Analog mixers offer tactile controls and a warm, natural sound favored by many audio professionals, while digital mixers provide greater flexibility, advanced effects, and easier integration with digital audio workstations. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each can help you choose the right mixer for your audio setup; explore the rest of the article to learn more about their key differences and applications.
Table of Comparison
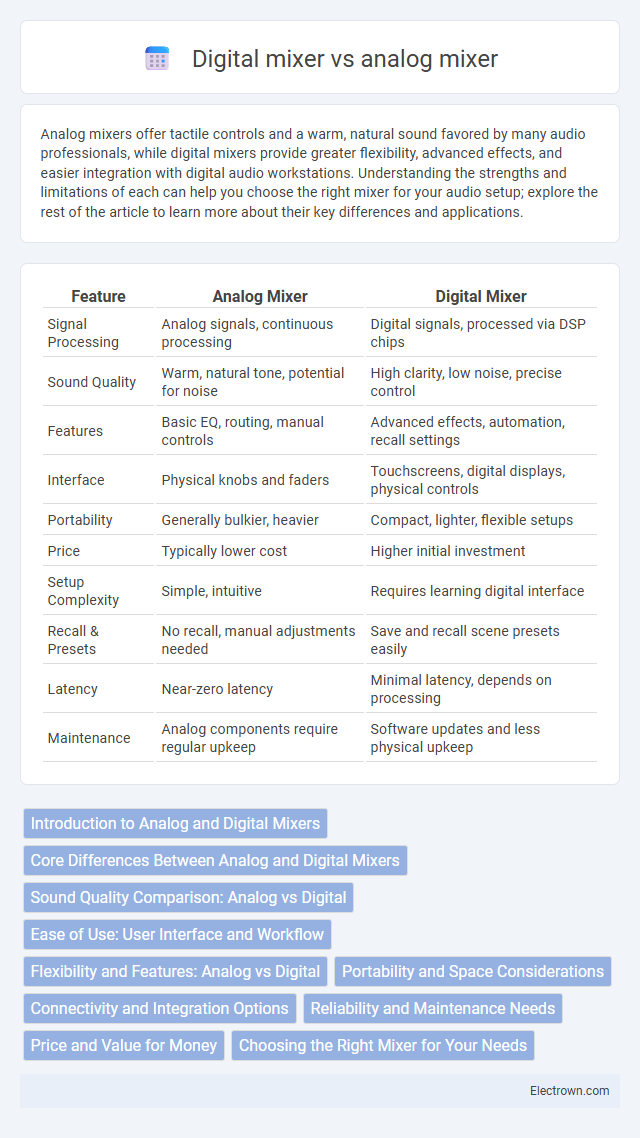
| Feature | Analog Mixer | Digital Mixer |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Processing | Analog signals, continuous processing | Digital signals, processed via DSP chips |
| Sound Quality | Warm, natural tone, potential for noise | High clarity, low noise, precise control |
| Features | Basic EQ, routing, manual controls | Advanced effects, automation, recall settings |
| Interface | Physical knobs and faders | Touchscreens, digital displays, physical controls |
| Portability | Generally bulkier, heavier | Compact, lighter, flexible setups |
| Price | Typically lower cost | Higher initial investment |
| Setup Complexity | Simple, intuitive | Requires learning digital interface |
| Recall & Presets | No recall, manual adjustments needed | Save and recall scene presets easily |
| Latency | Near-zero latency | Minimal latency, depends on processing |
| Maintenance | Analog components require regular upkeep | Software updates and less physical upkeep |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Mixers
Analog mixers use physical knobs, faders, and circuits to combine audio signals in real-time, delivering warmth and tactile control favored by many sound engineers. Digital mixers convert audio signals into digital data, allowing advanced features such as recallable presets, built-in effects, and remote control via software. The choice between analog and digital mixers depends on factors like workflow preferences, required features, and budget constraints.
Core Differences Between Analog and Digital Mixers
Analog mixers process audio signals through physical circuits, providing warm, natural sound with tactile control via knobs and faders. Digital mixers convert audio into digital data, offering advanced features like onboard effects, recallable settings, and flexible routing within compact hardware. Your choice depends on the need for hands-on simplicity versus versatile processing and integration capabilities.
Sound Quality Comparison: Analog vs Digital
Analog mixers deliver warm, natural sound characterized by continuous signal processing and subtle harmonic distortion favored in music production. Digital mixers provide precise, clear sound with extensive signal manipulation capabilities, offering consistent quality through advanced algorithms and digital signal processing (DSP). The choice between analog and digital mixers often depends on the desired tonal character and workflow preferences rather than pure sound quality differences.
Ease of Use: User Interface and Workflow
Analog mixers offer a tactile user interface with physical knobs and faders that provide immediate, intuitive control, allowing users to quickly adjust audio levels and effects by feel. Digital mixers feature touchscreen interfaces and customizable layouts that streamline workflow by enabling easy scene recalls, integration with DAWs, and advanced signal routing options. While analog mixers excel in hands-on simplicity, digital mixers enhance efficiency through flexible, software-driven control and automation capabilities.
Flexibility and Features: Analog vs Digital
Analog mixers offer straightforward, tactile controls with immediate access to all channels, making real-time manipulation intuitive, but they lack the extensive onboard processing features found in digital mixers. Digital mixers provide unmatched flexibility through customizable signal routing, built-in effects, and recallable presets, enabling you to tailor your sound environment efficiently for various live or studio settings. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hands-on simplicity or advanced, versatile functionality in audio mixing.
Portability and Space Considerations
Analog mixers are typically bulkier and heavier, making them less portable and requiring more space in your setup compared to digital mixers. Digital mixers offer compact designs that integrate multiple functions, reducing the need for extra equipment and optimizing your workspace. Choosing a digital mixer enhances portability and conserves valuable space without compromising audio quality.
Connectivity and Integration Options
Analog mixers offer straightforward connectivity with traditional XLR, TRS, and RCA inputs and outputs, supporting easy integration with classic audio gear and stage setups. Digital mixers provide extensive connectivity options including USB, Ethernet, and wireless, enabling seamless integration with DAWs, remote control apps, and networked audio systems. Advanced routing capabilities in digital mixers allow flexible signal paths and automation, making them ideal for complex live sound and recording environments.
Reliability and Maintenance Needs
Analog mixers offer unmatched reliability due to their straightforward circuitry and fewer software dependencies, making them less prone to glitches or crashes during live performances. Digital mixers, while feature-rich, require regular firmware updates and complex troubleshooting, which can increase maintenance time and costs. Your choice depends on the balance you seek between low-maintenance operation and advanced functionality.
Price and Value for Money
Analog mixers typically offer lower upfront costs compared to digital mixers, making them attractive for budget-conscious users seeking straightforward functionality. Digital mixers provide greater value for money over time through enhanced features like built-in effects, automation, and recallable presets, which reduce the need for external equipment and streamline workflow. Users prioritizing cost efficiency and expanded capabilities often find digital mixers deliver a stronger return on investment despite higher initial prices.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Needs
Choosing the right mixer depends on your workflow and sound preferences, with analog mixers offering intuitive tactile control and warm, natural sound ideal for live performances and quick adjustments. Digital mixers provide advanced features like built-in effects, recallable scenes, and compact integration, making them suitable for complex setups and studio environments. Evaluate factors such as budget, portability, signal routing flexibility, and required processing capabilities to determine the best fit for your audio production needs.
analog mixer vs digital mixer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com