An Image Rejection Mixer significantly enhances signal clarity by effectively eliminating unwanted image frequencies, unlike a Standard Mixer which processes all frequencies indiscriminately, potentially causing interference and signal distortion. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right mixer for your application--explore the full article to learn more about their specific advantages and use cases.
Table of Comparison
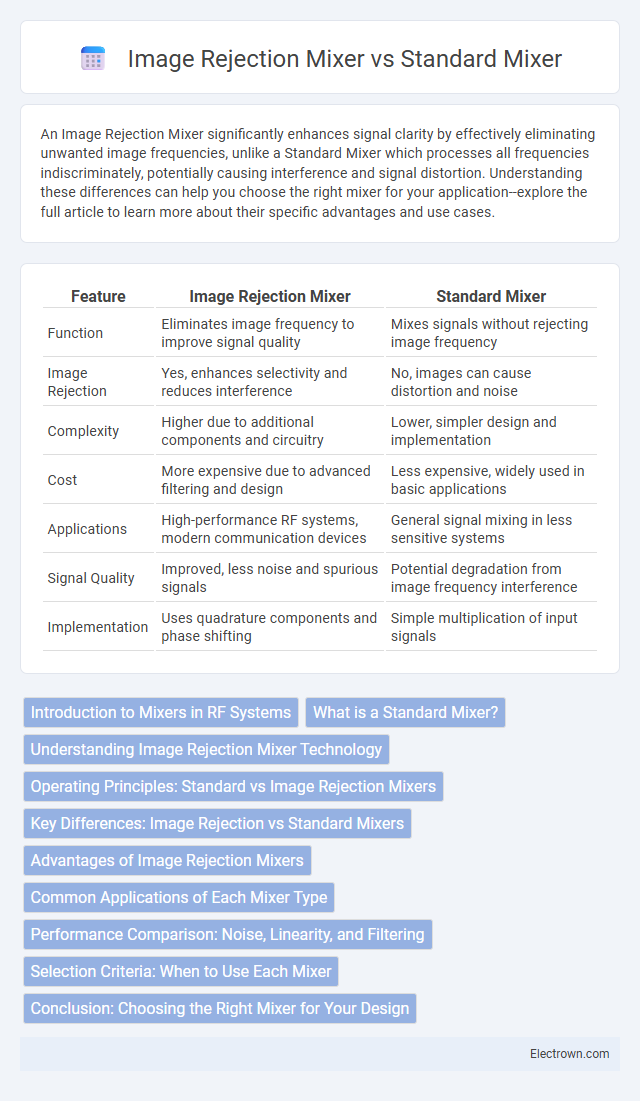
| Feature | Image Rejection Mixer | Standard Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Eliminates image frequency to improve signal quality | Mixes signals without rejecting image frequency |
| Image Rejection | Yes, enhances selectivity and reduces interference | No, images can cause distortion and noise |
| Complexity | Higher due to additional components and circuitry | Lower, simpler design and implementation |
| Cost | More expensive due to advanced filtering and design | Less expensive, widely used in basic applications |
| Applications | High-performance RF systems, modern communication devices | General signal mixing in less sensitive systems |
| Signal Quality | Improved, less noise and spurious signals | Potential degradation from image frequency interference |
| Implementation | Uses quadrature components and phase shifting | Simple multiplication of input signals |
Introduction to Mixers in RF Systems
Mixers play a crucial role in RF systems by converting signals from one frequency to another to facilitate effective signal processing. Image rejection mixers improve system performance by suppressing unwanted image frequencies that can cause interference. Your choice between an image rejection mixer and a standard mixer depends on the need for enhanced signal clarity versus simpler design requirements.
What is a Standard Mixer?
A standard mixer is a fundamental RF component that combines or converts signals by mixing an input RF frequency with a local oscillator frequency to produce output signals at sum and difference frequencies. It typically produces both desired intermediate frequency (IF) signals and unwanted image signals, requiring additional filtering to suppress the image. Standard mixers are widely used in communication systems for frequency translation but lack inherent image rejection capabilities, making them less efficient than image rejection mixers in applications sensitive to interference.
Understanding Image Rejection Mixer Technology
Image rejection mixer technology enhances signal clarity by effectively suppressing unwanted image frequencies that can interfere with desired signals, a common limitation in standard mixers. By employing balanced or quadrature mixing techniques, image rejection mixers improve the signal-to-noise ratio and reduce the need for complex filtering after mixing stages. This technology is essential in high-frequency communication systems where precision and minimizing spurious responses are critical for optimal performance.
Operating Principles: Standard vs Image Rejection Mixers
Standard mixers combine input signals without distinguishing between desired and unwanted frequency components, often resulting in image frequency interference. Image rejection mixers employ phase shifting and balanced circuitry to suppress image frequencies, enhancing signal clarity. This design difference enables image rejection mixers to provide improved selectivity and reduce noise in RF communication systems.
Key Differences: Image Rejection vs Standard Mixers
Image rejection mixers significantly improve signal quality by suppressing unwanted image frequencies that standard mixers typically allow, resulting in cleaner intermediate frequencies (IF). Unlike standard mixers, which can introduce image interference and degrade overall system performance, image rejection mixers integrate filtering mechanisms to enhance selectivity and reduce noise. Your choice between the two impacts receiver design complexity, with image rejection mixers offering superior performance in congested signal environments.
Advantages of Image Rejection Mixers
Image rejection mixers enhance signal quality by significantly reducing image frequency interference, which improves receiver sensitivity and selectivity. They achieve better performance in crowded frequency environments, enabling clearer and more accurate signal processing compared to standard mixers. Your communication systems benefit from reduced noise and unwanted signals, leading to higher fidelity and reliability.
Common Applications of Each Mixer Type
Image rejection mixers are primarily utilized in communication systems such as quadrature receivers and software-defined radios to suppress unwanted image frequencies and improve signal quality. Standard mixers are commonly found in applications like frequency conversion for radio transmitters, receivers, and general signal processing tasks where image frequency rejection is less critical. The choice between image rejection and standard mixers depends on the specific application requirements for signal clarity and complexity.
Performance Comparison: Noise, Linearity, and Filtering
Image rejection mixers outperform standard mixers by significantly reducing image frequency interference, resulting in lower noise figures and enhanced signal clarity. Their inherent architecture improves linearity, minimizing intermodulation distortion and improving overall system dynamic range. Enhanced filtering capabilities in image rejection mixers reduce spurious signals, enabling more efficient suppression of unwanted frequencies compared to conventional mixers.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Each Mixer
Choose an Image Rejection Mixer when suppressing unwanted sideband signals is crucial for enhancing signal clarity in communication systems. A Standard Mixer suits applications where simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and broad frequency mixing without sideband suppression are sufficient. Your selection depends on the importance of image rejection in your system's performance versus the design complexity and cost constraints.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Design
Selecting the right mixer hinges on your application's requirement for signal purity and noise reduction; an Image Rejection Mixer minimizes unwanted image frequencies, enhancing overall system performance in complex RF environments. Standard Mixers offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness but may require additional filtering to manage image interference. Careful evaluation of system specifications, including desired dynamic range and integration complexity, guides the optimal mixer choice for efficient and reliable signal processing.
Image Rejection Mixer vs Standard Mixer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com