RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received signal, while SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) assesses the quality of the signal by comparing it to background noise. Understanding the differences between RSSI and SNR can help you optimize wireless network performance; explore the full article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
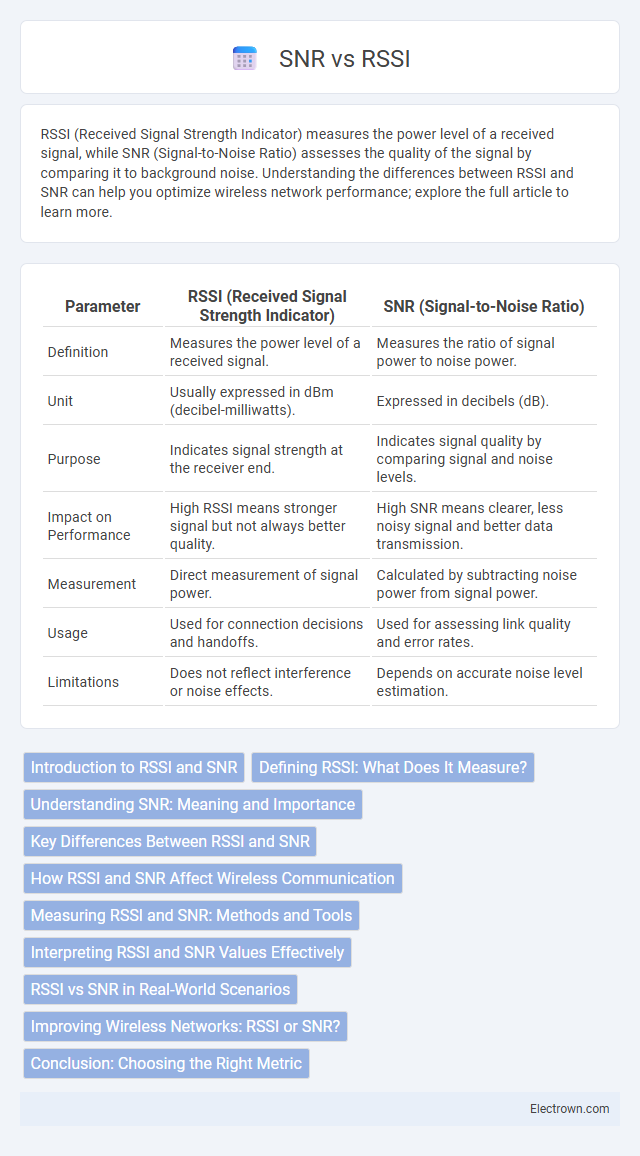
| Parameter | RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) | SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the power level of a received signal. | Measures the ratio of signal power to noise power. |
| Unit | Usually expressed in dBm (decibel-milliwatts). | Expressed in decibels (dB). |
| Purpose | Indicates signal strength at the receiver end. | Indicates signal quality by comparing signal and noise levels. |
| Impact on Performance | High RSSI means stronger signal but not always better quality. | High SNR means clearer, less noisy signal and better data transmission. |
| Measurement | Direct measurement of signal power. | Calculated by subtracting noise power from signal power. |
| Usage | Used for connection decisions and handoffs. | Used for assessing link quality and error rates. |
| Limitations | Does not reflect interference or noise effects. | Depends on accurate noise level estimation. |
Introduction to RSSI and SNR
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a wireless signal received by your device, providing insight into signal strength. SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) quantifies the ratio between the desired signal and background noise, reflecting signal quality and clarity. Understanding both RSSI and SNR is essential for optimizing wireless communication performance and diagnosing connectivity issues.
Defining RSSI: What Does It Measure?
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received radio signal in a wireless communication system. It quantifies signal strength in decibels (dBm), reflecting how strong the signal is at the receiver end, but does not account for noise or interference. RSSI is crucial for assessing signal coverage and connection quality but differs from SNR, which measures the ratio between signal power and background noise to evaluate signal clarity.
Understanding SNR: Meaning and Importance
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) quantifies the strength of a desired signal relative to background noise, expressed in decibels (dB), serving as a critical metric for communication quality assessment. A higher SNR indicates clearer signal reception, directly impacting data transmission reliability and network performance. Understanding SNR enables optimization of wireless systems by minimizing interference and maximizing signal clarity for improved connectivity.
Key Differences Between RSSI and SNR
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received radio signal, indicating signal strength but not its quality, while SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) quantifies the ratio between the signal power and background noise, reflecting communication quality. Your wireless device relies on RSSI to detect signal availability, but SNR is crucial for assessing the clarity and reliability of the connection. Understanding these key differences helps optimize network performance by balancing signal strength with noise interference.
How RSSI and SNR Affect Wireless Communication
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a received wireless signal, which directly impacts Your device's ability to connect and maintain communication with access points. SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) quantifies the signal quality by comparing the strength of the desired signal to background noise, crucial for reducing data errors and improving transmission reliability. High RSSI ensures strong connection strength, while a high SNR guarantees clearer, more stable wireless communication performance.
Measuring RSSI and SNR: Methods and Tools
Measuring RSSI involves using signal analyzers or Wi-Fi adapters with built-in RSSI reporting capabilities, which quantify the received signal strength in dBm. SNR measurement requires capturing both the signal power and background noise levels using spectrum analyzers or advanced network diagnostic tools to calculate the ratio, typically expressed in decibels (dB). Tools like NetSpot, Wireshark, and specialized RF spectrum analyzers facilitate accurate data collection for both RSSI and SNR in wireless network environments.
Interpreting RSSI and SNR Values Effectively
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measures the power level of a wireless signal, while SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) quantifies the quality of that signal relative to background noise. Interpreting RSSI alone may not reflect connection quality accurately, but combining RSSI with SNR provides a clearer understanding of signal integrity and performance. Your ability to optimize wireless networks improves significantly by analyzing both metrics to identify interference and signal degradation sources.
RSSI vs SNR in Real-World Scenarios
RSSI measures the total received signal strength including noise, offering a basic indicator of signal power, while SNR represents the ratio between signal strength and background noise, providing a clearer assessment of signal quality. In real-world scenarios, high RSSI does not always guarantee good performance if SNR is low due to interference or noise, impacting Your wireless connection reliability. Understanding both metrics helps optimize network setup by balancing signal strength with signal clarity for improved communication efficiency.
Improving Wireless Networks: RSSI or SNR?
Improving wireless networks relies heavily on understanding the difference between RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) and SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio). RSSI measures the power level of the received signal, indicating signal strength without accounting for noise or interference, while SNR evaluates signal quality by comparing signal power to background noise, directly impacting data transmission reliability. Optimizing wireless network performance requires prioritizing high SNR values to ensure clearer, more stable connections beyond just strong RSSI readings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metric
Choosing the right metric between RSSI and SNR depends on your specific wireless communication goals, as RSSI measures the strength of the received signal while SNR evaluates the quality by comparing signal power to noise. For scenarios prioritizing signal strength in a stable environment, RSSI provides a straightforward indicator, whereas SNR is more reliable in assessing overall link performance in noisy or interference-prone settings. Your decision should align with whether signal intensity or clarity is more critical to achieving optimal connectivity and data integrity.
RSSI vs SNR Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com