Dual band routers operate on two frequencies--2.4 GHz and 5 GHz--offering a balance between range and speed, while tri band routers add an extra 5 GHz band to reduce congestion and improve performance for multiple devices. To understand which router best suits your home network and streaming needs, read on for a detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
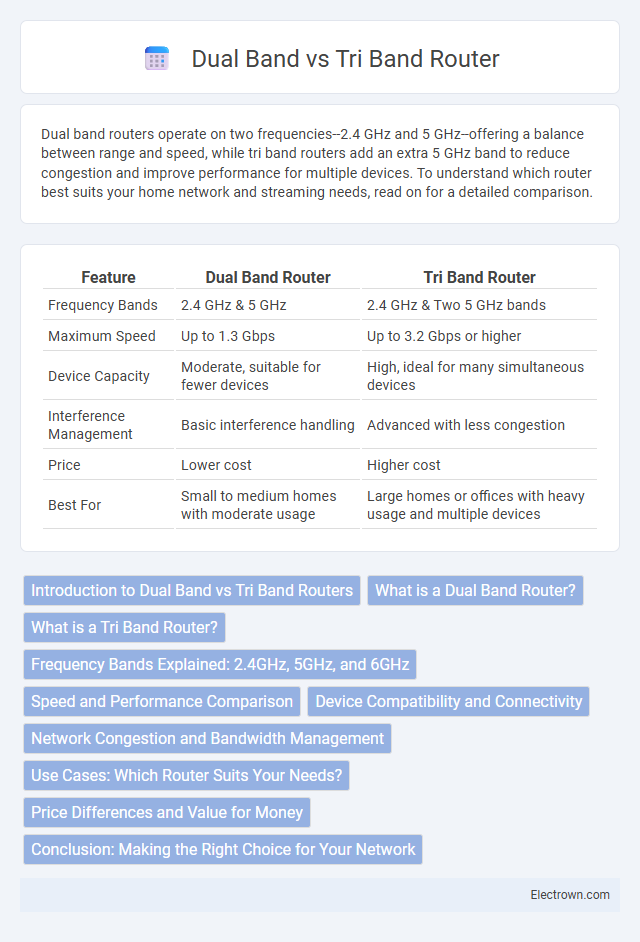
| Feature | Dual Band Router | Tri Band Router |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz & Two 5 GHz bands |
| Maximum Speed | Up to 1.3 Gbps | Up to 3.2 Gbps or higher |
| Device Capacity | Moderate, suitable for fewer devices | High, ideal for many simultaneous devices |
| Interference Management | Basic interference handling | Advanced with less congestion |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Best For | Small to medium homes with moderate usage | Large homes or offices with heavy usage and multiple devices |
Introduction to Dual Band vs Tri Band Routers
Dual band routers operate on two frequencies, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, offering improved connectivity and reduced interference for home and small office networks. Tri band routers add an extra 5 GHz band, enabling better performance and higher throughput in environments with multiple devices and heavy data usage. This distinction makes tri band routers ideal for gaming, 4K streaming, and smart home integration where bandwidth demand is significant.
What is a Dual Band Router?
A Dual Band Router operates on two frequency bands, typically 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, to provide better wireless performance and reduced interference. The 2.4 GHz band offers wider coverage but slower speeds, while the 5 GHz band delivers faster data rates with shorter range. Your choice of a Dual Band Router can improve network stability and speed for multiple connected devices in a home or office setting.
What is a Tri Band Router?
A Tri Band Router operates on three separate frequency bands, typically one 2.4 GHz band and two 5 GHz bands, allowing for increased network capacity and reduced congestion compared to Dual Band routers, which use only one 2.4 GHz and one 5 GHz band. This additional 5 GHz band in Tri Band routers supports more simultaneous devices and higher data throughput, optimizing performance in busy environments or smart homes with multiple connected devices. Tri Band technology enhances wireless stability and minimizes interference, making it ideal for gaming, 4K streaming, and large household networks.
Frequency Bands Explained: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz
Dual band routers operate on 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, with 2.4GHz offering broader range but slower speeds, and 5GHz providing faster data transfer with a shorter range. Tri band routers add a third frequency band, typically 6GHz, which supports faster speeds and lower latency ideal for high-density environments and newer Wi-Fi 6E devices. Understanding these frequency bands helps you optimize your network for speed, coverage, and device compatibility.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Dual band routers operate on two frequencies, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, offering sufficient speed for everyday internet use and moderate streaming. Tri band routers include an additional 5 GHz band, enabling simultaneous connections with less interference and higher aggregate bandwidth, resulting in improved performance in dense network environments. For users requiring maximum speed and seamless connectivity for multiple devices, tri band routers outperform dual band by reducing congestion and enhancing data throughput.
Device Compatibility and Connectivity
Dual band routers operate on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies, offering solid device compatibility with most smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices, ensuring reliable connectivity for everyday use. Tri band routers include an extra 5 GHz band, which enhances network capacity and reduces congestion, especially in environments with multiple high-bandwidth devices or heavy streaming. Choosing between them depends on your device ecosystem and connectivity demands, with tri band routers providing superior performance for complex, device-dense networks.
Network Congestion and Bandwidth Management
Dual band routers operate on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies, effectively reducing network congestion by distributing devices between these two bands. Tri band routers add an extra 5 GHz band, significantly improving bandwidth management by allocating more devices to less crowded channels, which enhances overall network performance. You will experience faster speeds and lower latency in environments with many connected devices when using a tri band router.
Use Cases: Which Router Suits Your Needs?
Dual band routers are ideal for average households where internet usage includes streaming, browsing, and gaming on multiple devices, providing both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands for balanced performance. Tri band routers, offering an additional 5 GHz band, suit larger homes or environments with heavy network traffic, such as multiple 4K streams, online gaming, and smart home devices simultaneously connected. Your choice depends on the number of connected devices and the demand for bandwidth-intensive activities to ensure optimal network efficiency and speed.
Price Differences and Value for Money
Dual band routers typically cost less than tri band routers due to having fewer frequency bands, making them a more budget-friendly option for general home use. Tri band routers offer increased bandwidth and reduced network congestion by adding an extra 5 GHz band, which is beneficial for high-density environments or multiple simultaneous users, but come with a higher price tag. For most users, dual band routers provide sufficient speed and coverage, delivering better value for money, while tri band routers justify their premium cost primarily in demanding, high-traffic network setups.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Network
Choosing between a dual-band and tri-band router depends on your network's size, device count, and usage patterns. Dual-band routers provide reliable performance for general households with moderate device demands, while tri-band routers offer enhanced capacity and reduced interference ideal for large homes or heavy streaming and gaming. Assessing your network needs ensures you select the router that optimizes speed, coverage, and overall connectivity for your environment.
Dual Band vs Tri Band Router Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com