Cat 6 and Cat 7 cables differ primarily in speed, shielded construction, and maximum frequency transmission, with Cat 7 offering higher performance ideal for demanding network environments. Explore the full article to discover which cable best suits your connectivity needs and enhances your network's efficiency.
Table of Comparison
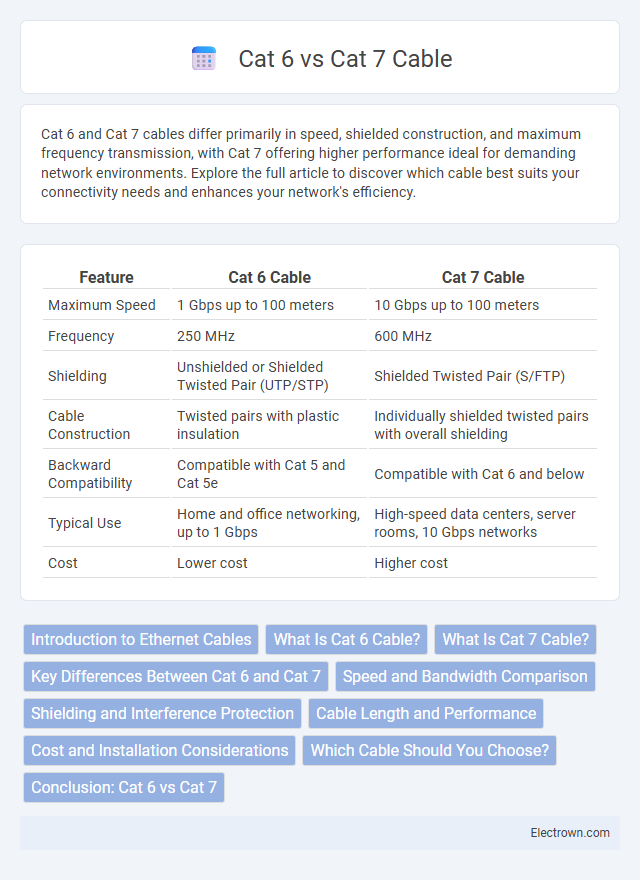
| Feature | Cat 6 Cable | Cat 7 Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Speed | 1 Gbps up to 100 meters | 10 Gbps up to 100 meters |
| Frequency | 250 MHz | 600 MHz |
| Shielding | Unshielded or Shielded Twisted Pair (UTP/STP) | Shielded Twisted Pair (S/FTP) |
| Cable Construction | Twisted pairs with plastic insulation | Individually shielded twisted pairs with overall shielding |
| Backward Compatibility | Compatible with Cat 5 and Cat 5e | Compatible with Cat 6 and below |
| Typical Use | Home and office networking, up to 1 Gbps | High-speed data centers, server rooms, 10 Gbps networks |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Ethernet Cables
Cat 6 and Cat 7 cables are types of Ethernet cables used for network connections, each offering different performance levels and transmission capabilities. Cat 6 supports speeds up to 10 Gbps over distances up to 55 meters, whereas Cat 7 can handle 10 Gbps at distances up to 100 meters with improved shielding for reduced interference. Ethernet cables like Cat 6 and Cat 7 are essential for establishing reliable, high-speed data transmission in both residential and commercial network infrastructures.
What Is Cat 6 Cable?
Cat 6 cable, also known as Category 6 cable, is a standardized twisted pair cable designed to support high-speed Ethernet networks with data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps over distances up to 55 meters. It features improved shielding and reduced crosstalk compared to Cat 5e cables, making it suitable for modern networking environments that demand reliable performance and high bandwidth. When choosing network cables, understanding Cat 6's capabilities helps ensure your infrastructure supports fast and stable connections.
What Is Cat 7 Cable?
Cat 7 cable, also known as Category 7, is an advanced Ethernet cable designed to support high-speed data transmission up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters, making it ideal for demanding network environments. It features shielded twisted pairs (S/FTP or F/FTP) to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference, ensuring superior signal quality and reliability compared to Cat 6 cables. For your network infrastructure, choosing Cat 7 cable can future-proof connectivity by providing enhanced bandwidth of up to 600 MHz, suitable for 10 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond.
Key Differences Between Cat 6 and Cat 7
Cat 6 cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps at 55 meters with a frequency of 250 MHz, while Cat 7 cables offer up to 10 Gbps at 100 meters and a higher frequency of 600 MHz, enabling better performance over longer distances. Shielding in Cat 7 cables reduces crosstalk and electromagnetic interference more effectively than the unshielded or shielded twisted pair options in Cat 6. Choosing Cat 7 enhances your network's reliability and bandwidth capacity, especially in environments requiring superior signal integrity and future-proofing.
Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Cat 7 cables support higher speeds up to 10 Gbps and bandwidths of 600 MHz, compared to Cat 6 cables which typically handle speeds up to 1 Gbps and bandwidths of 250 MHz. The enhanced shielding in Cat 7 reduces interference, making it suitable for high-performance networking environments requiring stable, high-speed data transfer. Cat 6 cables remain cost-effective for standard home and office networks, while Cat 7 is ideal for data centers and advanced applications demanding greater bandwidth and future-proofing.
Shielding and Interference Protection
Cat 6 cables typically use unshielded twisted pairs (UTP) but are also available in shielded twisted pair (STP) variants that reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Cat 7 cables exclusively feature shielded twisted pairs with individual shielding for each pair plus an overall shield, providing superior protection against crosstalk and external interference. The enhanced shielding in Cat 7 cables supports higher data integrity and performance in environments with significant electronic noise compared to Cat 6 cables.
Cable Length and Performance
Cat 6 cables typically support lengths up to 100 meters while maintaining performance suitable for 1 Gbps Ethernet speeds, making them ideal for most residential and commercial applications. Cat 7 cables also support this length but deliver enhanced shielding and higher frequencies up to 600 MHz, enabling better performance for 10 Gbps Ethernet over similar distances. Differences in cable construction affect latency and crosstalk, with Cat 7 offering superior transmission quality in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Cat 6 cables generally offer a lower cost compared to Cat 7 cables, making them a more budget-friendly option for most networking setups. Installation of Cat 6 is straightforward due to its thinner design and greater flexibility, whereas Cat 7 cables, with their thicker shielding and rigid structure, require more careful handling and professional installation. Choosing between Cat 6 and Cat 7 should consider both the upfront cable price and the potential increased labor costs associated with Cat 7's complex installation requirements.
Which Cable Should You Choose?
Choosing between Cat 6 and Cat 7 cables depends on your network speed requirements and future-proofing needs. Cat 6 supports speeds up to 10 Gbps over 55 meters and is suitable for most home and small business networks, while Cat 7 offers up to 10 Gbps over 100 meters with enhanced shielding for reduced crosstalk and better performance in high-interference environments. Opt for Cat 7 if you need longer cable runs and advanced shielding, but Cat 6 remains a cost-effective choice for standard networking applications.
Conclusion: Cat 6 vs Cat 7
Cat 7 cables offer superior shielding and support higher frequencies up to 600 MHz compared to Cat 6's 250 MHz, making them ideal for demanding network environments. Your choice depends on the required bandwidth, distance, and budget, with Cat 6 suitable for most home and office setups while Cat 7 excels in professional or future-proof installations. Investing in Cat 7 ensures enhanced performance and reduced crosstalk for high-speed data transmission.
Cat 6 vs Cat 7 Cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com