TTL and RS232 are two different communication standards where TTL uses 0 to 5V logic levels suitable for microcontrollers, while RS232 employs higher voltage levels (-12V to +12V) for reliable long-distance serial communication. Understanding the differences between TTL and RS232 can help you choose the right interface for your electronics projects--continue reading to explore their key features and applications.
Table of Comparison
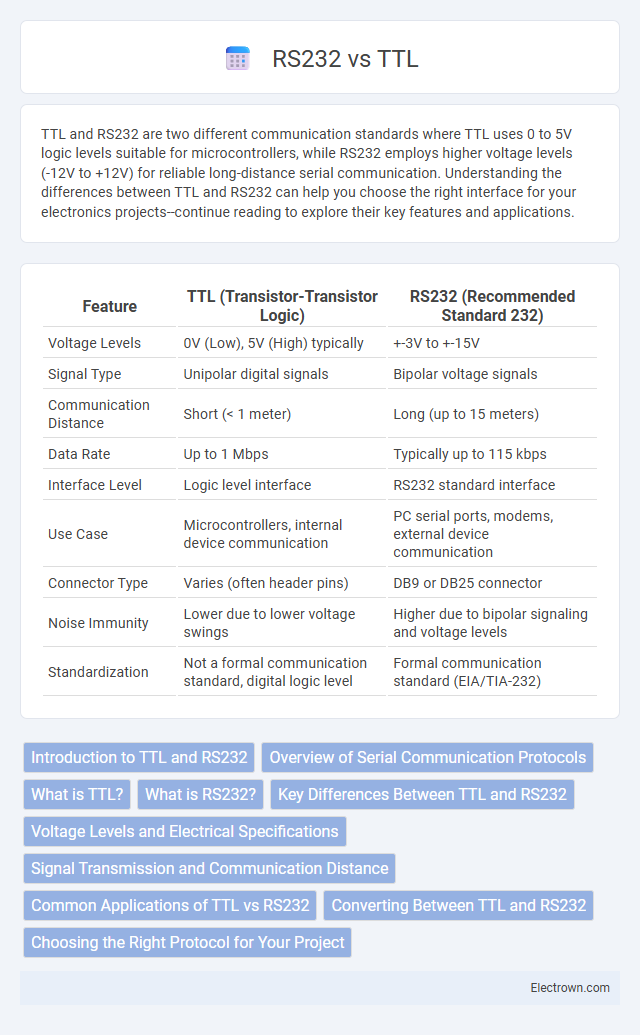
| Feature | TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) | RS232 (Recommended Standard 232) |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Levels | 0V (Low), 5V (High) typically | +-3V to +-15V |
| Signal Type | Unipolar digital signals | Bipolar voltage signals |
| Communication Distance | Short (< 1 meter) | Long (up to 15 meters) |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Mbps | Typically up to 115 kbps |
| Interface Level | Logic level interface | RS232 standard interface |
| Use Case | Microcontrollers, internal device communication | PC serial ports, modems, external device communication |
| Connector Type | Varies (often header pins) | DB9 or DB25 connector |
| Noise Immunity | Lower due to lower voltage swings | Higher due to bipolar signaling and voltage levels |
| Standardization | Not a formal communication standard, digital logic level | Formal communication standard (EIA/TIA-232) |
Introduction to TTL and RS232
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) operates at low voltage levels, typically 0 to 5V, making it ideal for direct interfacing with microcontrollers and digital circuits. RS232 is a standard for serial communication that uses higher voltage levels, ranging from -15V to +15V, to enable long-distance data transmission between devices like computers and modems. Understanding the voltage differences and signal conventions between TTL and RS232 is essential for ensuring compatible and reliable serial communication in your electronic projects.
Overview of Serial Communication Protocols
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) and RS232 are serial communication protocols used for data exchange between devices. TTL operates at logic voltages typically between 0V and 5V or 3.3V, making it suitable for microcontroller-level communication, while RS232 uses higher voltage levels, usually between +-3V to +-15V, allowing for longer cable lengths and noise resistance. RS232 supports single-ended signaling with defined control signals, whereas TTL employs simpler voltage level signaling, often requiring converters when interfacing with RS232 devices.
What is TTL?
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) is a type of digital signal standard that operates at a voltage range typically between 0V (logic low) and 5V (logic high), commonly used for microcontroller communication and logic circuits. Unlike RS232, which uses higher voltage levels and inverted logic suitable for long-distance serial communication, TTL signals are low voltage and used primarily for short-distance, direct connection between devices. Understanding TTL's voltage levels ensures your devices communicate properly without damage or misinterpretation of data signals.
What is RS232?
RS232 is a standard protocol for serial communication that defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, enabling data exchange between computers and peripheral devices. It uses voltage levels typically ranging from +3 to +15 volts for a logical '0' and -3 to -15 volts for a logical '1', which distinguishes it from TTL signaling. RS232 supports longer cable lengths and is widely used in legacy systems and industrial equipment for reliable asynchronous serial communication.
Key Differences Between TTL and RS232
TTL and RS232 differ primarily in voltage levels and signal integrity; TTL operates at 0-5V with logic levels typically at 0V for LOW and 5V for HIGH, whereas RS232 uses higher voltage swings ranging from -15V to +15V for data transmission. TTL is suited for short-distance communication within devices, while RS232 supports longer distances up to 50 feet with robust noise immunity. Your choice between TTL and RS232 depends on the required signal voltage compatibility and transmission range for your electronic project.
Voltage Levels and Electrical Specifications
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) operates at voltage levels of 0 to 5 volts, with a typical logic high defined as 2.0 to 5.0 V and logic low as 0 to 0.8 V, making it compatible with most microcontrollers. RS232 signals use voltage levels ranging from -15 V to +15 V, where logic high (space) is represented by a voltage between -3 V and -15 V, and logic low (mark) is between +3 V and +15 V, providing greater noise immunity over longer distances. Electrical specifications for TTL emphasize low voltage and current for short-distance communication, whereas RS232 specifies higher voltages and negative/positive swings to ensure signal integrity across serial cables.
Signal Transmission and Communication Distance
TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) signals operate at lower voltage levels, typically 0 to 5V, which limits their communication distance to around 1 to 2 meters due to susceptibility to noise and signal degradation. RS232, with voltage levels ranging from +-3 to +-15V, supports longer communication distances up to 15 meters or more by providing better noise immunity and signal integrity over wired connections. The higher voltage swings in RS232 enable more reliable data transmission over extended distances compared to TTL's short-range, low-voltage signaling.
Common Applications of TTL vs RS232
TTL interfaces are commonly used in embedded systems, microcontroller communication, and robotics due to their low voltage compatibility and direct connection to digital circuits. RS232 remains prevalent in industrial automation, serial communication with legacy equipment, and computer peripherals because of its robust signal range and noise immunity over longer distances. Both standards serve crucial roles, with TTL favored for short-distance, low-voltage data exchange and RS232 preferred for reliable, longer-distance serial communication.
Converting Between TTL and RS232
Converting between TTL and RS232 levels requires a level shifter or a dedicated converter module since TTL operates at 0-5V logic levels while RS232 uses higher voltage swings typically between +-12V. Using ICs like the MAX232 ensures signal compatibility by translating TTL's low-voltage signals into RS232's standardized levels for reliable serial communication. Properly converting signals protects your microcontroller and enables seamless interfacing with RS232-enabled devices such as computers and modems.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Project
Choosing the right protocol between TTL and RS232 depends on device compatibility, voltage levels, and communication distance. TTL signals operate at 5V or 3.3V, making them ideal for microcontroller communication and short-distance data transfer, while RS232 uses higher voltage levels (+-12V) suited for long-distance serial communication and robust noise immunity. Consider the operating environment, required data rate, and hardware to ensure optimal performance and signal integrity in your project.
TTL vs RS232 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com