The 4:3 aspect ratio offers a more square-like frame that is ideal for viewing traditional content and older media, while the 16:9 ratio provides a wider, more cinematic view perfect for modern HD videos and gaming. Understanding the differences between these aspect ratios can help you choose the best display or format for your viewing needs--discover more insights in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
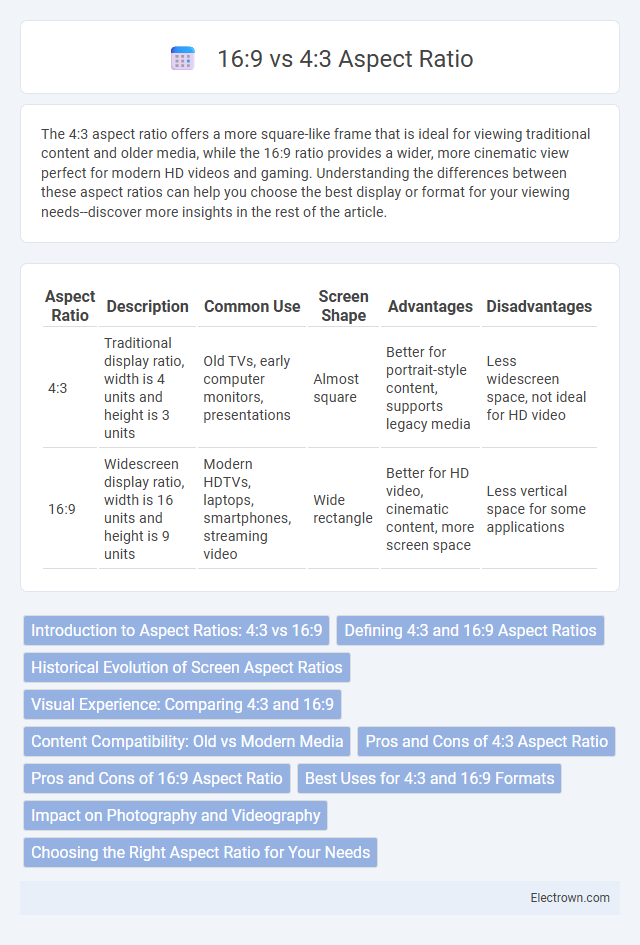
| Aspect Ratio | Description | Common Use | Screen Shape | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4:3 | Traditional display ratio, width is 4 units and height is 3 units | Old TVs, early computer monitors, presentations | Almost square | Better for portrait-style content, supports legacy media | Less widescreen space, not ideal for HD video |
| 16:9 | Widescreen display ratio, width is 16 units and height is 9 units | Modern HDTVs, laptops, smartphones, streaming video | Wide rectangle | Better for HD video, cinematic content, more screen space | Less vertical space for some applications |
Introduction to Aspect Ratios: 4:3 vs 16:9
The 4:3 aspect ratio, traditionally used in older televisions and computer monitors, offers a more square-like viewing experience ideal for presentations and legacy content. The 16:9 aspect ratio, now the industry standard for HDTV, widescreen monitors, and most streaming platforms, provides a wider, cinematic view that enhances modern video content and gaming experiences. Understanding these differences helps you choose the appropriate display format that best suits your media consumption or production needs.
Defining 4:3 and 16:9 Aspect Ratios
The 4:3 aspect ratio, traditionally used in older televisions and computer monitors, features a width that is 1.33 times its height, resulting in a nearly square display. The 16:9 aspect ratio, now the standard for modern HDTVs, laptops, and smartphones, offers a widescreen format with a width 1.78 times its height. This wider 16:9 ratio enhances visual immersion, making it ideal for cinematic content and gaming compared to the more compact 4:3 format.
Historical Evolution of Screen Aspect Ratios
The 4:3 aspect ratio, originally rooted in early television and cinema formats like Academy Ratio, dominated screens throughout the mid-20th century due to technological limitations and content standards. The transition to the 16:9 aspect ratio emerged with the rise of high-definition television (HDTV) and widescreen cinema, enhancing the viewing experience by matching human peripheral vision more closely. This evolution reflects significant shifts in broadcasting technology, content creation, and consumer demand for immersive multimedia experiences.
Visual Experience: Comparing 4:3 and 16:9
The 16:9 aspect ratio offers a wider field of view, enhancing your visual experience with more immersive and cinematic content suitable for modern HD displays. In contrast, the 4:3 aspect ratio provides a more squared frame, often preferred for older television shows and classic media but can feel restrictive on contemporary screens. Choosing between these ratios impacts how content fits your display and affects the overall viewing comfort and engagement.
Content Compatibility: Old vs Modern Media
The 4:3 aspect ratio is primarily compatible with older media formats such as classic television shows and vintage films, preserving their original visual integrity without cropping or distortion. In contrast, the 16:9 aspect ratio is the standard for modern content, including HDTV broadcasts, streaming platforms, and most contemporary video games, offering a widescreen experience that enhances immersive viewing. Your choice between these ratios affects how content is displayed, with 16:9 providing broader compatibility for current media while 4:3 suits archival or retro content best.
Pros and Cons of 4:3 Aspect Ratio
The 4:3 aspect ratio offers a more square-like display, providing advantages for viewing older television shows, classic movies, and certain professional settings like presentations and video conferencing due to its better vertical space utilization. This ratio's limitations include less immersive widescreen experience compared to 16:9 and black bars appearing on modern widescreen displays when viewing content not formatted in 4:3. Your choice of aspect ratio should consider the type of media you consume and the compatibility with your display devices to ensure optimal viewing comfort and quality.
Pros and Cons of 16:9 Aspect Ratio
The 16:9 aspect ratio offers a widescreen viewing experience ideal for modern HDTVs, streaming platforms, and gaming, providing a more immersive field of view compared to the traditional 4:3 format. It supports high-definition resolutions like 1080p and 4K, enhancing video quality and compatibility with contemporary media content. However, 16:9 can lead to letterboxing or cropping issues when displaying older 4:3 content, and some users find it less suitable for certain applications such as classic television programming or vintage video games.
Best Uses for 4:3 and 16:9 Formats
The 4:3 aspect ratio is best suited for presentations, traditional television broadcasts, and older computer monitors where a more square-like display enhances readability and focus on centered content. The 16:9 aspect ratio dominates modern video production, streaming platforms, and gaming, offering a widescreen experience that aligns with HDTV standards and maximizes visual immersion. Content creators choose 4:3 for legacy content or when a balanced vertical and horizontal field is needed, while 16:9 excels in cinematic viewing, multitasking environments, and devices with wide-format screens.
Impact on Photography and Videography
The 4:3 aspect ratio offers photographers a balanced frame ideal for portrait and still-life compositions, maximizing vertical space and detail capture, whereas the 16:9 ratio dominates videography for its widescreen cinematic feel, enhancing panoramic landscapes and motion sequences. In photography, 4:3 sensors often yield higher resolution images due to their shape, while 16:9 is preferred in video production for compatibility with HD, Full HD, and 4K display standards. Choosing between these ratios influences framing, storytelling style, and the final output's adaptability across different media platforms.
Choosing the Right Aspect Ratio for Your Needs
Choosing the right aspect ratio depends on the intended use and content display preferences, with 4:3 offering a classic, boxier format ideal for tasks requiring vertical space, such as reading documents or displaying presentation slides. In contrast, 16:9 provides a widescreen experience suited for modern video content, gaming, and cinematic presentations, maximizing screen real estate for immersive viewing. Evaluating device compatibility, content type, and viewing environment ensures optimal visual performance and user satisfaction.
4:3 vs 16:9 Aspect Ratio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com