A constant current source delivers a fixed current regardless of the voltage across its terminals, ensuring stable current flow in circuits sensitive to current variations, while a constant voltage source maintains a steady voltage output regardless of the load current, ideal for powering devices requiring consistent voltage levels. Understanding the differences between these two sources can help you choose the right power supply for your electronic projects; read on to explore their applications, advantages, and practical considerations.
Table of Comparison
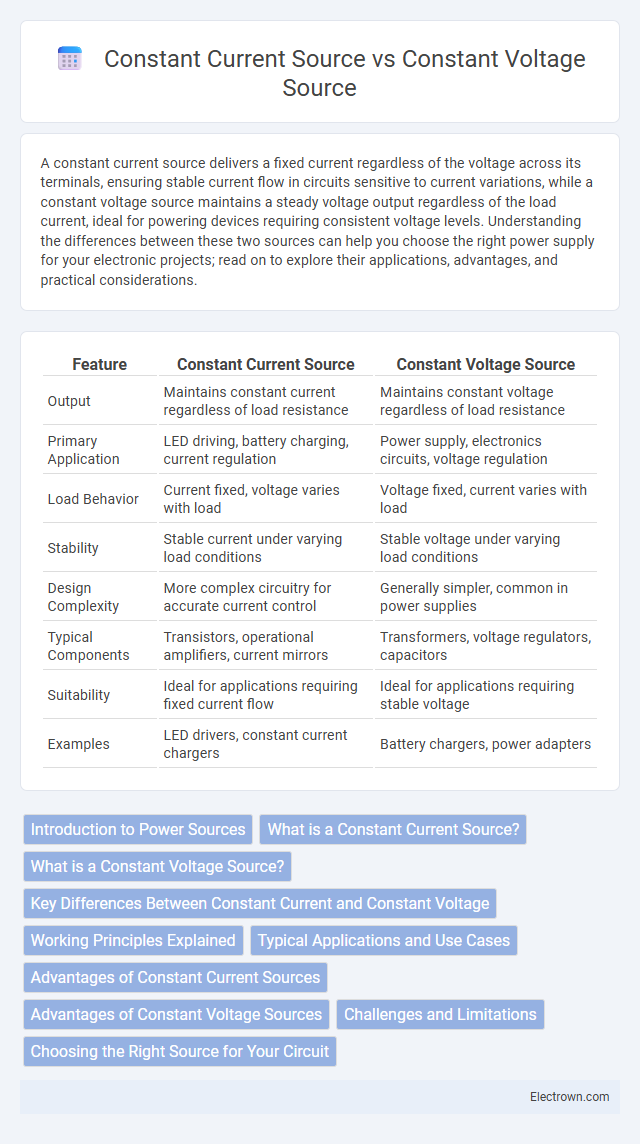
| Feature | Constant Current Source | Constant Voltage Source |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Maintains constant current regardless of load resistance | Maintains constant voltage regardless of load resistance |
| Primary Application | LED driving, battery charging, current regulation | Power supply, electronics circuits, voltage regulation |
| Load Behavior | Current fixed, voltage varies with load | Voltage fixed, current varies with load |
| Stability | Stable current under varying load conditions | Stable voltage under varying load conditions |
| Design Complexity | More complex circuitry for accurate current control | Generally simpler, common in power supplies |
| Typical Components | Transistors, operational amplifiers, current mirrors | Transformers, voltage regulators, capacitors |
| Suitability | Ideal for applications requiring fixed current flow | Ideal for applications requiring stable voltage |
| Examples | LED drivers, constant current chargers | Battery chargers, power adapters |
Introduction to Power Sources
Constant current sources regulate the flow of electrical current to maintain a steady current regardless of load changes, making them ideal for applications like LED lighting or battery charging. Constant voltage sources maintain a fixed voltage output even when the load varies, which is essential for devices such as power supplies in electronics or household appliances. Understanding your power source type ensures optimal performance and protects your electronic components from damage caused by improper current or voltage levels.
What is a Constant Current Source?
A constant current source is an electronic circuit or device designed to deliver a steady and unchanging electric current to a load regardless of changes in voltage or resistance. It regulates current flow precisely, ensuring the current remains stable even when the load varies, making it essential in applications such as LED driving, battery charging, and sensor excitation. This contrasts with constant voltage sources, which maintain a fixed voltage level but allow current to fluctuate depending on the load.
What is a Constant Voltage Source?
A constant voltage source maintains a fixed voltage level across its terminals regardless of changes in the load or current drawn from it, ensuring stable voltage supply in electrical circuits. It is commonly used in power supplies and battery chargers where consistent voltage is critical for device operation and safety. Unlike a constant current source, which regulates current, a constant voltage source adjusts output current to preserve a predetermined voltage value.
Key Differences Between Constant Current and Constant Voltage
A constant current source delivers a fixed current regardless of load resistance, ensuring stable current flow for applications like LED driving or battery charging. In contrast, a constant voltage source provides a steady voltage output, adjusting current based on load changes, commonly used in power supplies and electronics. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right source for maintaining reliable performance and preventing damage in your electrical circuits.
Working Principles Explained
A constant current source regulates the current flowing through a circuit regardless of voltage fluctuations by adjusting its output voltage to maintain a fixed current level. In contrast, a constant voltage source maintains a steady output voltage despite changes in load resistance, allowing the current to vary accordingly. Both sources use feedback mechanisms and control circuitry to dynamically adapt their outputs, ensuring either current or voltage stability based on application requirements.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Constant current sources are typically used in LED driving, battery charging, and electroplating applications where maintaining a stable current is crucial for consistent performance and safety. Constant voltage sources are preferred in power supply units, electronic device operation, and battery-powered systems where a fixed voltage level ensures reliable device operation and protects components. Your choice between these sources depends on whether current regulation or voltage regulation is critical for your specific application requirements.
Advantages of Constant Current Sources
Constant current sources provide stable and precise current regardless of load resistance variations, making them ideal for applications like LED driving and battery charging where consistent current is crucial. You benefit from enhanced device protection because constant current sources prevent overcurrent conditions that can damage sensitive components. Their ability to maintain current stability results in improved performance and extended lifespan of electronic circuits.
Advantages of Constant Voltage Sources
Constant voltage sources maintain a stable voltage output regardless of load variations, ensuring consistent performance in electronic circuits and devices. They protect sensitive components by preventing voltage fluctuations that could cause damage or malfunction. Your applications benefit from reliable power delivery, making constant voltage sources ideal for powering LEDs, batteries, and other electronic equipment requiring steady voltage.
Challenges and Limitations
Constant current sources face challenges in maintaining a stable output under varying load conditions, often requiring complex feedback mechanisms to avoid overheating or efficiency loss. Constant voltage sources struggle with voltage drops and regulation issues when driving non-linear or fluctuating loads, which can lead to performance degradation or device damage. Both sources have limitations related to power dissipation and stability, necessitating careful design considerations for reliable operation in real-world applications.
Choosing the Right Source for Your Circuit
Choosing the right source for your circuit depends on whether you need to maintain a stable current or a stable voltage. A constant current source delivers a fixed current regardless of load changes, ideal for LED driving or battery charging applications, while a constant voltage source maintains a steady voltage output, suitable for powering most electronic devices and circuits. Understanding your circuit's requirements ensures that you select a source that optimizes performance and prevents damage.
constant current source vs constant voltage source Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com