A hysteresis comparator includes positive feedback to create different threshold levels for switching, reducing noise and providing stable output, while a window comparator uses two comparators to detect if an input voltage falls within a predefined range or window. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right comparator for your specific circuit needs; read on to explore their applications and advantages in detail.
Table of Comparison
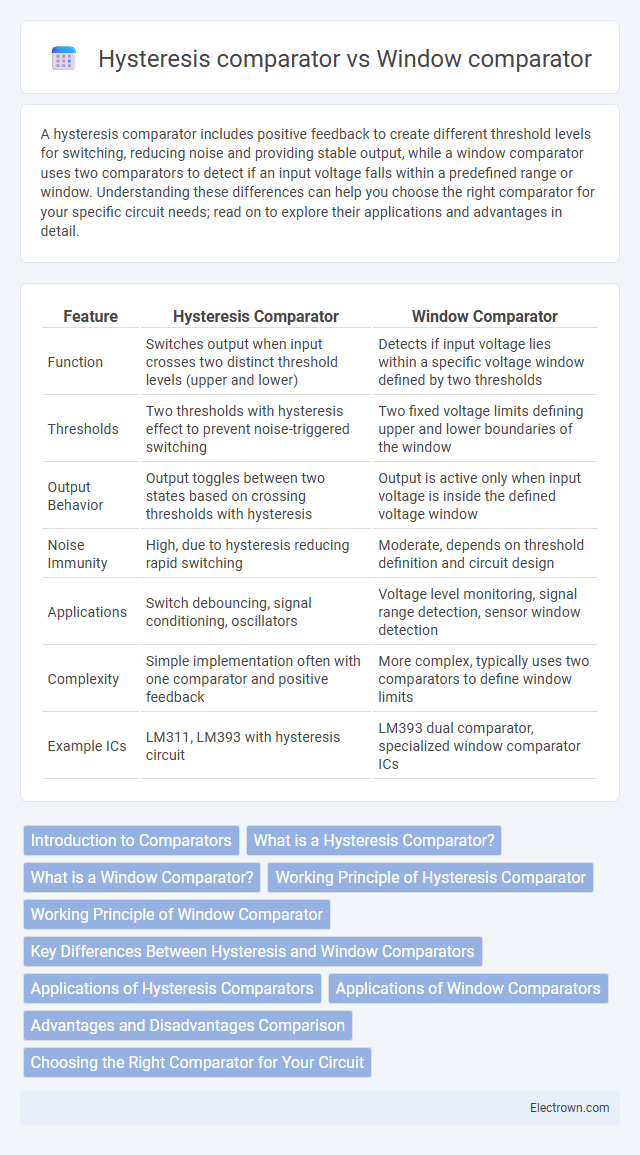
| Feature | Hysteresis Comparator | Window Comparator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Switches output when input crosses two distinct threshold levels (upper and lower) | Detects if input voltage lies within a specific voltage window defined by two thresholds |
| Thresholds | Two thresholds with hysteresis effect to prevent noise-triggered switching | Two fixed voltage limits defining upper and lower boundaries of the window |
| Output Behavior | Output toggles between two states based on crossing thresholds with hysteresis | Output is active only when input voltage is inside the defined voltage window |
| Noise Immunity | High, due to hysteresis reducing rapid switching | Moderate, depends on threshold definition and circuit design |
| Applications | Switch debouncing, signal conditioning, oscillators | Voltage level monitoring, signal range detection, sensor window detection |
| Complexity | Simple implementation often with one comparator and positive feedback | More complex, typically uses two comparators to define window limits |
| Example ICs | LM311, LM393 with hysteresis circuit | LM393 dual comparator, specialized window comparator ICs |
Introduction to Comparators
Comparators are essential analog devices that compare input voltages and output a digital signal indicating which is higher. A hysteresis comparator incorporates positive feedback to create two distinct threshold voltages, reducing noise and preventing rapid switching. In contrast, a window comparator uses two comparators to define an upper and lower voltage limit, allowing Your circuit to detect when an input voltage falls within a specific range.
What is a Hysteresis Comparator?
A hysteresis comparator is an electronic circuit designed to provide stable switching output by incorporating two distinct threshold voltage levels: an upper and a lower threshold. This dual-threshold feature prevents rapid toggling or noise-induced fluctuations when the input voltage hovers near the switching point, enhancing signal reliability. Unlike a window comparator, which detects when an input voltage falls within a specific range, a hysteresis comparator focuses on eliminating output chatter by maintaining output state until the input crosses defined hysteresis limits.
What is a Window Comparator?
A window comparator is an electronic circuit designed to detect whether an input signal falls within a specific voltage range, defined by two reference thresholds called the upper and lower limits. It outputs a high signal only when the input voltage lies between these predefined boundaries, making it ideal for applications requiring voltage level monitoring and fault detection. Unlike a hysteresis comparator, which provides noise immunity through positive feedback to avoid rapid switching, a window comparator strictly focuses on defining and sensing a voltage "window" for precise operation.
Working Principle of Hysteresis Comparator
A hysteresis comparator operates by incorporating positive feedback to create two distinct voltage thresholds, known as the upper and lower trigger points, which prevent output oscillations in noisy signals. It switches its output state only when the input voltage crosses these set threshold levels, thus providing noise immunity and stable switching behavior. This operation contrasts with a window comparator that detects whether an input voltage lies within or outside a specified voltage range without hysteresis.
Working Principle of Window Comparator
A window comparator operates by using two voltage thresholds--an upper and a lower limit--to determine whether an input voltage lies within a specific range or "window." It outputs a signal indicating if the input voltage is inside or outside this predefined voltage range. The device typically involves two comparators, each comparing the input voltage to one of the thresholds, creating a stable and noise-immune detection region between the thresholds.
Key Differences Between Hysteresis and Window Comparators
Hysteresis comparators use two different threshold voltages to prevent noise from causing false triggering, providing stable switching behavior in noisy environments. Window comparators consist of two threshold levels that define a voltage range, allowing output signals to indicate whether an input voltage lies within that specific range. Your choice depends on whether you need noise immunity with a single switching action or precise detection within a voltage window.
Applications of Hysteresis Comparators
Hysteresis comparators are extensively used in applications requiring noise immunity and stable switching, such as in oscillators, Schmitt triggers, and temperature control systems. They prevent rapid toggling of output due to small input signal fluctuations, making them ideal for signal conditioning and sensor interface circuits. Compared to window comparators, hysteresis comparators provide enhanced stability in environments with noisy or slowly varying input signals.
Applications of Window Comparators
Window comparators are widely used in applications requiring voltage monitoring within a specific range, such as battery level detection, sensor signal validation, and overvoltage/undervoltage protection circuits. They provide precise control by generating an output only when an input voltage falls inside or outside a predefined voltage window, enhancing system reliability in embedded systems and analog signal processing. Common uses include level detectors in power supplies, fault detection in industrial automation, and threshold monitoring in medical devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
Hysteresis comparators offer noise immunity and stable switching by incorporating positive feedback, reducing false triggering in noisy signals, but they have a fixed threshold range limiting sensitivity adjustments. Window comparators detect if an input falls within a specific voltage range with high precision, enabling precise level detection, yet they consume more power and may introduce complexity in circuit design. Choosing between them depends on the need for noise resilience versus precise range detection in applications.
Choosing the Right Comparator for Your Circuit
Selecting the right comparator for your circuit hinges on application requirements such as noise immunity and voltage threshold detection. A hysteresis comparator excels in eliminating output chatter in noisy environments by incorporating positive feedback, creating distinct upper and lower switching thresholds. Window comparators, in contrast, detect when an input voltage falls within a specific range, making them ideal for level monitoring and control tasks demanding precise voltage window detection.
Hysteresis comparator vs window comparator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com