C offers simplicity and direct hardware manipulation ideal for low-level embedded systems, while C++ provides object-oriented features enabling more complex abstractions and code reuse in embedded development. Explore the rest of the article to determine which language best suits your embedded project needs.
Table of Comparison
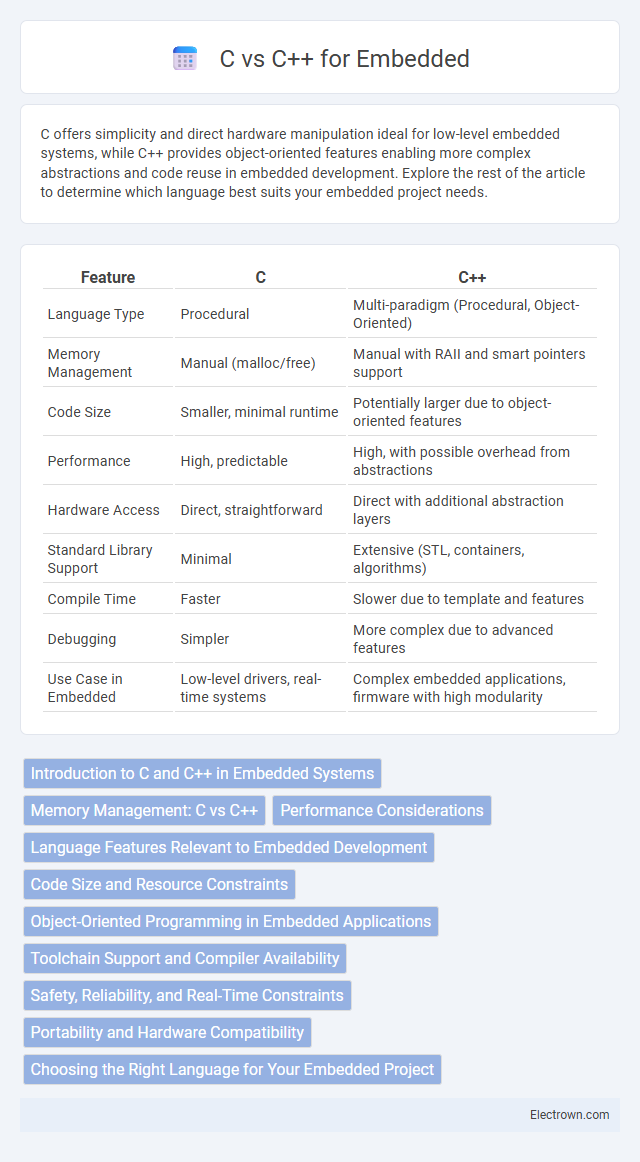
| Feature | C | C++ |
|---|---|---|
| Language Type | Procedural | Multi-paradigm (Procedural, Object-Oriented) |
| Memory Management | Manual (malloc/free) | Manual with RAII and smart pointers support |
| Code Size | Smaller, minimal runtime | Potentially larger due to object-oriented features |
| Performance | High, predictable | High, with possible overhead from abstractions |
| Hardware Access | Direct, straightforward | Direct with additional abstraction layers |
| Standard Library Support | Minimal | Extensive (STL, containers, algorithms) |
| Compile Time | Faster | Slower due to template and features |
| Debugging | Simpler | More complex due to advanced features |
| Use Case in Embedded | Low-level drivers, real-time systems | Complex embedded applications, firmware with high modularity |
Introduction to C and C++ in Embedded Systems
C remains the foundational programming language in embedded systems due to its low-level hardware access, deterministic behavior, and minimal runtime footprint, making it ideal for resource-constrained environments. C++ extends C with object-oriented features, stronger type checking, and richer libraries, enabling more complex system designs and improved code reuse while maintaining performance close to C. Embedded developers often choose C++ when scalability, abstraction, and software maintenance are priorities, without sacrificing the fine-grained control required in embedded applications.
Memory Management: C vs C++
C provides manual memory management through functions like malloc and free, offering fine-grained control but increasing the risk of memory leaks and fragmentation in embedded systems. C++ introduces constructors, destructors, and smart pointers, enabling automatic resource management via RAII (Resource Acquisition Is Initialization) to enhance reliability and reduce memory errors. In embedded development, C++ facilitates safer and more predictable memory usage while maintaining performance constraints critical to resource-limited environments.
Performance Considerations
C offers minimal runtime overhead and direct memory manipulation, making it highly efficient for embedded systems with tight performance constraints. C++ introduces features like classes and templates that can optimize code reuse and inline functions, potentially enhancing performance without significant cost when carefully managed. Your choice depends on balancing the need for low-level control in C with the abstraction benefits of C++ that can improve maintainability and performance in embedded applications.
Language Features Relevant to Embedded Development
C offers low-level memory access and minimal runtime overhead, making it highly efficient for embedded systems with strict resource constraints. C++ introduces object-oriented programming, strong type checking, and features like templates and exception handling that enhance code organization, reuse, and maintainability in complex embedded projects. Both languages provide direct hardware manipulation capabilities, but C++'s abstraction mechanisms enable scalable application design without significantly compromising performance on embedded platforms.
Code Size and Resource Constraints
C typically produces smaller code size compared to C++ due to its procedural nature and minimal runtime overhead, making it ideal for resource-constrained embedded systems. C++ offers features like object-oriented programming and abstraction but may increase code size and memory usage, potentially challenging strict resource limits. Careful use of C++ features such as templates and inline functions can mitigate overhead while leveraging its advanced capabilities in embedded applications.
Object-Oriented Programming in Embedded Applications
C++ offers Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) features such as classes, inheritance, and polymorphism, which enable modular and reusable code in embedded applications, enhancing maintainability and scalability. Unlike C, which relies on procedural programming, C++ allows encapsulation of hardware-specific functions within objects, making complex firmware easier to manage. You can leverage C++'s OOP capabilities to design more structured and extensible embedded systems without sacrificing performance when used with thoughtful resource management.
Toolchain Support and Compiler Availability
C dominates embedded development due to its widespread toolchain support and mature compiler availability, with platforms like GCC and Clang providing robust, optimized code generation. C++ compilers for embedded systems, such as ARM's Keil and IAR Embedded Workbench, have improved significantly, offering advanced features like templates and object-oriented programming while maintaining efficiency. Your choice should balance the complexity of the application with the availability of tailored compiler optimizations and debugging tools in the respective toolchains.
Safety, Reliability, and Real-Time Constraints
C++ offers enhanced safety features like stronger type checking and encapsulation compared to C, reducing common programming errors in embedded systems. Its object-oriented capabilities improve code reliability through modular design and reuse, which is crucial for maintaining complex real-time embedded applications. You should choose C++ when your project demands stricter safety standards and manageable real-time constraints without sacrificing performance.
Portability and Hardware Compatibility
C offers exceptional portability and broad hardware compatibility due to its close-to-metal programming model and widespread support across microcontrollers and processors. C++ introduces advanced features like object-oriented programming but can be less portable on constrained embedded systems because of complex runtime requirements and larger memory footprints. Your choice depends on the specific hardware constraints and portability needs of your embedded application.
Choosing the Right Language for Your Embedded Project
Choosing the right language for your embedded project depends on factors like system complexity, performance requirements, and memory constraints. C offers low-level hardware control and minimal runtime overhead ideal for resource-constrained systems, while C++ provides object-oriented features and stronger abstraction for managing complex codebases and scalability. Your decision should weigh C's efficiency against C++'s flexibility to ensure maintainable, high-performance embedded software.
C vs C++ for embedded Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com