Thunderbolt 3 and USB 4 both offer high-speed data transfer and versatile connectivity, but Thunderbolt 3 delivers up to 40 Gbps with support for PCIe and DisplayPort protocols, while USB 4 also reaches 40 Gbps but emphasizes broader compatibility and power delivery. Discover how these technologies differ in performance, compatibility, and use cases to find the best fit for your devices by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
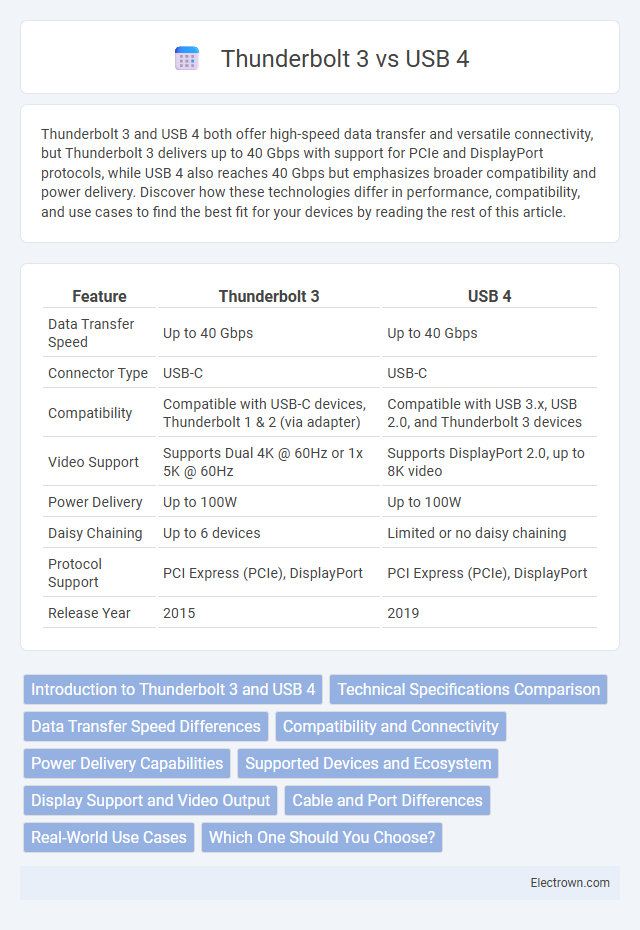
| Feature | Thunderbolt 3 | USB 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Connector Type | USB-C | USB-C |
| Compatibility | Compatible with USB-C devices, Thunderbolt 1 & 2 (via adapter) | Compatible with USB 3.x, USB 2.0, and Thunderbolt 3 devices |
| Video Support | Supports Dual 4K @ 60Hz or 1x 5K @ 60Hz | Supports DisplayPort 2.0, up to 8K video |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100W | Up to 100W |
| Daisy Chaining | Up to 6 devices | Limited or no daisy chaining |
| Protocol Support | PCI Express (PCIe), DisplayPort | PCI Express (PCIe), DisplayPort |
| Release Year | 2015 | 2019 |
Introduction to Thunderbolt 3 and USB 4
Thunderbolt 3 offers a high-speed data transfer rate of up to 40 Gbps, combining PCIe and DisplayPort protocols over a USB-C connector. USB 4, building on the Thunderbolt 3 specification, standardizes these capabilities to deliver similar bandwidth and versatile device compatibility. Your choice between the two impacts connection speed and peripheral support for modern computing needs.
Technical Specifications Comparison
Thunderbolt 3 offers data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, supports PCIe 3.0 x4, and delivers up to 100W power via USB-C connectors, ideal for high-performance peripherals. USB 4 aligns closely with Thunderbolt 3 speeds, also reaching 40 Gbps, but standardizes compatibility across multiple protocols including USB 3.2 and DisplayPort 1.4, enhancing device interoperability. Both technologies support daisy-chaining and external GPU configurations, but Thunderbolt 3 maintains a stricter certification process, ensuring consistent performance across certified devices.
Data Transfer Speed Differences
Thunderbolt 3 offers data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, doubling the 20 Gbps maximum speed originally found in USB 3.2 Gen 2x2. USB4, based on Thunderbolt 3 technology, also supports up to 40 Gbps but includes backward compatibility with USB 3.2 and DisplayPort protocols, enhancing versatility across devices. The key difference lies in implementation, where Thunderbolt 3 consistently delivers 40 Gbps, while USB4 speeds may vary depending on device support and cable quality.
Compatibility and Connectivity
Thunderbolt 3 offers backward compatibility with USB-C and supports data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps, enabling seamless connectivity with a wide range of devices, including external GPUs and high-resolution displays. USB 4, built on the Thunderbolt 3 protocol, enhances compatibility by supporting USB-C and USB 3.2 devices while maintaining data rates up to 40 Gbps. Both standards use the USB-C connector, but Thunderbolt 3 provides more consistent support for multiple protocols like PCIe and DisplayPort, ensuring broader compatibility in professional and high-performance environments.
Power Delivery Capabilities
Thunderbolt 3 supports power delivery up to 100 watts, enabling fast charging for laptops and high-power devices through a single cable. USB 4 also offers power delivery up to 100 watts, maintaining compatibility with USB Power Delivery (USB PD) standards for efficient charging and powering of peripherals. Your choice between Thunderbolt 3 and USB 4 will depend on device compatibility and the need for integrated data transfer speeds alongside power delivery.
Supported Devices and Ecosystem
Thunderbolt 3 supports a wide range of devices including external GPUs, high-speed storage drives, and multiple 4K displays, making it ideal for professional setups. USB 4 embraces backward compatibility with USB-C devices and integrates Thunderbolt 3 features, broadening its ecosystem significantly. Your choice depends on whether you need specialized Thunderbolt peripherals or prefer the versatile, widely adopted USB 4 standard.
Display Support and Video Output
Thunderbolt 3 supports dual 4K displays at 60Hz or a single 5K display at 60Hz, leveraging DisplayPort 1.2 protocol for high-resolution video output. USB 4 integrates Thunderbolt 3 technology and offers similar display capabilities but also supports DisplayPort 2.0, enabling higher resolutions such as 8K displays with improved bandwidth efficiency. Both standards provide versatile video output options, but USB 4's support for newer display protocols ensures better future-proofing for advanced monitors.
Cable and Port Differences
Thunderbolt 3 and USB 4 use the same USB Type-C connector, but Thunderbolt 3 cables often include active electronics to support higher data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps, while USB 4 cables vary between 20 Gbps and 40 Gbps depending on the specification. Thunderbolt 3 ports provide full compatibility with USB 3.1 and DisplayPort protocols, supporting daisy-chaining and external GPUs, whereas USB 4 aims to unify data, video, and power delivery with broader device compatibility but may offer less guaranteed performance. Your device's port labeling and cable quality directly impact the achievable speed and functionality, so verifying Thunderbolt 3 certification or USB 4 support ensures optimal connectivity.
Real-World Use Cases
Thunderbolt 3 offers superior performance in professional video editing and high-speed external GPU setups, supporting 40Gbps data transfer and dual 4K displays. USB 4, while matching Thunderbolt 3's speed in theory, provides broader device compatibility and more affordable docking station options for everyday users. Gamers and content creators benefit most from Thunderbolt 3's low latency, whereas USB 4 suits general data transfer and peripheral connectivity.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between Thunderbolt 3 and USB 4 depends on your need for data transfer speed and device compatibility, with Thunderbolt 3 offering up to 40 Gbps and widespread support for high-performance peripherals. USB 4 also supports 40 Gbps but is designed to unify USB-C and Thunderbolt protocols, improving versatility across various devices and ecosystems. Your decision should consider the specific hardware support and whether you prioritize maximum speed or broader compatibility for everyday use.
Thunderbolt 3 vs USB 4 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com