Single-ended inputs measure voltage with respect to a common ground, making them simpler but more susceptible to noise and interference. Differential inputs compare the voltage difference between two signals, offering better noise rejection and improved signal integrity--read on to discover which input type suits Your application best.
Table of Comparison
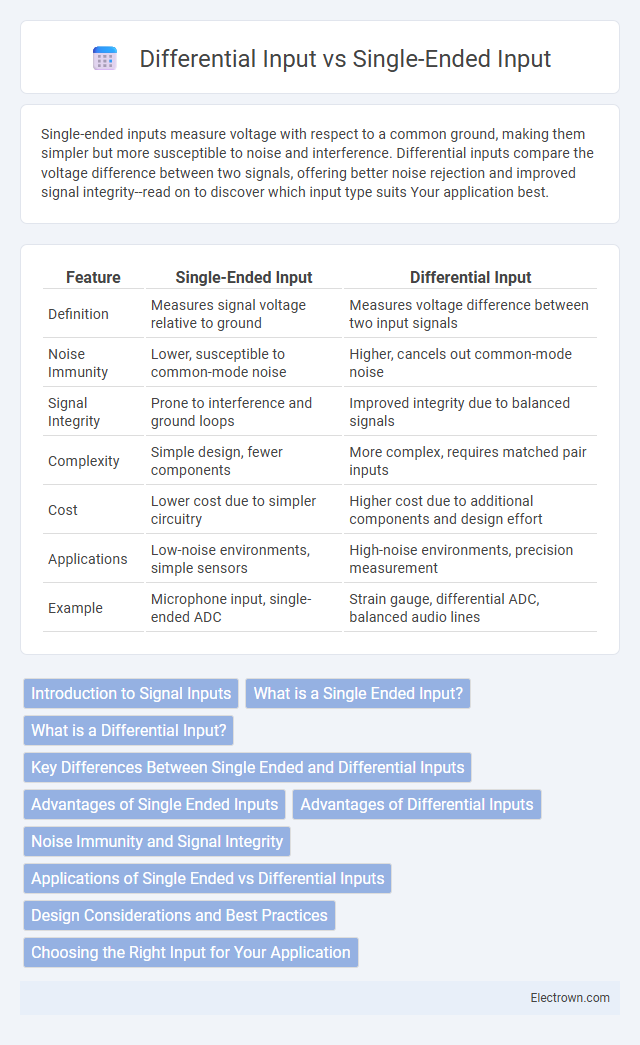
| Feature | Single-Ended Input | Differential Input |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures signal voltage relative to ground | Measures voltage difference between two input signals |
| Noise Immunity | Lower, susceptible to common-mode noise | Higher, cancels out common-mode noise |
| Signal Integrity | Prone to interference and ground loops | Improved integrity due to balanced signals |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex, requires matched pair inputs |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler circuitry | Higher cost due to additional components and design effort |
| Applications | Low-noise environments, simple sensors | High-noise environments, precision measurement |
| Example | Microphone input, single-ended ADC | Strain gauge, differential ADC, balanced audio lines |
Introduction to Signal Inputs
Signal inputs can be categorized into single-ended and differential types, each affecting noise immunity and signal integrity differently. Single-ended inputs measure voltage relative to a common ground, making them more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and ground noise. Differential inputs compare the voltage difference between two signals, enhancing noise rejection and improving accuracy in electrically noisy environments.
What is a Single Ended Input?
A single ended input measures voltage referenced to a common ground, using one input signal line while the other is connected to ground. This input type is simpler and more cost-effective but is more susceptible to noise and interference in electrically noisy environments. Single ended inputs are commonly found in applications like audio equipment and basic analog measurements where signal integrity requirements are moderate.
What is a Differential Input?
A differential input measures the voltage difference between two input terminals, rejecting common-mode noise and interference present on both lines. This configuration enhances signal integrity and improves noise immunity, making it ideal for precision measurements and communication systems. Differential inputs are widely used in operational amplifiers, instrumentation amplifiers, and balanced audio equipment to ensure accurate signal processing.
Key Differences Between Single Ended and Differential Inputs
Single-ended inputs measure voltage referenced to a common ground, making them more susceptible to noise and interference in electrically noisy environments. Differential inputs compare the voltage between two signal lines, effectively rejecting common-mode interference and enhancing signal integrity. This fundamental disparity results in differential inputs offering improved noise immunity and accuracy, especially in high-precision or long-distance signal transmission applications.
Advantages of Single Ended Inputs
Single ended inputs offer simplicity in design and lower cost due to requiring fewer components and connections compared to differential inputs. They are effective in applications where noise interference is minimal, making them suitable for straightforward signal processing tasks. Your system benefits from reduced complexity and easier implementation when using single ended inputs in low-noise environments.
Advantages of Differential Inputs
Differential inputs provide improved noise immunity by rejecting common-mode signals, making them ideal for environments with electrical interference. They enhance signal integrity and accuracy by measuring the voltage difference between two input lines rather than referencing a single ground. This configuration reduces susceptibility to ground loops and electromagnetic interference, ensuring more reliable data acquisition and measurement.
Noise Immunity and Signal Integrity
Differential inputs provide superior noise immunity and signal integrity compared to single-ended inputs because they measure voltage differences between two lines, effectively canceling out common-mode noise. Single-ended inputs are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and ground loop noise, which can degrade signal quality, especially over long distances. Your choice between these input types significantly impacts the performance and reliability of sensitive electronic measurements in noisy environments.
Applications of Single Ended vs Differential Inputs
Single-ended inputs are commonly used in applications like audio equipment, sensor measurements, and low-cost instrumentation where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities. Differential inputs excel in environments with high electrical noise, such as industrial automation, data acquisition systems, and communication interfaces, by rejecting common-mode interference and improving signal integrity. Your choice between single-ended and differential inputs depends on the noise environment and accuracy requirements of your specific application.
Design Considerations and Best Practices
Single-ended inputs measure voltage referenced to a common ground, making them simpler but more susceptible to noise and interference, especially in electrically noisy environments. Differential inputs compare the voltage difference between two signals, offering superior noise rejection, improved signal integrity, and better performance in long-distance or high-speed applications. When designing your system, prioritize differential input configurations for environments with high electromagnetic interference and consider proper PCB layout, shielding, and grounding techniques to maximize signal quality and minimize noise in both input types.
Choosing the Right Input for Your Application
Selecting between single-ended and differential inputs depends on signal integrity requirements and noise environment; single-ended inputs are suitable for low-noise, short-distance signals, while differential inputs offer superior noise rejection and are ideal for long-distance or electrically noisy conditions. Differential inputs use two complementary signals to cancel out common-mode noise, enhancing accuracy in sensitive measurements. Application-specific factors such as cable length, electromagnetic interference, and required resolution guide the optimal input type choice.
single ended vs differential input Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com