Isolation amplifiers provide electrical isolation between input and output while measuring signals, protecting your system from high voltages and noise interference. Differential amplifiers accurately amplify the difference between two input signals without isolation, crucial for noise reduction in sensitive measurements; explore the rest of the article to understand which amplifier suits your application best.
Table of Comparison
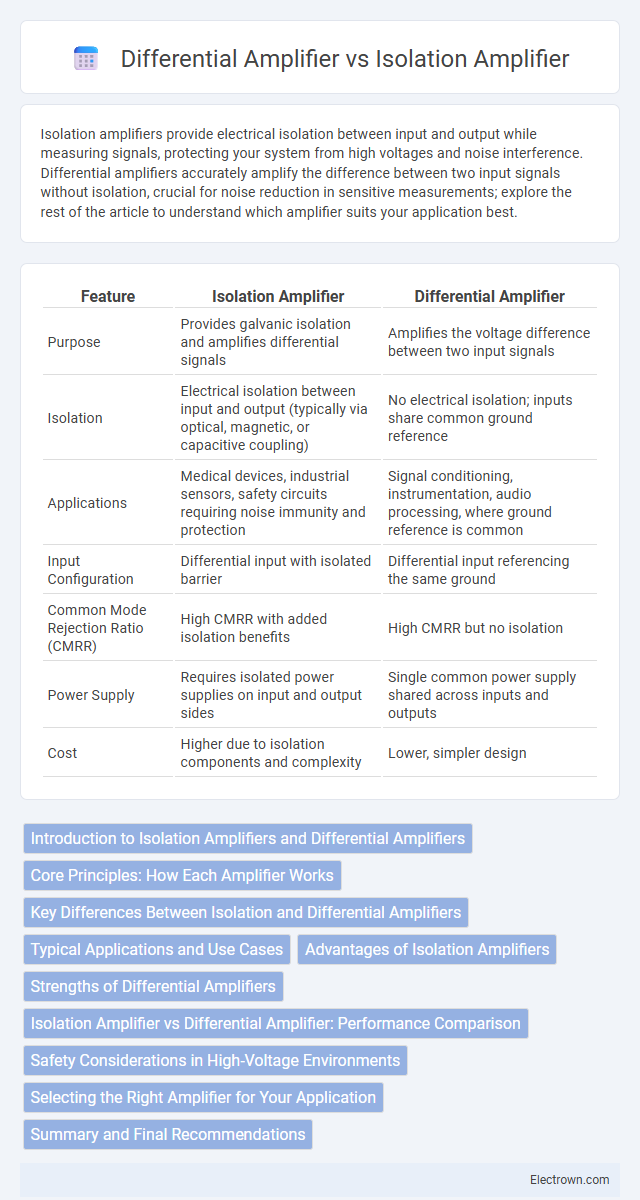
| Feature | Isolation Amplifier | Differential Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides galvanic isolation and amplifies differential signals | Amplifies the voltage difference between two input signals |
| Isolation | Electrical isolation between input and output (typically via optical, magnetic, or capacitive coupling) | No electrical isolation; inputs share common ground reference |
| Applications | Medical devices, industrial sensors, safety circuits requiring noise immunity and protection | Signal conditioning, instrumentation, audio processing, where ground reference is common |
| Input Configuration | Differential input with isolated barrier | Differential input referencing the same ground |
| Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) | High CMRR with added isolation benefits | High CMRR but no isolation |
| Power Supply | Requires isolated power supplies on input and output sides | Single common power supply shared across inputs and outputs |
| Cost | Higher due to isolation components and complexity | Lower, simpler design |
Introduction to Isolation Amplifiers and Differential Amplifiers
Isolation amplifiers provide galvanic isolation between input and output, eliminating ground loops and enhancing signal integrity in noisy industrial environments. Differential amplifiers amplify the voltage difference between two input signals while rejecting common-mode noise, making them essential for accurate low-level signal measurements. Both play crucial roles in signal conditioning but differ primarily in isolation capability and application scenarios.
Core Principles: How Each Amplifier Works
Isolation amplifiers use galvanic isolation to separate input and output signals, often employing transformers or optical couplers to prevent ground loops and protect against high voltages. Differential amplifiers measure the voltage difference between two input terminals without reference to ground, amplifying the signal while rejecting common-mode noise. Your choice depends on whether electrical isolation or precise differential measurement is the primary requirement.
Key Differences Between Isolation and Differential Amplifiers
Isolation amplifiers provide galvanic isolation between input and output, preventing ground loops and enhancing noise immunity, making them ideal for high-voltage or medical applications. Differential amplifiers amplify the voltage difference between two input signals without isolation, offering high common-mode rejection but lacking protection against ground potential differences. Key differences include isolation capability, safety features, and typical use cases, with isolation amplifiers suited for signal integrity in noisy environments.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Isolation amplifiers are commonly used in medical instrumentation, industrial process control, and high-voltage measurement to prevent ground loops and ensure patient safety by providing galvanic isolation. Differential amplifiers excel in audio signal processing, sensor signal conditioning, and communication systems by accurately amplifying the voltage difference between two input signals while rejecting common-mode noise. Selecting between the two depends on the need for electrical isolation or precise differential signal amplification in applications such as ECG machines for isolation amplifiers and operational amplifiers in data acquisition systems for differential amplifiers.
Advantages of Isolation Amplifiers
Isolation amplifiers provide excellent galvanic isolation, protecting your measurement system from high voltages and ground loops, which enhances safety and signal integrity. They effectively eliminate noise and common-mode interference, resulting in more accurate and stable signal transmission in harsh industrial environments. Their ability to isolate and amplify weak signals makes them ideal for medical, industrial, and instrumentation applications where precision and safety are critical.
Strengths of Differential Amplifiers
Differential amplifiers excel at rejecting common-mode noise and interference, making them ideal for precise signal measurements in noisy environments. Their high input impedance and ability to amplify the voltage difference between two signals improve accuracy and stability in applications such as sensor signal conditioning and instrumentation. This performance advantage supports enhanced signal integrity and reliable data acquisition in various electronic systems.
Isolation Amplifier vs Differential Amplifier: Performance Comparison
Isolation amplifiers provide galvanic isolation, effectively eliminating ground loops and enhancing safety in high-voltage or noisy environments, unlike differential amplifiers that only amplify the voltage difference without isolation. Differential amplifiers excel in accurately measuring small differential signals amidst common-mode noise but may suffer from interference if common-mode voltages exceed their rejection capabilities. The choice between isolation and differential amplifiers depends on application requirements such as noise immunity, signal integrity, and electrical isolation needs.
Safety Considerations in High-Voltage Environments
Isolation amplifiers provide essential galvanic isolation, protecting you and sensitive equipment from high-voltage surges and electrical noise, which is critical in hazardous environments. Differential amplifiers measure voltage differences directly but lack isolation, increasing the risk of damage or injury in high-voltage applications. Choosing an isolation amplifier enhances safety compliance by preventing ground loops and minimizing fault current paths in high-voltage measurement systems.
Selecting the Right Amplifier for Your Application
Selecting the right amplifier for your application depends on the need for signal integrity and electrical isolation. Isolation amplifiers provide galvanic isolation, protecting sensitive equipment from high voltages and ground loops, making them ideal for medical devices and industrial sensors. Differential amplifiers offer precise measurement of voltage differences between two inputs without isolation, suitable for low-noise, balanced signal environments.
Summary and Final Recommendations
Isolation amplifiers provide galvanic isolation, preventing ground loops and protecting sensitive circuits from high voltages, making them ideal for medical and industrial applications. Differential amplifiers excel in accurately measuring small differential signals in noisy environments but lack isolation features. For your application, choose isolation amplifiers when electrical isolation and safety are critical, while differential amplifiers suit scenarios demanding precise signal amplification without the need for isolation.
isolation amplifier vs differential amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com