A board support package (BSP) provides low-level drivers and initialization code tailored specifically for a hardware platform, enabling the operating system to function correctly on that board, while a hardware abstraction layer (HAL) offers a uniform interface to hardware peripherals, allowing software to work across different devices without modification. Understanding the differences between BSP and HAL is essential for optimizing your embedded system development; continue reading to explore their roles and benefits in detail.
Table of Comparison
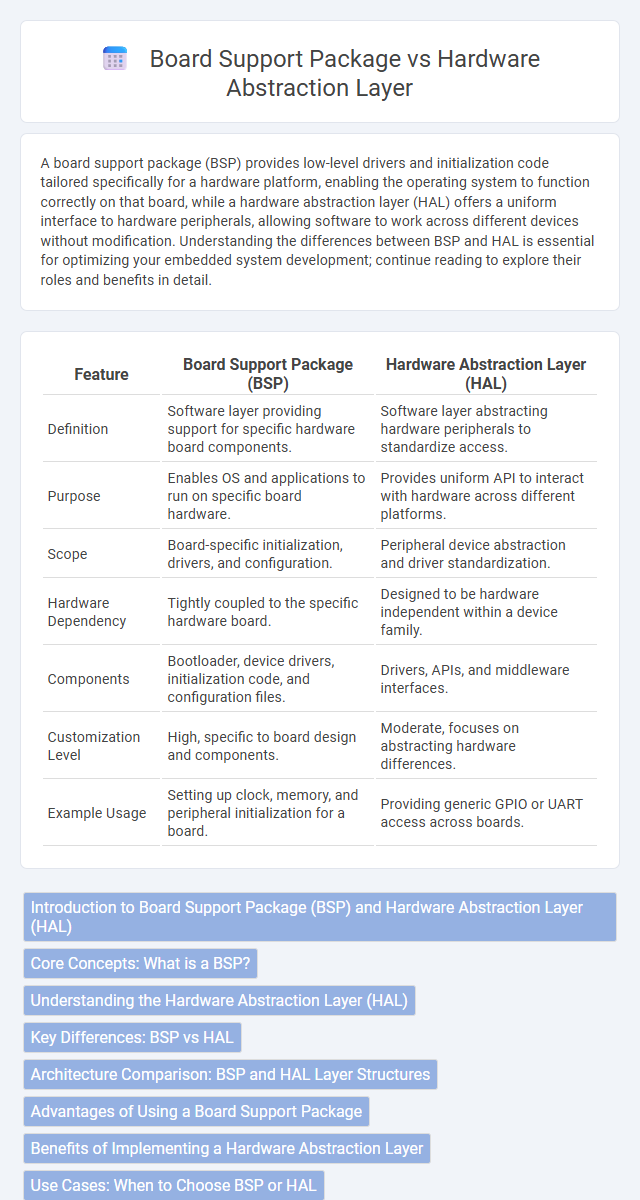
| Feature | Board Support Package (BSP) | Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software layer providing support for specific hardware board components. | Software layer abstracting hardware peripherals to standardize access. |
| Purpose | Enables OS and applications to run on specific board hardware. | Provides uniform API to interact with hardware across different platforms. |
| Scope | Board-specific initialization, drivers, and configuration. | Peripheral device abstraction and driver standardization. |
| Hardware Dependency | Tightly coupled to the specific hardware board. | Designed to be hardware independent within a device family. |
| Components | Bootloader, device drivers, initialization code, and configuration files. | Drivers, APIs, and middleware interfaces. |
| Customization Level | High, specific to board design and components. | Moderate, focuses on abstracting hardware differences. |
| Example Usage | Setting up clock, memory, and peripheral initialization for a board. | Providing generic GPIO or UART access across boards. |
Introduction to Board Support Package (BSP) and Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)
A Board Support Package (BSP) includes low-level drivers and initialization code tailored for specific hardware platforms, enabling operating systems to run efficiently on embedded devices. The Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides a standardized API that abstracts hardware specifics, facilitating portability and easier application development across different platforms. BSP is tightly coupled with the hardware and OS integration, while HAL focuses on offering a uniform interface to interact with various hardware components.
Core Concepts: What is a BSP?
A Board Support Package (BSP) is a collection of software components that provides a low-level interface between the operating system and the hardware, enabling the OS to function on a specific board. It includes device drivers, bootloader, and board-specific initialization code tailored to the hardware architecture. In contrast, the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) offers a higher-level interface, abstracting hardware details to provide standardized access across different platforms without hardware-specific customization.
Understanding the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)
The Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides a unified API that abstracts the underlying hardware specifics, facilitating portable and scalable software development across different microcontroller platforms. Unlike the Board Support Package (BSP), which includes device drivers and initialization code tailored to a specific hardware board, HAL focuses on standardizing hardware access for components like timers, GPIOs, and communication interfaces. Understanding HAL is crucial for developers aiming to write hardware-independent code, improving maintainability and reducing development time in embedded systems.
Key Differences: BSP vs HAL
Board Support Package (BSP) provides low-level drivers and initialization code specific to a particular hardware platform, enabling the operating system to function correctly on that board. Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) offers a standardized API to abstract hardware details, promoting portability across different platforms by hiding hardware complexity. BSP is tightly coupled with hardware implementation, while HAL ensures software modularity through hardware-independent interfaces.
Architecture Comparison: BSP and HAL Layer Structures
The Board Support Package (BSP) provides a low-level software layer closely tied to the hardware, integrating device drivers, startup code, and board-specific initialization routines that facilitate direct interaction with physical components. In contrast, the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) offers a more generalized and portable interface by abstracting hardware details through a standardized API, enabling application-level code to interact with hardware independently of specific platforms. BSP architecture is inherently hardware-specific and tailored for a particular board, while HAL structures emphasize modularity and portability across varying hardware configurations.
Advantages of Using a Board Support Package
A Board Support Package (BSP) provides a comprehensive set of drivers and initialization code tailored specifically for a hardware platform, enabling faster development cycles and reducing integration complexity. It ensures seamless compatibility between the operating system and the underlying hardware, improving system stability and performance. Using a BSP accelerates prototyping and deployment by encapsulating hardware-specific details while allowing developers to focus on application-level code.
Benefits of Implementing a Hardware Abstraction Layer
Implementing a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) enhances software portability by decoupling hardware-specific code from application logic, allowing your projects to run seamlessly across different hardware platforms. HAL simplifies maintenance and scalability by providing standardized interfaces to hardware components, reducing the complexity of driver updates when hardware changes. This abstraction accelerates development cycles and improves system robustness by isolating hardware dependencies from core software functionalities.
Use Cases: When to Choose BSP or HAL
A Board Support Package (BSP) is ideal when you need low-level, hardware-specific initialization and drivers tailored to your exact board, making it essential for embedded systems requiring direct hardware control and optimization. A Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) is more suitable for projects prioritizing portability across multiple hardware platforms, as it provides a uniform API that abstracts away the underlying hardware details. You should choose BSP for deep customization and performance, while HAL is best when your goal is ease of portability and code reuse across different devices.
Integration Challenges and Best Practices
Board Support Package (BSP) integration often involves hardware-specific configurations, device drivers, and bootloader settings, requiring careful alignment with the underlying hardware to ensure seamless operation. Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) simplifies this by providing a standardized interface that abstracts hardware differences, improving portability and reducing complexity during integration. Best practices emphasize modular design, thorough documentation, and rigorous testing across different hardware platforms to minimize integration issues and enhance maintainability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution for Your Embedded System
Selecting the right solution for your embedded system depends on the specific requirements and goals of your project. Board Support Packages (BSPs) provide low-level initialization and hardware-specific drivers tailored for a particular board, ensuring optimal performance and direct hardware control. Hardware Abstraction Layers (HALs) offer a more generalized interface to abstract hardware details, enhancing portability and ease of development across multiple platforms.
Board support package vs hardware abstraction layer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com