AP (Access Point) extends your existing wired network by providing wireless connectivity, while STA (Station) refers to any device that connects to a wireless network, like laptops or smartphones. Discover how understanding the differences between AP and STA can improve your network setup and performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
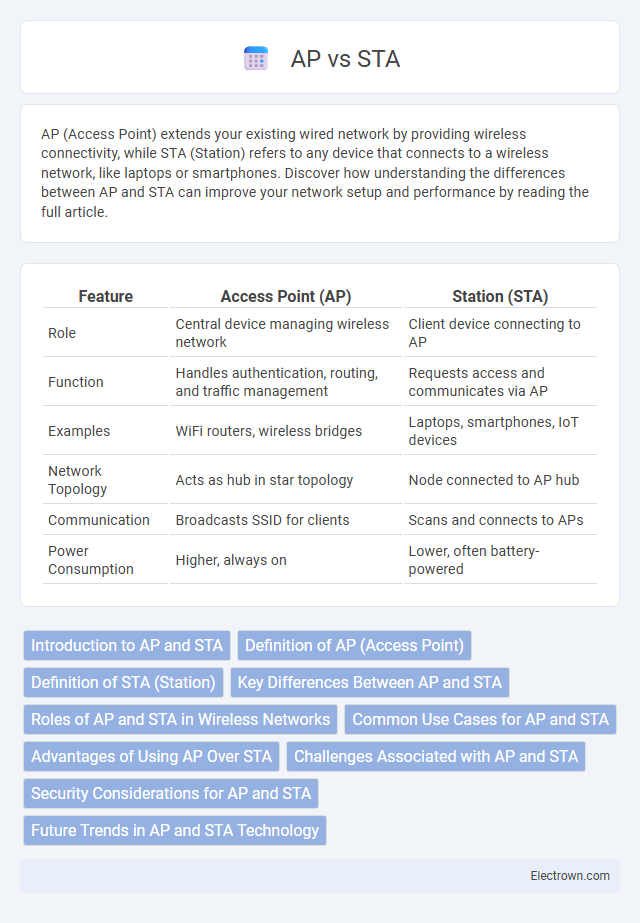
| Feature | Access Point (AP) | Station (STA) |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Central device managing wireless network | Client device connecting to AP |
| Function | Handles authentication, routing, and traffic management | Requests access and communicates via AP |
| Examples | WiFi routers, wireless bridges | Laptops, smartphones, IoT devices |
| Network Topology | Acts as hub in star topology | Node connected to AP hub |
| Communication | Broadcasts SSID for clients | Scans and connects to APs |
| Power Consumption | Higher, always on | Lower, often battery-powered |
Introduction to AP and STA
Access Point (AP) acts as a central hub allowing multiple devices to connect to a wired network wirelessly, facilitating communication and internet access in environments like homes or offices. Station (STA) refers to any device, such as a laptop or smartphone, that connects to an AP to access network resources or the internet. Understanding the fundamental roles of AP as a provider and STA as a client helps optimize your wireless network setup for better performance and coverage.
Definition of AP (Access Point)
An Access Point (AP) is a networking device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, serving as a bridge between wireless clients and the Ethernet network. APs manage wireless communication by authenticating users, encrypting data, and routing traffic to maintain network security and efficiency. Your wireless devices rely on APs to extend network coverage and provide seamless connectivity within Wi-Fi environments.
Definition of STA (Station)
A Station (STA) in wireless networks refers to any device equipped with a wireless network interface controller that communicates over a Wi-Fi connection, such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices. It serves as an endpoint that connects to an Access Point (AP) to access the network and transmit or receive data packets. Your STA operates based on IEEE 802.11 standards to manage authentication, association, and data exchange with the AP, enabling seamless wireless communication.
Key Differences Between AP and STA
AP (Access Point) serves as a central hub that enables multiple STAs (Stations) to connect to a wireless network, managing data traffic and extending network range. STA represents individual devices, like laptops or smartphones, that associate with an AP to access network resources and communicate wirelessly. Understanding the distinction between AP setting infrastructure and STA functioning as clients is crucial for optimizing your wireless network performance and coverage.
Roles of AP and STA in Wireless Networks
Access Points (APs) function as centralized devices that manage network traffic and facilitate communication within wireless local area networks (WLANs). Stations (STAs), typically client devices like laptops and smartphones, connect to APs to access network resources and services. APs handle tasks such as signal transmission, authentication, and data routing, while STAs primarily send and receive data over the wireless connection established by the AP.
Common Use Cases for AP and STA
Access Points (AP) commonly serve environments requiring centralized wireless network management such as offices, schools, and public hotspots, enabling multiple devices to connect and communicate seamlessly. Stations (STA), typically found in client devices like laptops, smartphones, and IoT gadgets, are used for accessing network services through APs or routers. In industrial settings, APs facilitate large-scale device connectivity, while STAs support individual device communication within these networks.
Advantages of Using AP Over STA
Using an Access Point (AP) over a Station (STA) enhances network scalability by supporting multiple simultaneous device connections and providing centralized management and security controls. APs enable seamless roaming within large wireless environments, maintaining consistent connectivity and reducing network congestion compared to individual STA devices. Centralized control through APs simplifies network monitoring, configuration, and firmware updates, improving overall network efficiency and performance.
Challenges Associated with AP and STA
Access Points (APs) face challenges such as signal interference, limited coverage areas, and high user density leading to network congestion. Stations (STAs) encounter issues including variable connection quality due to mobility, limited power resources affecting communication stability, and difficulty maintaining consistent throughput in crowded environments. Both APs and STAs must address security vulnerabilities and compatibility problems with diverse wireless standards.
Security Considerations for AP and STA
Access Points (APs) implement robust security protocols such as WPA3 to safeguard the wireless network against unauthorized access and eavesdropping, employing encryption and authentication mechanisms. Stations (STAs), or client devices, must support these security standards and keep firmware updated to protect user data and prevent vulnerabilities like man-in-the-middle attacks. Your choice of AP and STA security settings critically influences overall network integrity and data confidentiality.
Future Trends in AP and STA Technology
Future trends in AP (Access Point) and STA (Station) technology emphasize enhanced Wi-Fi 7 capabilities, promising multi-gigabit speeds, ultra-low latency, and improved spectral efficiency for robust connectivity. Innovations focus on integrating AI-driven network optimization, advanced MIMO techniques, and seamless mesh networking, which together will elevate performance and reliability in dense environments. Your wireless experience will benefit from smarter, faster, and more adaptive networks that support emerging IoT and AR/VR applications.
AP vs STA Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com