Measurement
Future trends in wireless signal quality measurement emphasize enhanced integration of RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) and LQI (Link Quality Indicator) for more accurate network diagnostics and adaptive performance optimization. Advanced machine learning algorithms will leverage combined RSSI and LQI data to predict and mitigate signal degradation in real-time, improving reliability in IoT and 5G networks. Your wireless systems will benefit from these innovations by achieving higher precision in connectivity assessments and more efficient resource allocation.
RSSI vs LQI Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com