RG6 cables provide better signal quality and longer transmission distances compared to RG59, making them ideal for modern cable and satellite TV installations. Discover which cable suits your setup by exploring the detailed differences and applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
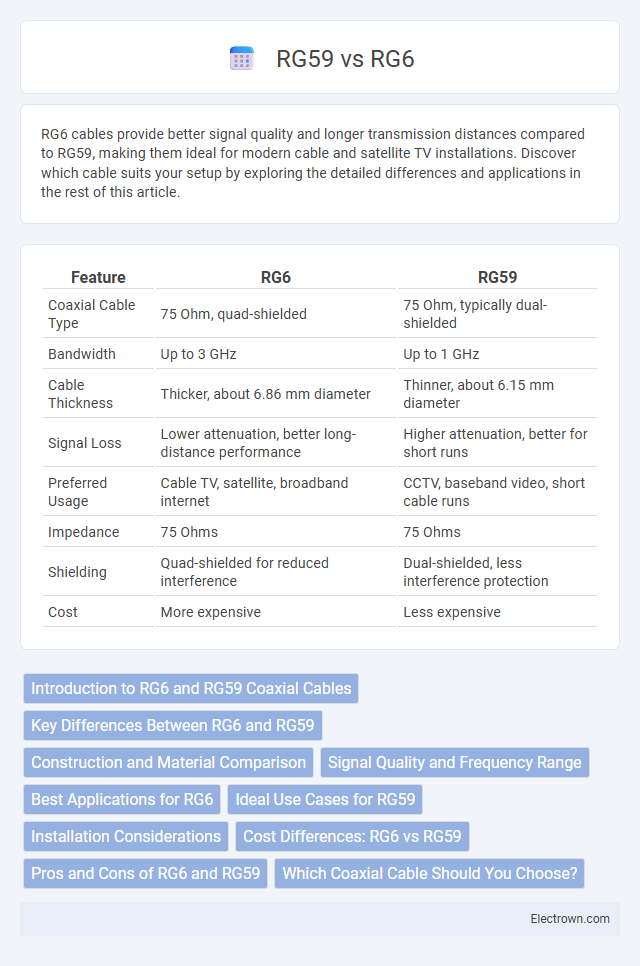
| Feature | RG6 | RG59 |
|---|---|---|
| Coaxial Cable Type | 75 Ohm, quad-shielded | 75 Ohm, typically dual-shielded |
| Bandwidth | Up to 3 GHz | Up to 1 GHz |
| Cable Thickness | Thicker, about 6.86 mm diameter | Thinner, about 6.15 mm diameter |
| Signal Loss | Lower attenuation, better long-distance performance | Higher attenuation, better for short runs |
| Preferred Usage | Cable TV, satellite, broadband internet | CCTV, baseband video, short cable runs |
| Impedance | 75 Ohms | 75 Ohms |
| Shielding | Quad-shielded for reduced interference | Dual-shielded, less interference protection |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
Introduction to RG6 and RG59 Coaxial Cables
RG6 and RG59 coaxial cables are essential components in telecommunications, each designed for specific signal transmission needs. RG6 cables feature a thicker core conductor and superior shielding, making them ideal for high-frequency signals such as satellite TV and broadband internet. RG59 cables, with a thinner core and less shielding, are better suited for low-frequency applications like analog video and CCTV systems.
Key Differences Between RG6 and RG59
RG6 cables feature a thicker core and better shielding, making them ideal for high-frequency signals such as satellite and cable TV. RG59 cables have a thinner conductor and less shielding, which limits their performance primarily to low-frequency analog video and shorter cable runs. Your choice between RG6 and RG59 should consider signal quality requirements, distance, and interference resistance to ensure optimal transmission.
Construction and Material Comparison
RG6 cables feature a thicker core conductor, typically 18 AWG copper-clad steel or solid copper, providing lower signal loss and better shielding with multiple layers, including a foil and braid. RG59 cables have a thinner 20 AWG conductor and less robust shielding, making them more suitable for short-distance, low-frequency applications. Choosing RG6 enhances your signal quality and durability due to superior construction and materials.
Signal Quality and Frequency Range
RG6 cables offer superior signal quality compared to RG59 due to thicker copper cores and better shielding, which reduce signal loss and interference. RG6 supports higher frequency ranges up to 3 GHz, making it ideal for modern digital cable and satellite TV signals, while RG59 is typically limited to frequencies around 1 GHz, suitable for older analog video applications. Choosing RG6 ensures enhanced performance and future-proofing for high-bandwidth transmissions.
Best Applications for RG6
RG6 coaxial cable is best suited for high-frequency signal transmission, making it ideal for satellite TV, cable TV, and broadband internet connections. Its thicker insulation and lower attenuation improve signal quality over longer distances compared to RG59. RG6 cables are commonly used in residential and commercial installations where signal clarity and minimal interference are critical.
Ideal Use Cases for RG59
RG59 coaxial cable is best suited for short-distance video applications, such as CCTV camera installations or older analog TV setups, where signal loss is minimal. It is ideal for runs under 100 feet due to its higher attenuation compared to RG6, making it less effective for long cable lengths. Your choice of RG59 is practical for budget-conscious projects with low-frequency signals that do not demand advanced shielding or high bandwidth.
Installation Considerations
RG6 cable offers lower signal loss and better shielding compared to RG59, making it more suitable for longer cable runs and high-frequency applications such as satellite or digital cable TV installations. RG59 is thinner and more flexible, which can simplify installation in tight spaces but may result in signal degradation over extended distances. Choosing RG6 ensures enhanced durability and performance, particularly in modern residential or commercial wiring setups where signal quality is critical.
Cost Differences: RG6 vs RG59
RG6 coaxial cables typically cost more than RG59 due to their thicker insulation and better shielding, which improves signal quality and reduces interference. RG59 cables are cheaper, making them suitable for shorter, low-frequency applications like CCTV or analog video, but they may suffer signal loss over longer distances compared to RG6. Choosing between RG6 and RG59 largely depends on the application requirements and budget constraints, with RG6 providing better long-term value despite the higher upfront cost.
Pros and Cons of RG6 and RG59
RG6 cables offer superior shielding and lower signal loss, making them ideal for high-frequency transmissions like satellite and cable TV, while their thicker insulation provides enhanced durability. RG59 cables, being thinner and more flexible, are easier to install in tight spaces but suffer from higher signal attenuation over long distances, limiting their effectiveness for HD signals. You should choose RG6 for better performance and future-proofing, whereas RG59 suits shorter runs and analog setups.
Which Coaxial Cable Should You Choose?
RG6 coaxial cable offers superior signal quality and lower attenuation over longer distances compared to RG59, making it ideal for modern cable TV, satellite, and internet applications. RG59 is better suited for short-distance analog video and CCTV setups where budget and flexibility are priorities. Choosing RG6 ensures future-proofing and enhanced performance, especially for HD and digital signals.
RG6 vs RG59 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com