Bit Error Rate (BER) measures the rate of incorrect bits received over a communication channel, while Symbol Error Rate (SER) counts the incorrect symbols transmitted, which may represent multiple bits per symbol; understanding their distinction is crucial for optimizing digital communication systems and improving your data transmission reliability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how these metrics impact system performance and error correction techniques.
Table of Comparison
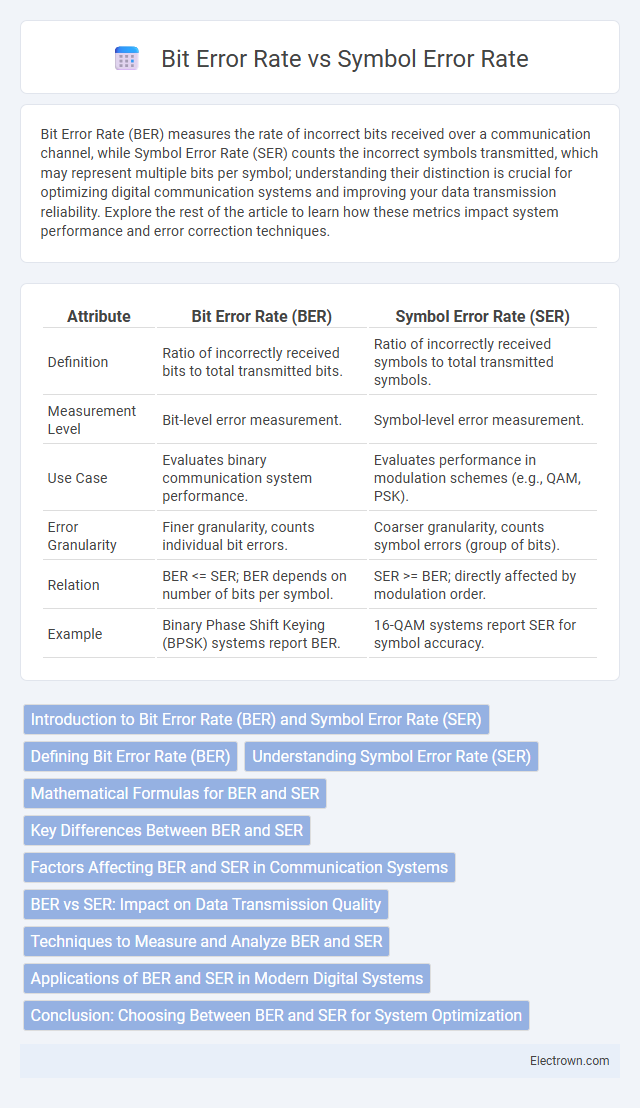
| Attribute | Bit Error Rate (BER) | Symbol Error Rate (SER) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of incorrectly received bits to total transmitted bits. | Ratio of incorrectly received symbols to total transmitted symbols. |
| Measurement Level | Bit-level error measurement. | Symbol-level error measurement. |
| Use Case | Evaluates binary communication system performance. | Evaluates performance in modulation schemes (e.g., QAM, PSK). |
| Error Granularity | Finer granularity, counts individual bit errors. | Coarser granularity, counts symbol errors (group of bits). |
| Relation | BER <= SER; BER depends on number of bits per symbol. | SER >= BER; directly affected by modulation order. |
| Example | Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK) systems report BER. | 16-QAM systems report SER for symbol accuracy. |
Introduction to Bit Error Rate (BER) and Symbol Error Rate (SER)
Bit Error Rate (BER) measures the proportion of incorrectly received bits in digital communication, reflecting the reliability of data transmission at the bit level. Symbol Error Rate (SER) quantifies the frequency of incorrectly decoded symbols, where each symbol may represent multiple bits depending on the modulation scheme. BER and SER are critical performance metrics in evaluating modulation techniques, error correction methods, and overall communication system efficiency.
Defining Bit Error Rate (BER)
Bit Error Rate (BER) measures the fraction of bits received incorrectly over a communication channel, quantifying the reliability of digital transmission. BER is calculated as the number of bit errors divided by the total number of transmitted bits during a given time interval. This metric is critical for assessing the performance of binary modulation schemes and comparing error control techniques in communication systems.
Understanding Symbol Error Rate (SER)
Symbol Error Rate (SER) measures the probability that a transmitted symbol is incorrectly decoded at the receiver, directly reflecting the performance of digital communication systems. Unlike Bit Error Rate (BER), which counts errors in individual bits, SER accounts for errors affecting entire symbol units, making it essential for modulation schemes where symbols represent multiple bits. Understanding SER helps you optimize system designs and modulation techniques to improve overall signal integrity and data transmission quality.
Mathematical Formulas for BER and SER
Bit Error Rate (BER) quantifies the ratio of incorrectly received bits to the total transmitted bits, mathematically expressed as BER = (Number of bit errors) / (Total transmitted bits). Symbol Error Rate (SER) measures the ratio of incorrectly decoded symbols to the total transmitted symbols and is given by SER = (Number of symbol errors) / (Total transmitted symbols). Your communication system's performance evaluation relies on these formulas to optimize error correction and modulation schemes effectively.
Key Differences Between BER and SER
Bit Error Rate (BER) measures the fraction of individual bits received incorrectly, while Symbol Error Rate (SER) evaluates the ratio of incorrectly detected symbols, each symbol potentially representing multiple bits. BER is crucial for assessing the overall quality of a digital communication channel at the bit level, whereas SER provides insights into the performance of modulation schemes and their susceptibility to noise and interference. Understanding the distinction helps optimize Your communication system's error correction techniques and modulation strategies.
Factors Affecting BER and SER in Communication Systems
Bit Error Rate (BER) and Symbol Error Rate (SER) in communication systems are heavily influenced by factors such as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), modulation scheme, channel conditions, and interference levels. Higher SNR typically reduces both BER and SER, while complex modulation formats like QAM increase susceptibility to errors. Multipath fading, Doppler shift, and channel noise further degrade performance, leading to higher error rates in wireless communication environments.
BER vs SER: Impact on Data Transmission Quality
Bit Error Rate (BER) measures the frequency of bit errors in a transmitted data stream, providing a granular view of data integrity at the binary level, while Symbol Error Rate (SER) evaluates errors based on signal symbols, reflecting the impact on the overall modulation scheme. A low BER signifies higher data transmission quality by ensuring accurate bit delivery, whereas a low SER indicates fewer symbol misinterpretations which directly enhance decoding accuracy in complex modulation formats such as QAM. Understanding the interplay between BER and SER is crucial for optimizing communication system performance, especially in environments with noise, interference, or fading effects.
Techniques to Measure and Analyze BER and SER
Techniques to measure Bit Error Rate (BER) and Symbol Error Rate (SER) typically involve the use of error detection algorithms and statistical sampling of transmitted and received data. Common methods include utilizing pseudo-random bit sequences (PRBS) for test signal generation, followed by error counting through hardware or software-based analyzers that compare received bits or symbols against known references. Signal processing tools, such as constellation diagrams and eye pattern analysis, aid in analyzing SER by visually assessing modulation accuracy and noise impacts, while BER analysis often relies on threshold-based detection and forward error correction (FEC) performance metrics.
Applications of BER and SER in Modern Digital Systems
Bit Error Rate (BER) and Symbol Error Rate (SER) are critical metrics in assessing the performance and reliability of modern digital communication systems, including wireless networks, satellite communications, and data storage devices. BER is widely used to evaluate the accuracy of bit-level transmissions in applications such as broadband internet and mobile communications, where minimizing bit errors ensures data integrity and user experience. SER is particularly important in modulation schemes with multi-level signaling, such as QAM and PSK used in 5G and Wi-Fi, helping optimize error correction and channel coding to enhance overall system efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing Between BER and SER for System Optimization
Bit Error Rate (BER) and Symbol Error Rate (SER) serve as critical metrics for evaluating communication system performance, with BER measuring the fraction of erroneous bits and SER assessing the proportion of incorrectly detected symbols. Choosing between BER and SER depends on the modulation scheme and error correction capabilities, as SER directly relates to symbol-level errors while BER offers finer granularity at the bit level, impacting overall system optimization. Your system's modulation format and required error sensitivity guide whether prioritizing BER or SER yields the most effective balance between performance and complexity.
Bit Error Rate vs Symbol Error Rate Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com