NR (New Radio) is the 5G wireless communication standard designed to deliver ultra-fast data speeds, low latency, and enhanced capacity compared to LTE (Long-Term Evolution), which is the widely adopted 4G technology optimized for reliable broadband connectivity. Understanding the key differences between NR and LTE will help you grasp how next-generation networks transform your mobile experience--read on to explore the detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
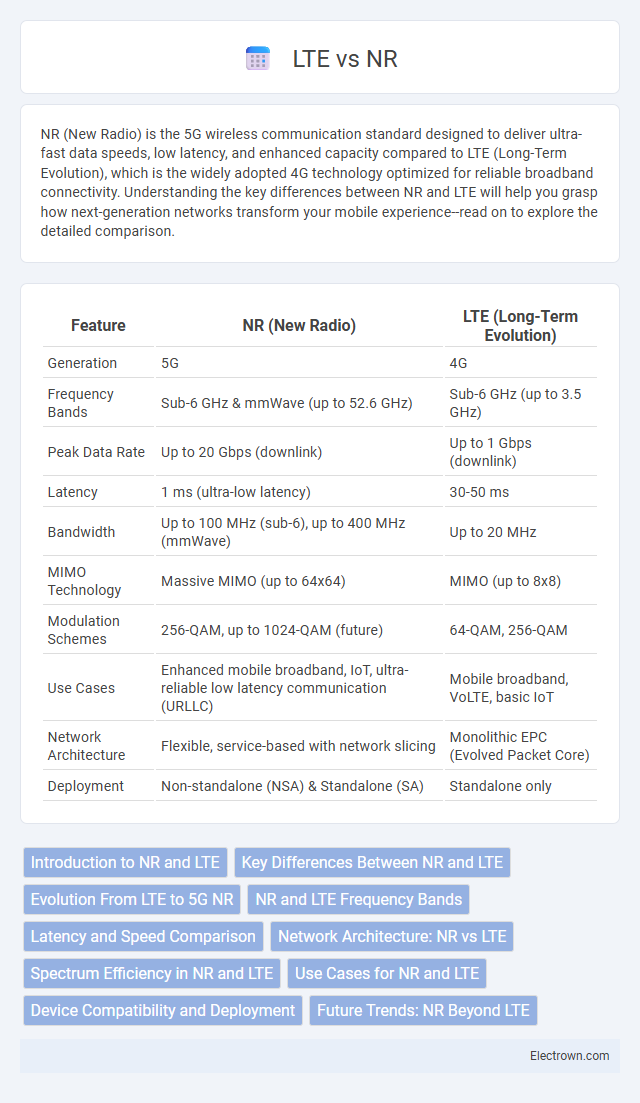
| Feature | NR (New Radio) | LTE (Long-Term Evolution) |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | 5G | 4G |
| Frequency Bands | Sub-6 GHz & mmWave (up to 52.6 GHz) | Sub-6 GHz (up to 3.5 GHz) |
| Peak Data Rate | Up to 20 Gbps (downlink) | Up to 1 Gbps (downlink) |
| Latency | 1 ms (ultra-low latency) | 30-50 ms |
| Bandwidth | Up to 100 MHz (sub-6), up to 400 MHz (mmWave) | Up to 20 MHz |
| MIMO Technology | Massive MIMO (up to 64x64) | MIMO (up to 8x8) |
| Modulation Schemes | 256-QAM, up to 1024-QAM (future) | 64-QAM, 256-QAM |
| Use Cases | Enhanced mobile broadband, IoT, ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC) | Mobile broadband, VoLTE, basic IoT |
| Network Architecture | Flexible, service-based with network slicing | Monolithic EPC (Evolved Packet Core) |
| Deployment | Non-standalone (NSA) & Standalone (SA) | Standalone only |
Introduction to NR and LTE
NR (New Radio) and LTE (Long-Term Evolution) are key wireless communication standards, with NR representing the foundation of 5G technology and LTE serving as the dominant 4G network standard. NR offers enhanced data speeds, ultra-low latency, and support for massive Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, while LTE provides reliable high-speed mobile broadband with widespread global adoption. Your mobile experience evolves significantly by transitioning from LTE to NR, enabling faster downloads, improved network capacity, and advanced applications like augmented reality and smart cities.
Key Differences Between NR and LTE
NR (New Radio) utilizes a flexible numerology with scalable subcarrier spacing, enabling more efficient use of spectrum compared to LTE's fixed 15 kHz spacing. NR supports advanced technologies like massive MIMO and beamforming, enhancing capacity and coverage beyond LTE's capabilities. Furthermore, NR is designed to accommodate diverse deployment scenarios including mmWave frequencies, while LTE primarily operates in sub-6 GHz bands.
Evolution From LTE to 5G NR
5G NR (New Radio) represents the next evolution from LTE, offering significantly enhanced data speeds, reduced latency, and improved network capacity through advanced technologies like massive MIMO and beamforming. Unlike LTE's reliance on sub-6 GHz frequencies, NR expands to mmWave bands, enabling ultra-high bandwidth and connectivity for your devices. This transition supports new applications such as IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles by delivering more reliable, scalable, and versatile wireless communication.
NR and LTE Frequency Bands
NR (New Radio) operates across a broader and more flexible range of frequency bands, including both sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave (mmWave) spectrums, enhancing capacity and low-latency performance. LTE primarily utilizes bands below 3 GHz, offering reliable coverage and wide compatibility but limited bandwidth compared to NR. Your network's efficiency and speed can significantly improve by leveraging NR's advanced frequency bands alongside existing LTE infrastructure.
Latency and Speed Comparison
NR (New Radio) offers significantly lower latency compared to LTE, with 5G networks achieving as low as 1 millisecond, while LTE typically ranges from 30 to 50 milliseconds. Speed-wise, NR supports peak data rates exceeding 10 Gbps, vastly outperforming LTE's maximum of around 1 Gbps. Your network experiences faster response times and greater throughput with NR, ideal for applications demanding real-time data transfer and high bandwidth.
Network Architecture: NR vs LTE
NR (New Radio) and LTE (Long-Term Evolution) differ significantly in network architecture, with NR designed to support 5G's flexible and scalable infrastructure through a service-based architecture (SBA) that enables modular and cloud-native network functions. LTE utilizes a more traditional, hierarchical architecture centered around the Evolved Packet Core (EPC), which is less adaptable to the dynamic demands of modern connectivity. Your network can benefit from NR's architecture by achieving lower latency, higher throughput, and enhanced support for diverse use cases such as massive IoT and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.
Spectrum Efficiency in NR and LTE
NR (New Radio) significantly outperforms LTE in spectrum efficiency due to advanced technologies like massive MIMO and flexible subcarrier spacing, enabling better utilization of available bandwidth. LTE, while efficient, relies on fixed subcarrier spacing and less sophisticated antenna techniques, limiting its ability to maximize data throughput in congested spectrum environments. Your network's performance can be greatly enhanced by adopting NR, optimizing spectrum allocation, and supporting higher data rates with lower latency.
Use Cases for NR and LTE
NR (New Radio) supports enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low-latency communications, and massive machine-type communications, enabling applications like augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and smart manufacturing. LTE excels in providing reliable, widespread coverage for mobile internet, voice over LTE (VoLTE), and IoT devices with moderate latency requirements. NR's flexible spectrum usage and advanced features position it as the foundation for 5G use cases, while LTE remains critical for existing 4G networks and fallback connectivity.
Device Compatibility and Deployment
NR (New Radio) supports a wide range of devices, including smartphones, IoT gadgets, and industrial equipment, ensuring seamless integration across existing LTE infrastructure during deployment. LTE devices remain prevalent due to mature ecosystem support, but many newer models offer dual compatibility with LTE and NR for smooth transition. Your network deployment benefits from leveraging NR's higher capacity and lower latency while maintaining LTE's broad device compatibility for comprehensive coverage.
Future Trends: NR Beyond LTE
NR (New Radio) represents the evolution beyond LTE, incorporating advanced technologies like massive MIMO, millimeter waves, and ultra-low latency for enhanced 5G performance. Future trends indicate NR will support diverse applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and immersive AR/VR experiences through network slicing and edge computing. Your connectivity experience will dramatically improve as NR scales to meet the demands of increasingly data-intensive and latency-sensitive services.
NR vs LTE Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com