Guard Band and Guard Interval are two essential techniques used to minimize interference in communication systems; Guard Band refers to a frequency buffer zone between channels, while Guard Interval is a time gap inserted between data symbols. Understanding the differences and applications of these concepts can optimize Your system's performance, so continue reading to explore their impact in detail.
Table of Comparison
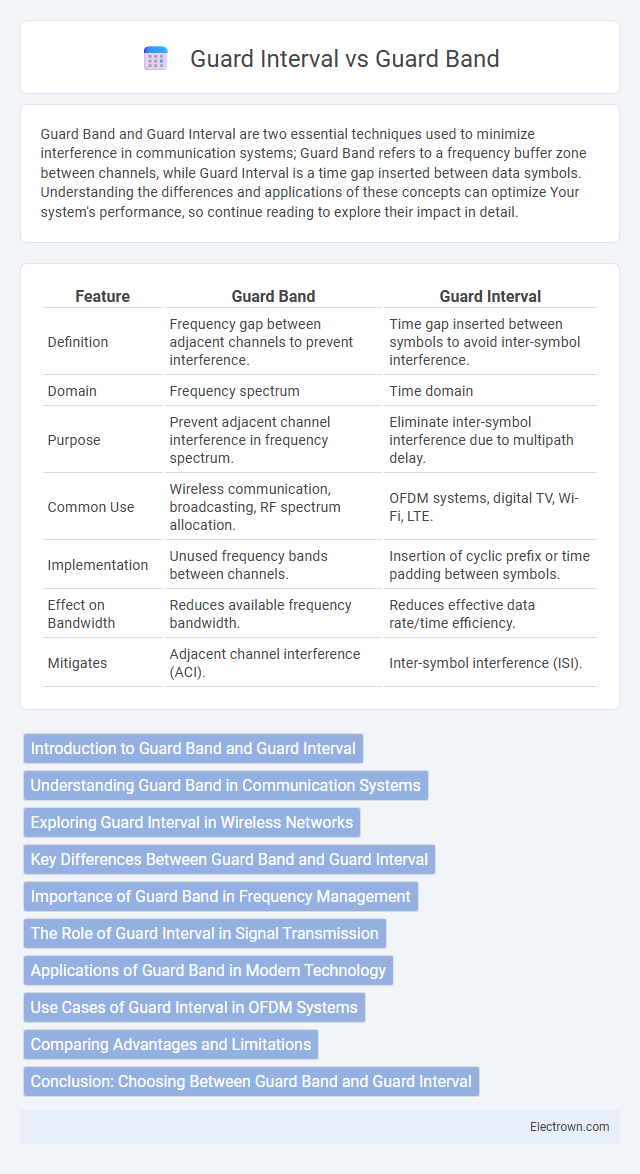
| Feature | Guard Band | Guard Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Frequency gap between adjacent channels to prevent interference. | Time gap inserted between symbols to avoid inter-symbol interference. |
| Domain | Frequency spectrum | Time domain |
| Purpose | Prevent adjacent channel interference in frequency spectrum. | Eliminate inter-symbol interference due to multipath delay. |
| Common Use | Wireless communication, broadcasting, RF spectrum allocation. | OFDM systems, digital TV, Wi-Fi, LTE. |
| Implementation | Unused frequency bands between channels. | Insertion of cyclic prefix or time padding between symbols. |
| Effect on Bandwidth | Reduces available frequency bandwidth. | Reduces effective data rate/time efficiency. |
| Mitigates | Adjacent channel interference (ACI). | Inter-symbol interference (ISI). |
Introduction to Guard Band and Guard Interval
Guard Band and Guard Interval are essential concepts in communication systems to minimize interference and improve signal integrity. Guard Band refers to the unused frequency range between adjacent channels, preventing frequency overlap and crosstalk. Guard Interval is the time gap inserted between symbols in time-domain transmissions, reducing inter-symbol interference and enhancing data transmission accuracy for your communication network.
Understanding Guard Band in Communication Systems
Guard Band in communication systems refers to the unused frequency spectrum between adjacent channels to prevent interference and signal overlap, ensuring clear transmission. It differs from Guard Interval, which is a time-based buffer inserted between symbols to reduce inter-symbol interference in time-domain signals. Both techniques are crucial for maintaining signal integrity but operate in distinct domains: frequency for Guard Band and time for Guard Interval.
Exploring Guard Interval in Wireless Networks
Guard intervals in wireless networks serve as vital timing gaps inserted between transmitted symbols to prevent inter-symbol interference caused by multipath propagation. Unlike guard bands that separate frequency channels, guard intervals operate in the time domain and enhance signal robustness by allowing delayed signal paths to settle before the next symbol is received. Optimizing guard interval duration improves overall network efficiency and reduces error rates in technologies like OFDM and Wi-Fi.
Key Differences Between Guard Band and Guard Interval
Guard Band refers to the unused frequency spectrum between channels to prevent interference, while Guard Interval is a time buffer inserted between symbols in digital communication to avoid inter-symbol interference. Guard Bands are measured in frequency units (Hz), whereas Guard Intervals are measured in time units (microseconds or nanoseconds). Understanding the distinction helps optimize your wireless system's performance by minimizing signal overlap and timing errors.
Importance of Guard Band in Frequency Management
Guard Band plays a crucial role in frequency management by preventing interference between adjacent frequency channels, ensuring clear signal transmission and reception. Unlike the Guard Interval, which focuses on time domain protection against signal overlap, Guard Band serves as a buffer zone in the frequency spectrum, maintaining signal integrity. Proper allocation of Guard Band in your communication systems enhances overall spectral efficiency and minimizes cross-channel interference.
The Role of Guard Interval in Signal Transmission
Guard intervals play a critical role in signal transmission by preventing inter-symbol interference (ISI) in wireless communications, ensuring signals do not overlap in time and degrade data integrity. Unlike guard bands that separate frequency channels, guard intervals provide a time buffer between transmitted symbols, allowing multipath reflections to settle and improving signal clarity. Incorporating an appropriate guard interval in your transmission system enhances data reliability and reduces the risk of errors caused by signal delay spread.
Applications of Guard Band in Modern Technology
Guard bands serve as critical spectral buffers in wireless communications, preventing interference between adjacent frequency channels in applications like 5G networks and Wi-Fi systems. They play a vital role in satellite communications and digital broadcasting by ensuring signal clarity and reducing cross-channel interference. In cognitive radio and spectrum sharing technologies, guard bands enable dynamic spectrum access while maintaining coexistence of multiple users.
Use Cases of Guard Interval in OFDM Systems
Guard Interval in OFDM systems is primarily used to mitigate inter-symbol interference (ISI) caused by multipath propagation in wireless communications. It provides a buffer time between transmitted symbols, ensuring signal integrity in environments like Wi-Fi, LTE, and 5G networks where reflections and delays are common. This technique enhances data reliability and network performance by preserving orthogonality among subcarriers.
Comparing Advantages and Limitations
Guard Band minimizes interference between adjacent frequency channels by providing a frequency buffer, enhancing signal clarity but reducing available bandwidth. Guard Interval improves resistance to multipath fading and inter-symbol interference in time-domain OFDM systems, boosting reliability without sacrificing frequency spectrum. Your choice depends on whether spectral efficiency or temporal signal robustness is more critical for your wireless communication system.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Guard Band and Guard Interval
Choosing between guard band and guard interval depends on your specific communication system requirements, such as bandwidth efficiency and interference mitigation. Guard bands provide frequency separation to prevent channel overlap, ideal for reducing adjacent channel interference, while guard intervals offer time spacing to combat multipath fading and inter-symbol interference in wireless networks. Your choice should balance spectral efficiency and resilience to signal distortion to optimize system performance.
Guard Band vs Guard Interval Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com