Wired charging delivers faster and more consistent power transfer, ensuring your device charges quickly and efficiently, while wireless charging offers unrivaled convenience and cable-free operation, perfect for those who value ease of use over speed. Explore the rest of the article to see which charging method best suits your lifestyle and device needs.
Table of Comparison
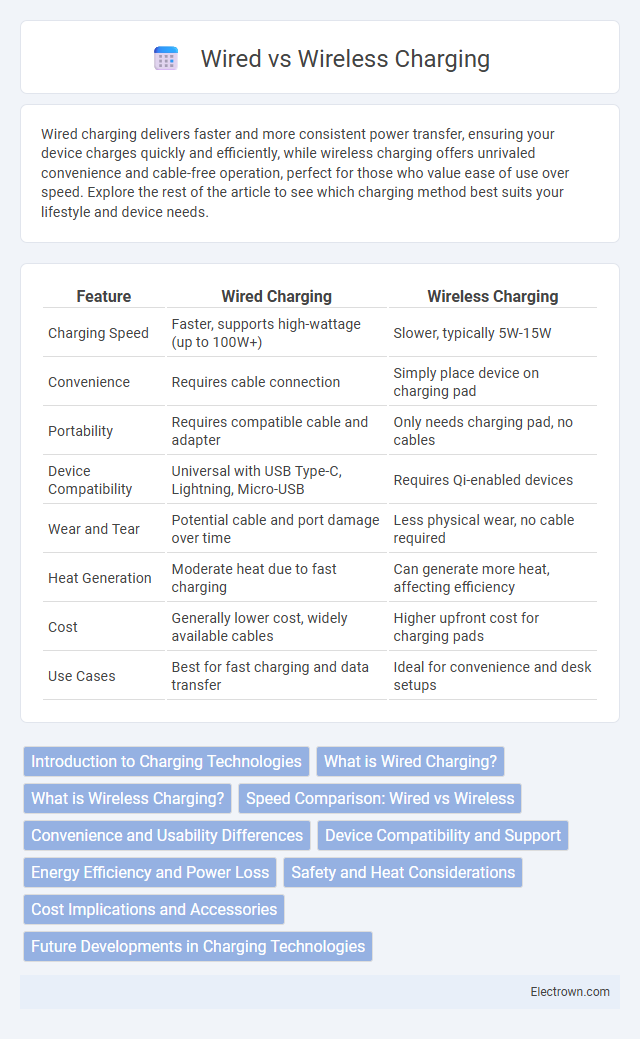
| Feature | Wired Charging | Wireless Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Faster, supports high-wattage (up to 100W+) | Slower, typically 5W-15W |
| Convenience | Requires cable connection | Simply place device on charging pad |
| Portability | Requires compatible cable and adapter | Only needs charging pad, no cables |
| Device Compatibility | Universal with USB Type-C, Lightning, Micro-USB | Requires Qi-enabled devices |
| Wear and Tear | Potential cable and port damage over time | Less physical wear, no cable required |
| Heat Generation | Moderate heat due to fast charging | Can generate more heat, affecting efficiency |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, widely available cables | Higher upfront cost for charging pads |
| Use Cases | Best for fast charging and data transfer | Ideal for convenience and desk setups |
Introduction to Charging Technologies
Wired charging uses physical cables to transfer power directly from a power source to your device, offering fast and stable energy delivery. Wireless charging relies on electromagnetic fields to transfer energy without cables, providing convenience but typically at a slower charging rate. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you choose the best charging technology suited for your device and lifestyle.
What is Wired Charging?
Wired charging involves connecting your device directly to a power source using a cable, typically USB or Lightning, allowing faster and more efficient energy transfer. This method supports higher power delivery, making it ideal for quickly charging smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Your device benefits from consistent voltage and current, leading to more reliable and stable charging performance compared to wireless alternatives.
What is Wireless Charging?
Wireless charging uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging station and a device, eliminating the need for physical cables. This technology typically relies on inductive coupling, where a charging pad generates a magnetic field that induces a current in the device's receiver coil. Wireless charging is widely used for smartphones, smartwatches, and earbuds, offering convenient, cable-free power replenishment.
Speed Comparison: Wired vs Wireless
Wired charging typically delivers faster power transfer, with speeds reaching up to 100W on some devices, enabling rapid battery replenishment within minutes. Wireless charging, while more convenient, usually operates at lower wattages--commonly ranging between 5W and 15W--resulting in longer charging times. Advances in wireless technology, such as magnetic alignment and higher watt protocols like Qi 15W, are narrowing the speed gap but wired charging remains superior for rapid energy transfer.
Convenience and Usability Differences
Wireless charging offers the convenience of placing a device on a pad without plugging in cables, reducing wear on charging ports and enabling easier access in public or shared spaces. Wired charging typically provides faster power transfer and compatibility with a wider range of devices, making it more reliable for quick energy replenishment. Users prioritize wireless charging for daily ease and clutter reduction, while wired charging remains preferred for efficiency and uninterrupted connection during use.
Device Compatibility and Support
Wireless charging supports a wide range of devices equipped with Qi-compatible technology, making it convenient for smartphones, earbuds, and smartwatches from various manufacturers. Wired charging, however, offers broader compatibility with devices that may not support wireless standards, including many laptops, gaming consoles, and older smartphones. To ensure optimal charging performance, you should check your device's specifications for supported charging methods and compatible adapters.
Energy Efficiency and Power Loss
Wired charging typically offers higher energy efficiency than wireless charging due to direct power transfer with minimal energy loss, often exceeding 85% efficiency. Wireless charging experiences increased power loss caused by electromagnetic induction and alignment issues, resulting in efficiency rates between 60% to 75%. Optimizing your device's position on a wireless charger can help reduce power loss but wired charging remains superior for maximizing energy efficiency.
Safety and Heat Considerations
Wired charging offers more controlled power delivery, reducing the risk of overheating and ensuring safer operation for your devices. Wireless charging generates more heat due to energy loss during induction, which can potentially affect battery health over time if not properly managed. Choosing wired charging minimizes thermal stress, enhancing both safety and device longevity.
Cost Implications and Accessories
Wired charging typically involves lower initial costs due to the widespread availability of affordable cables and adapters, whereas wireless charging pads often require a higher investment for compatible devices and accessories. Wireless chargers may necessitate additional purchases like charging stands or cases optimized for efficient power transfer, increasing your overall expense. Choosing between wired and wireless charging impacts long-term costs based on accessory durability, replacement frequency, and convenience preferences.
Future Developments in Charging Technologies
Future developments in charging technologies focus on enhancing efficiency, speed, and convenience for both wired and wireless methods. Innovations such as ultra-fast wired charging reaching up to 200W and advanced wireless charging pads supporting 50W or more are becoming increasingly common. Emerging technologies like magnetic resonance wireless charging and integration with smart surfaces promise seamless, cable-free power delivery for multiple devices simultaneously.
Wired vs Wireless Charging Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com