Compensation capacitors are designed to improve the stability and frequency response of amplifiers by adjusting phase shift and gain, while bypass capacitors primarily filter out noise and provide a stable voltage supply by shunting AC signals to ground. Understanding the distinct roles of these capacitors can enhance your circuit design efficiency; continue reading to explore their specific applications and selection criteria.
Table of Comparison
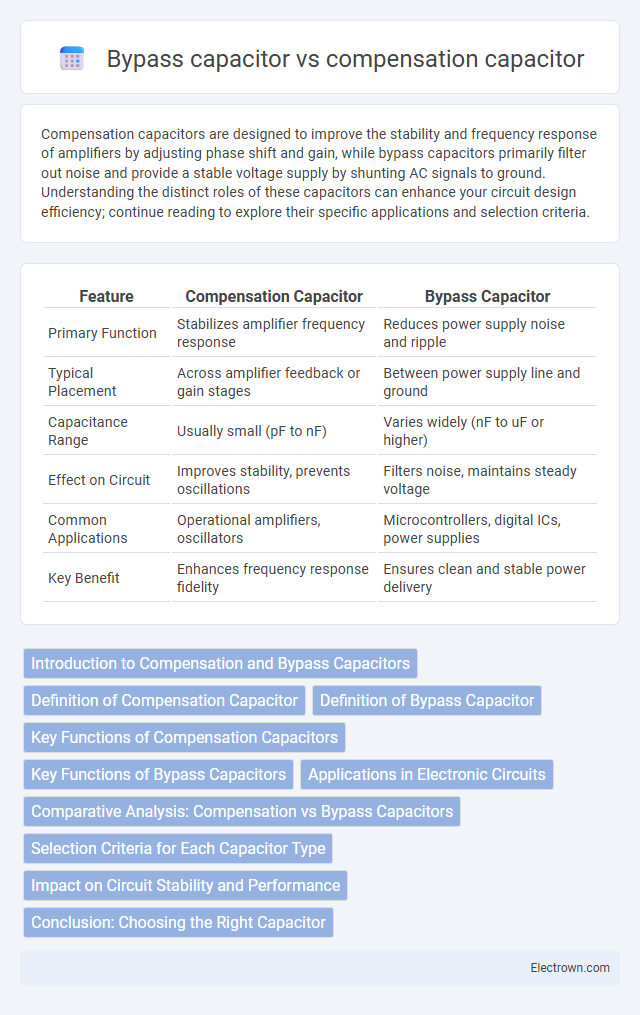
| Feature | Compensation Capacitor | Bypass Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Stabilizes amplifier frequency response | Reduces power supply noise and ripple |
| Typical Placement | Across amplifier feedback or gain stages | Between power supply line and ground |
| Capacitance Range | Usually small (pF to nF) | Varies widely (nF to uF or higher) |
| Effect on Circuit | Improves stability, prevents oscillations | Filters noise, maintains steady voltage |
| Common Applications | Operational amplifiers, oscillators | Microcontrollers, digital ICs, power supplies |
| Key Benefit | Enhances frequency response fidelity | Ensures clean and stable power delivery |
Introduction to Compensation and Bypass Capacitors
Compensation capacitors are designed to stabilize frequency response and improve the phase margin in amplifier circuits, minimizing distortion and enhancing signal integrity. Bypass capacitors provide a low impedance path to ground for AC signals, reducing noise and voltage fluctuations in power supply lines. Both capacitors play crucial roles in optimizing circuit performance but serve distinct functions targeted at frequency compensation and noise suppression respectively.
Definition of Compensation Capacitor
A compensation capacitor is an electronic component used in amplifier circuits to enhance frequency response and stability by counteracting phase shifts and unwanted feedback. It differs from a bypass capacitor, which primarily filters out noise and stabilizes voltage supply by providing a low impedance path to ground for AC signals. Compensation capacitors are critical in fine-tuning the gain and preventing oscillations in high-frequency applications.
Definition of Bypass Capacitor
A bypass capacitor is an electronic component used to shunt noise and unwanted AC signals from power lines to ground, providing a clean and stable DC voltage for active devices. Unlike compensation capacitors, which adjust frequency response or phase in circuits, bypass capacitors primarily enhance power supply stability and reduce voltage fluctuations by placing them close to integrated circuits or transistors. Commonly found in decoupling applications, bypass capacitors typically have low-value capacitance ranging from picofarads to microfarads.
Key Functions of Compensation Capacitors
Compensation capacitors play a critical role in stabilizing operational amplifiers by controlling the frequency response and preventing unwanted oscillations in analog circuits. Unlike bypass capacitors, which primarily filter noise and provide a low impedance path to ground for high-frequency signals, compensation capacitors adjust the phase margin and improve the overall gain bandwidth product. Your circuit's performance and stability depend on properly selecting these capacitors to ensure optimal transient response and prevent signal distortion.
Key Functions of Bypass Capacitors
Bypass capacitors primarily serve to stabilize voltage supply by filtering out high-frequency noise and providing a low-impedance path to ground for transient signals. They improve circuit performance and reliability by protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes and electromagnetic interference. Your electronic circuits benefit from enhanced signal integrity and reduced power supply fluctuations when using bypass capacitors.
Applications in Electronic Circuits
Compensation capacitors are primarily used in amplifier circuits to stabilize frequency response and improve phase margin, ensuring reliable operation in high-frequency and feedback applications. Bypass capacitors serve to reduce noise and voltage fluctuations by providing a low-impedance path to ground, crucial in power supply filtering and digital circuit performance. You can optimize circuit stability and signal integrity by selecting the appropriate capacitor type based on your specific electronic application needs.
Comparative Analysis: Compensation vs Bypass Capacitors
Compensation capacitors are designed to shape frequency response and stabilize amplifier circuits by adjusting phase and gain to prevent oscillations, while bypass capacitors primarily filter out noise and provide a low impedance path to ground for AC signals, enhancing power supply stability. The compensation capacitor typically influences the feedback loop and signal integrity, whereas the bypass capacitor is placed close to power pins to reduce voltage fluctuations and improve overall circuit performance. Your choice between these capacitors depends on the specific role in circuit design--whether controlling frequency behavior or minimizing supply noise.
Selection Criteria for Each Capacitor Type
Selection criteria for compensation capacitors focus on precise tuning to stabilize amplifier frequency response and improve phase margin, requiring capacitors with low dielectric absorption and tight tolerance. Bypass capacitors are selected based on their ability to reduce high-frequency noise and ripple in power supply lines, favoring low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) types like ceramic capacitors for effective decoupling. Your choice depends on whether the goal is signal integrity enhancement or power supply noise suppression in the circuit design.
Impact on Circuit Stability and Performance
Compensation capacitors improve circuit stability by shaping frequency response and reducing phase shift, which prevents oscillations in operational amplifiers. Bypass capacitors enhance performance by filtering out high-frequency noise and providing a low-impedance path to ground, stabilizing power supply voltages. Proper selection and placement of these capacitors are crucial to maintain optimal circuit stability and signal integrity in analog and digital applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Capacitor
Choosing the right capacitor depends on your circuit's specific needs, as compensation capacitors stabilize feedback loops to enhance amplifier performance, while bypass capacitors filter out noise and stabilize voltage supply lines. Compensation capacitors are typically used in high-frequency or feedback-sensitive applications, whereas bypass capacitors are essential for reducing power supply ripple and improving signal integrity. Understanding the functional differences ensures your design achieves optimal stability and noise reduction.
Compensation capacitor vs bypass capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com