The slew rate of an op-amp defines how quickly its output can change in response to rapid input signal variations, while bandwidth determines the range of frequencies the op-amp can effectively amplify without signal degradation. Understanding how these two parameters interact is crucial for optimizing your circuit's performance; read on to explore their relationship and impact in detail.
Table of Comparison
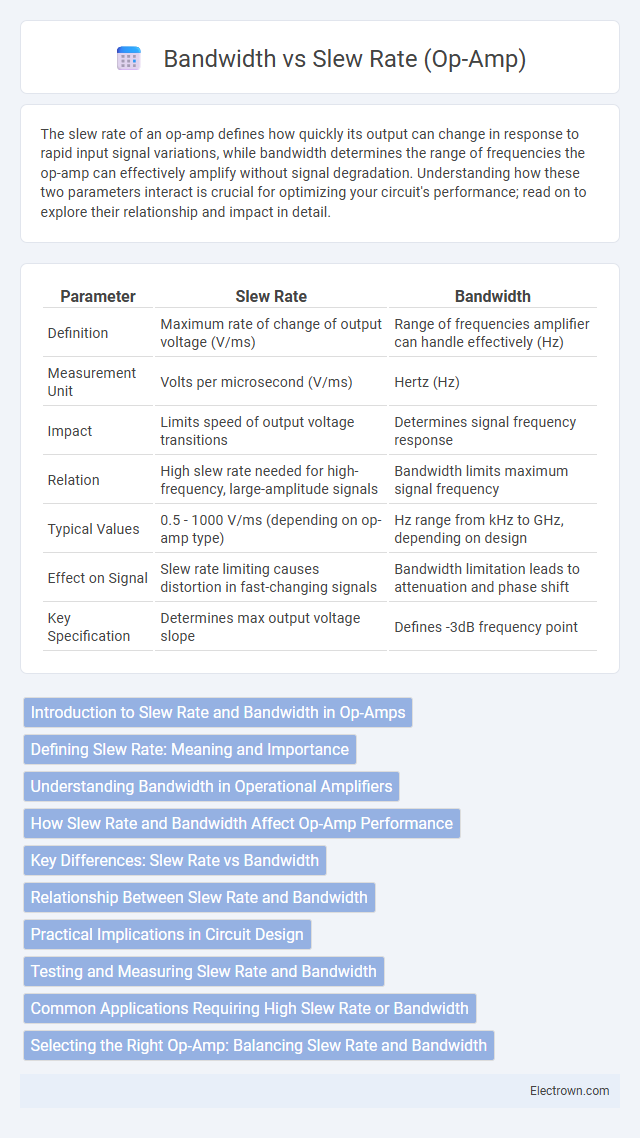
| Parameter | Slew Rate | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximum rate of change of output voltage (V/ms) | Range of frequencies amplifier can handle effectively (Hz) |
| Measurement Unit | Volts per microsecond (V/ms) | Hertz (Hz) |
| Impact | Limits speed of output voltage transitions | Determines signal frequency response |
| Relation | High slew rate needed for high-frequency, large-amplitude signals | Bandwidth limits maximum signal frequency |
| Typical Values | 0.5 - 1000 V/ms (depending on op-amp type) | Hz range from kHz to GHz, depending on design |
| Effect on Signal | Slew rate limiting causes distortion in fast-changing signals | Bandwidth limitation leads to attenuation and phase shift |
| Key Specification | Determines max output voltage slope | Defines -3dB frequency point |
Introduction to Slew Rate and Bandwidth in Op-Amps
Slew rate in op-amps defines the maximum rate at which the output voltage can change, typically measured in volts per microsecond (V/us), and directly impacts the amplifier's response to rapid input signal changes. Bandwidth, characterized by the frequency range over which the op-amp maintains consistent gain, affects signal integrity and overall performance at high frequencies. Understanding the relationship between slew rate and bandwidth is crucial for designing circuits where fast transient response and accurate signal reproduction are required.
Defining Slew Rate: Meaning and Importance
Slew rate in an op-amp defines the maximum rate of change of its output voltage per unit time, usually expressed in volts per microsecond (V/us). This parameter is crucial because it limits how quickly the op-amp can respond to rapid input signal changes, directly affecting the accuracy and fidelity of high-frequency or large-amplitude signals. Your choice of op-amp should consider its slew rate to ensure it matches the required signal bandwidth, preventing distortion and maintaining signal integrity.
Understanding Bandwidth in Operational Amplifiers
Bandwidth in operational amplifiers defines the frequency range over which the op-amp can amplify signals effectively, directly impacting signal fidelity. The slew rate limits the maximum rate of change of the output voltage, restricting the op-amp's ability to handle high-frequency signals without distortion. Understanding the interplay between slew rate and bandwidth helps optimize Your circuit design for high-speed and high-frequency applications.
How Slew Rate and Bandwidth Affect Op-Amp Performance
Slew rate and bandwidth are critical parameters that directly influence op-amp performance in signal processing applications. Slew rate determines the maximum rate of change of the output voltage, impacting how quickly the op-amp can respond to rapid input signal changes without distortion. Bandwidth defines the frequency range over which the op-amp maintains consistent gain, with both factors jointly affecting signal fidelity and your circuit's overall accuracy in high-speed or high-frequency environments.
Key Differences: Slew Rate vs Bandwidth
Slew rate and bandwidth are critical parameters that define an op-amp's performance in signal processing applications. Slew rate refers to the maximum rate of change of the output voltage, typically measured in volts per microsecond (V/us), determining how fast the op-amp can respond to rapid input changes. Bandwidth, measured in hertz (Hz), represents the frequency range over which the op-amp can amplify signals with minimal attenuation, with the gain-bandwidth product linking these two parameters in frequency response characterization.
Relationship Between Slew Rate and Bandwidth
The relationship between slew rate and bandwidth in an op-amp determines how fast the output can respond to changes in the input signal without distortion. Higher slew rates enable the op-amp to handle larger frequency signals effectively by maintaining signal integrity at the bandwidth limit. Understanding your op-amp's slew rate is essential for applications requiring precise high-frequency performance and avoiding slew-induced distortion.
Practical Implications in Circuit Design
Slew rate and bandwidth are critical parameters in op-amp selection that directly impact your circuit's performance in high-frequency and fast transient applications. A limited slew rate can cause signal distortion in large amplitude, high-speed signals, while insufficient bandwidth restricts the frequency range accurately amplified. Balancing these two ensures stable operation and optimal signal integrity in analog signal processing and data acquisition systems.
Testing and Measuring Slew Rate and Bandwidth
Testing and measuring slew rate involves applying a step input voltage and observing the output voltage transition time with an oscilloscope to determine the maximum rate of change, expressed in V/ms. Bandwidth measurement requires sweeping input frequencies while monitoring the gain to identify the -3dB cutoff point, ensuring the op-amp maintains consistent performance across the desired frequency range. Accurate evaluation of both parameters helps optimize your op-amp for high-speed applications and signal integrity.
Common Applications Requiring High Slew Rate or Bandwidth
High slew rate and bandwidth in op-amps are critical for applications such as high-speed data acquisition, RF signal processing, and video amplification where rapid signal changes and wide frequency response are essential. Precision instrumentation, fast analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), and audio amplifiers benefit from op-amps with slew rates above several V/us and bandwidths extending into the MHz range. These parameters ensure minimal distortion and accurate signal reproduction in demanding environments like telecommunications, medical imaging, and high-frequency test equipment.
Selecting the Right Op-Amp: Balancing Slew Rate and Bandwidth
Selecting the right op-amp requires balancing slew rate and bandwidth to ensure optimal performance in your application. A higher slew rate supports fast transient response and wide bandwidth allows handling of high-frequency signals, but increasing one often affects the other due to internal design trade-offs. Understanding your signal requirements helps you choose an op-amp with a suitable slew rate that matches the necessary bandwidth, avoiding distortion and maintaining signal integrity.
Slew rate vs bandwidth (op-amp) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com