Passive attenuators reduce signal strength using resistors without requiring external power, ensuring simplicity and reliability but with potential signal loss. Active attenuators, on the other hand, use powered components like transistors to maintain signal integrity while adjusting levels, offering greater precision and control; discover how each type can optimize Your audio setup in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
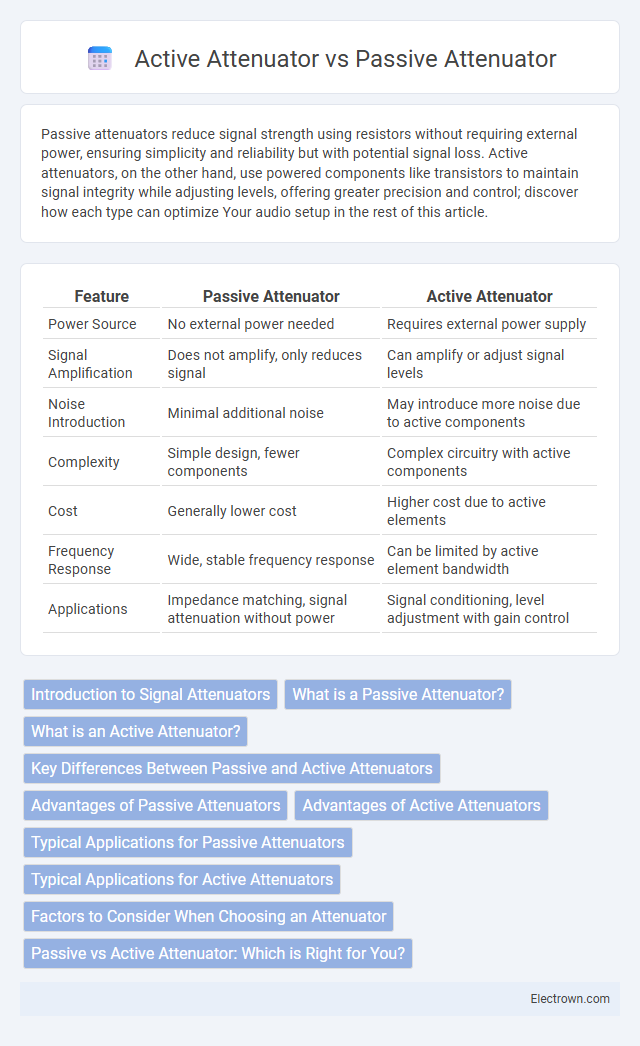
| Feature | Passive Attenuator | Active Attenuator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | No external power needed | Requires external power supply |
| Signal Amplification | Does not amplify, only reduces signal | Can amplify or adjust signal levels |
| Noise Introduction | Minimal additional noise | May introduce more noise due to active components |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | Complex circuitry with active components |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to active elements |
| Frequency Response | Wide, stable frequency response | Can be limited by active element bandwidth |
| Applications | Impedance matching, signal attenuation without power | Signal conditioning, level adjustment with gain control |
Introduction to Signal Attenuators
Signal attenuators reduce signal strength without significantly degrading the signal quality, with passive attenuators relying on resistive components and active attenuators using powered electronic circuits. Passive attenuators offer simplicity, reliability, and no power requirement, making them suitable for fixed attenuation in RF and audio applications. Active attenuators provide adjustable attenuation and improved signal integrity by compensating for insertion loss, ideal for dynamic signal control in communication and instrumentation systems.
What is a Passive Attenuator?
A passive attenuator is an electronic device that reduces signal power without requiring an external power source, relying solely on resistive components to dissipate excess signal energy. It is commonly used in audio and RF applications to lower signal levels while maintaining signal integrity and preventing distortion. Passive attenuators offer simplicity, reliability, and minimal maintenance compared to active attenuators, which use powered electronic circuits for signal control.
What is an Active Attenuator?
An active attenuator is an electronic device that reduces signal strength using powered components such as transistors or operational amplifiers, enabling precise control and amplification adjustment without significant signal degradation. Unlike passive attenuators, which dissipate energy as heat through resistors, active attenuators can provide gain compensation and maintain signal integrity, making them suitable for applications requiring variable attenuation with minimal noise. Active attenuators are commonly used in RF communication systems, audio equipment, and instrumentation to manage signal levels dynamically while preserving overall performance.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Attenuators
Passive attenuators reduce signal strength using resistive components without requiring power, offering simplicity and reliability but causing some signal loss and noise. Active attenuators utilize powered electronic circuits to precisely control attenuation levels, enabling amplification or impedance matching alongside signal reduction for improved performance in complex systems. Key differences include power dependency, signal integrity, adjustment precision, and noise introduction, making each suitable for distinct applications based on system requirements.
Advantages of Passive Attenuators
Passive attenuators offer advantages such as simplicity, reliability, and no need for external power sources, making them ideal in many audio and RF applications. Their design ensures linear attenuation with minimal signal distortion, preserving the integrity of Your audio or signal path. Moreover, passive attenuators are often more durable and require less maintenance compared to active attenuators.
Advantages of Active Attenuators
Active attenuators provide precise control over signal levels through electronic amplification, ensuring consistent attenuation across a wide frequency range and maintaining signal integrity. Unlike passive attenuators, active designs compensate for insertion loss by boosting the signal, enhancing system sensitivity and reducing noise. Their adaptability and improved performance make active attenuators ideal for applications requiring dynamic gain adjustment and high-fidelity signal processing.
Typical Applications for Passive Attenuators
Typical applications for passive attenuators include signal level adjustment in RF circuits, impedance matching between components, and noise reduction in sensitive measurement equipment. They are widely used in test and measurement setups, antenna systems, and audio engineering to lower signal strength without adding noise or distortion. Passive attenuators are favored for their reliability, simplicity, and ability to operate without a power source.
Typical Applications for Active Attenuators
Active attenuators are commonly used in wireless communication systems, audio processing, and signal modulation where consistent gain control and impedance matching are critical. These devices are essential in applications requiring low noise figures and variable attenuation, such as RF front-end modules and laboratory signal testing. Their ability to amplify signals while attenuating unwanted noise makes them ideal for precise signal conditioning in both commercial and military electronics.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Attenuator
Choosing between a passive attenuator and an active attenuator depends on factors such as signal integrity, power requirements, and noise performance. Passive attenuators are ideal for simple reduction tasks without power supply needs, offering low distortion and high reliability, while active attenuators provide gain control and signal amplification but demand power and may introduce noise. Your specific application and system constraints will guide the optimal choice for attenuation efficiency and signal quality.
Passive vs Active Attenuator: Which is Right for You?
Passive attenuators reduce signal strength without requiring power, offering simplicity, reliability, and minimal distortion, ideal for basic volume control in audio systems. Active attenuators use powered components to adjust signal amplitude, providing improved precision, less signal degradation, and the ability to amplify weak signals, suitable for complex or high-fidelity audio setups. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize simplicity and reliability or enhanced control and audio quality.
passive attenuator vs active attenuator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com