A passive radiator subwoofer uses a diaphragm to enhance bass response without the air noise typically associated with ported subwoofers, offering deeper and cleaner low-frequency sound. Discover how choosing the right design can significantly improve Your home audio experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
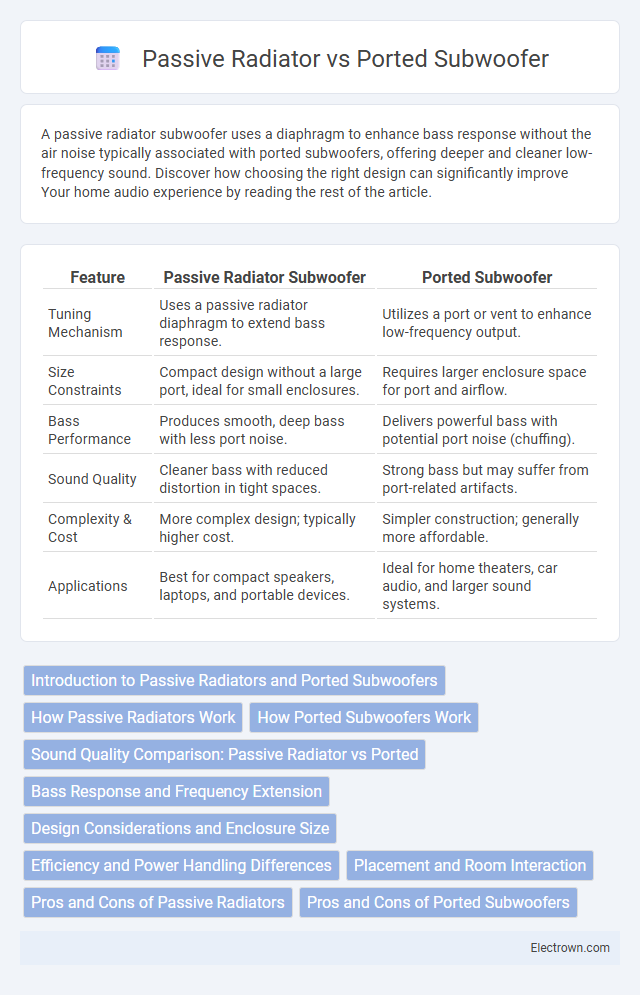
| Feature | Passive Radiator Subwoofer | Ported Subwoofer |
|---|---|---|
| Tuning Mechanism | Uses a passive radiator diaphragm to extend bass response. | Utilizes a port or vent to enhance low-frequency output. |
| Size Constraints | Compact design without a large port, ideal for small enclosures. | Requires larger enclosure space for port and airflow. |
| Bass Performance | Produces smooth, deep bass with less port noise. | Delivers powerful bass with potential port noise (chuffing). |
| Sound Quality | Cleaner bass with reduced distortion in tight spaces. | Strong bass but may suffer from port-related artifacts. |
| Complexity & Cost | More complex design; typically higher cost. | Simpler construction; generally more affordable. |
| Applications | Best for compact speakers, laptops, and portable devices. | Ideal for home theaters, car audio, and larger sound systems. |
Introduction to Passive Radiators and Ported Subwoofers
Passive radiators utilize an unpowered diaphragm that moves in response to the air pressure inside the speaker enclosure, enhancing low-frequency response without the noise associated with port turbulence. Ported subwoofers feature a tuned bass reflex port that allows air to escape from the enclosure, extending bass output by reinforcing specific low-frequency bands. Both designs aim to improve bass performance, but passive radiators often offer more compact enclosures and reduced port noise compared to traditional ported subwoofers.
How Passive Radiators Work
Passive radiators operate by using a woofer cone to transfer air pressure, causing the passive radiator diaphragm to move and produce sound without the need for a traditional port. This design reduces port noise and enhances low-frequency response in compact subwoofer enclosures. Your choice between a passive radiator and a ported subwoofer depends on desired sound quality and enclosure size.
How Ported Subwoofers Work
Ported subwoofers use a tuned enclosure with a port or vent that enhances bass output by allowing the sound from the rear side of the speaker cone to combine with the front, increasing efficiency and extending low-frequency response. This design reduces distortion and improves overall bass clarity by using the air in the port to reinforce deep bass notes. When selecting a subwoofer, understanding how ported systems work can help you achieve powerful and precise low-end sound in your audio setup.
Sound Quality Comparison: Passive Radiator vs Ported
Passive radiators offer tighter, more accurate bass with reduced port noise compared to ported subwoofers, delivering a cleaner and more controlled low-frequency response. Ported subwoofers typically produce louder output and extended bass but can introduce port turbulence and distortion at higher volumes. Your choice impacts sound quality, with passive radiators favored for precision and ported designs preferred for maximum bass extension.
Bass Response and Frequency Extension
Passive radiators enhance bass response by reducing port noise and providing deeper, punchier low frequencies without the chuffing sounds typical of ported subwoofers. Ported subwoofers achieve extended frequency response by using a tuned port to reinforce bass output, but they may suffer from port turbulence at high volumes. The choice between passive radiator and ported designs impacts the clarity and extension of bass, with passive radiators generally delivering smoother lows and ported subs offering higher efficiency at specific tuning frequencies.
Design Considerations and Enclosure Size
Passive radiators require precise tuning of mass and compliance for optimal performance, allowing smaller enclosure sizes compared to ported subwoofers. Ported subwoofers rely on a tuned vent to enhance bass response but often need larger enclosures to accommodate the port length and prevent air turbulence. Your choice depends on space constraints and desired bass characteristics, with passive radiators offering compact designs and ported subwoofers delivering higher efficiency at lower frequencies.
Efficiency and Power Handling Differences
Passive radiator subwoofers generally offer higher efficiency by reducing port noise and distortion, allowing for cleaner bass output at similar power levels compared to ported designs. Ported subwoofers, while capable of handling higher power inputs due to their vented design, often experience turbulence and port chuffing that can reduce overall efficiency. The passive radiator absorbs pressure fluctuations without port noise, resulting in better transient response and improved power handling efficiency in compact enclosures.
Placement and Room Interaction
Passive radiators require more flexible placement options since they don't rely on airflow through ports, allowing you to position your subwoofer without worrying about port noise or obstructions. Ported subwoofers depend on optimal placement to prevent port turbulence and maximize low-frequency output, often needing space away from walls or corners to avoid boomy bass. Your room's acoustics will influence the effectiveness of both designs, but passive radiators typically interact with the room more naturally, providing smoother bass response in tighter spaces.
Pros and Cons of Passive Radiators
Passive radiators enhance subwoofer performance by reducing port noise and tuning the enclosure for deeper bass without increasing size, making them ideal for compact systems. They do not require an additional amplifier, which simplifies setup and lowers power consumption, but their design complexity and cost can be higher compared to traditional ported subwoofers. Your choice depends on prioritizing quieter, tighter bass response versus affordability and straightforward construction.
Pros and Cons of Ported Subwoofers
Ported subwoofers offer enhanced bass output and improved efficiency by utilizing a tuned enclosure with a port to reinforce low frequencies, resulting in deeper and louder bass compared to sealed designs. However, ported designs can introduce port noise or "chuffing," and may sacrifice some accuracy and tightness in bass reproduction, making them less ideal for critical listening environments. Their larger cabinet size is necessary to accommodate the port, which can be a disadvantage for space-constrained setups.
passive radiator vs ported subwoofer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com