USB-C offers faster data transfer speeds, improved power delivery, and a reversible connector design compared to the older USB-A standard, making it ideal for modern devices. Discover how upgrading to USB-C can enhance your connectivity and why it's becoming the new industry standard in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
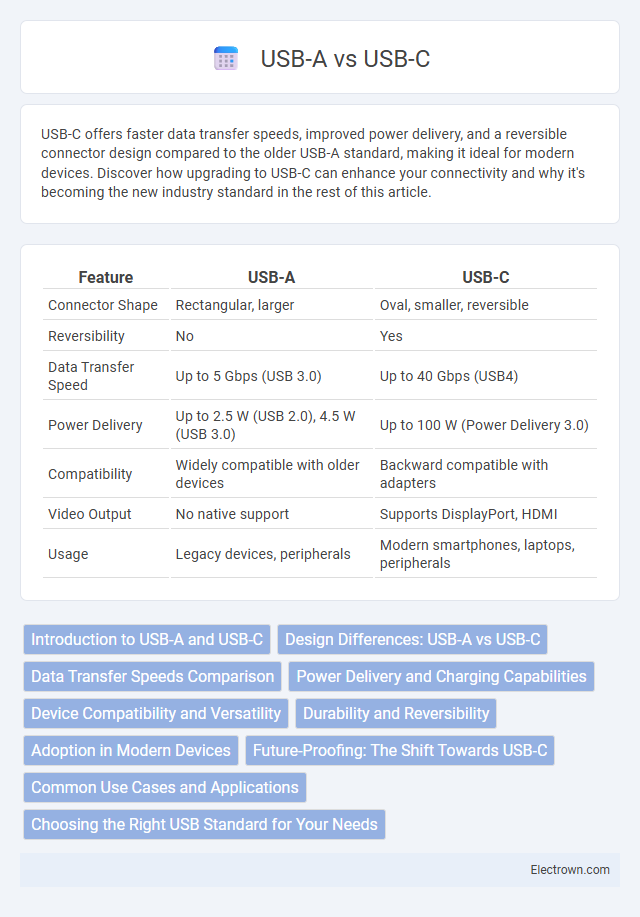
| Feature | USB-A | USB-C |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Shape | Rectangular, larger | Oval, smaller, reversible |
| Reversibility | No | Yes |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 5 Gbps (USB 3.0) | Up to 40 Gbps (USB4) |
| Power Delivery | Up to 2.5 W (USB 2.0), 4.5 W (USB 3.0) | Up to 100 W (Power Delivery 3.0) |
| Compatibility | Widely compatible with older devices | Backward compatible with adapters |
| Video Output | No native support | Supports DisplayPort, HDMI |
| Usage | Legacy devices, peripherals | Modern smartphones, laptops, peripherals |
Introduction to USB-A and USB-C
USB-A has been the standard connector for decades, widely recognized for its rectangular shape and compatibility with numerous devices such as keyboards, flash drives, and chargers. USB-C, a newer and more versatile connector, supports faster data transfer rates, higher power delivery, and reversible plug orientation, making it suitable for modern smartphones, laptops, and peripherals. Understanding the differences between USB-A and USB-C helps you choose the right cable or device for optimal performance and compatibility.
Design Differences: USB-A vs USB-C
USB-A connectors have a rectangular, flat design with a larger size, requiring precise orientation for insertion, whereas USB-C features a compact, oval shape with a reversible plug allowing easy, orientation-free connection. USB-C supports higher power delivery and faster data transfer rates due to its advanced pin configuration compared to the older USB-A design. The smaller USB-C design also enables thinner, more streamlined devices, making it the preferred port for modern laptops, smartphones, and peripherals.
Data Transfer Speeds Comparison
USB-C supports data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 or USB4, significantly outperforming USB-A's maximum speed of 5 Gbps with USB 3.0 and 10 Gbps with USB 3.1 Gen 2. This difference makes USB-C the preferred choice for high-speed data transfer tasks such as 4K video editing and large file backups. Your devices utilizing USB-C can benefit from faster data synchronization and reduced transfer times compared to older USB-A connections.
Power Delivery and Charging Capabilities
USB-C supports significantly higher Power Delivery (PD) standards than USB-A, enabling fast charging up to 100 watts, suitable for laptops, smartphones, and other high-power devices. USB-A typically offers maximum power output of 12 watts (5V/2.4A), making it less efficient for fast charging newer devices. The USB Power Delivery protocol in USB-C allows dynamic voltage and current adjustment, optimizing charging speed and device safety.
Device Compatibility and Versatility
USB-A ports remain widely compatible with numerous older devices such as external hard drives, keyboards, and printers, making them a staple in legacy technology ecosystems. USB-C supports a broader range of devices, including smartphones, laptops, and docking stations, due to its reversible design and higher data transfer rates. The versatility of USB-C enables seamless power delivery and video output, which USB-A cannot natively support, driving its adoption in modern tech infrastructure.
Durability and Reversibility
USB-C offers greater durability compared to USB-A due to its sturdier connector design that withstands more insertion cycles, typically around 10,000, versus USB-A's approximate 1,500 cycles. The reversible nature of USB-C allows you to plug in the connector either way, eliminating the frustration associated with USB-A's one-way insertion. Your devices benefit from USB-C's advanced durability and user-friendly reversible feature, enhancing overall connectivity experience.
Adoption in Modern Devices
USB-C has rapidly become the dominant standard in modern devices due to its reversible design and superior data transfer speeds, supporting up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 and USB4 protocols. USB-A remains prevalent in legacy and budget devices, but its slower transfer rates and bulkier connector are limiting its adoption in new smartphones, laptops, and peripherals. The widespread integration of USB-C in flagship models across industries signals a near-future phase-out of USB-A interfaces.
Future-Proofing: The Shift Towards USB-C
USB-C is rapidly becoming the universal standard for data transfer and charging due to its faster speeds, higher power delivery, and reversible connector design. Devices supporting USB-C ensure compatibility with upcoming technology, making your gadgets more durable and adaptable. Investing in USB-C technology offers future-proofing benefits by aligning with the industry's shift away from USB-A ports.
Common Use Cases and Applications
USB-A ports are widely used for connecting peripherals such as keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage devices in desktops and older laptops. USB-C supports faster data transfer, video output, and power delivery, making it ideal for modern smartphones, tablets, laptops, and docking stations. Your choice between USB-A and USB-C depends on device compatibility and the need for higher speeds or versatile connectivity.
Choosing the Right USB Standard for Your Needs
Selecting between USB-A and USB-C depends on device compatibility and data transfer requirements; USB-C offers faster speeds up to 10 Gbps with USB 3.1 and supports power delivery up to 100W, making it ideal for modern laptops and smartphones. USB-A remains prevalent in older devices and peripherals, supporting data rates up to 5 Gbps with USB 3.0, suitable for basic charging and data transfer. Consider the type of connection ports available on your devices and the need for reversible connectors when determining the optimal USB standard.
USB-A vs USB-C Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com