Active speakers engage their audience through dynamic, confident language that fosters connection and clarity, while passive speakers often convey messages indirectly, which can lead to misunderstandings or disengagement. Discover how mastering the balance between active and passive communication can enhance Your speaking skills by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
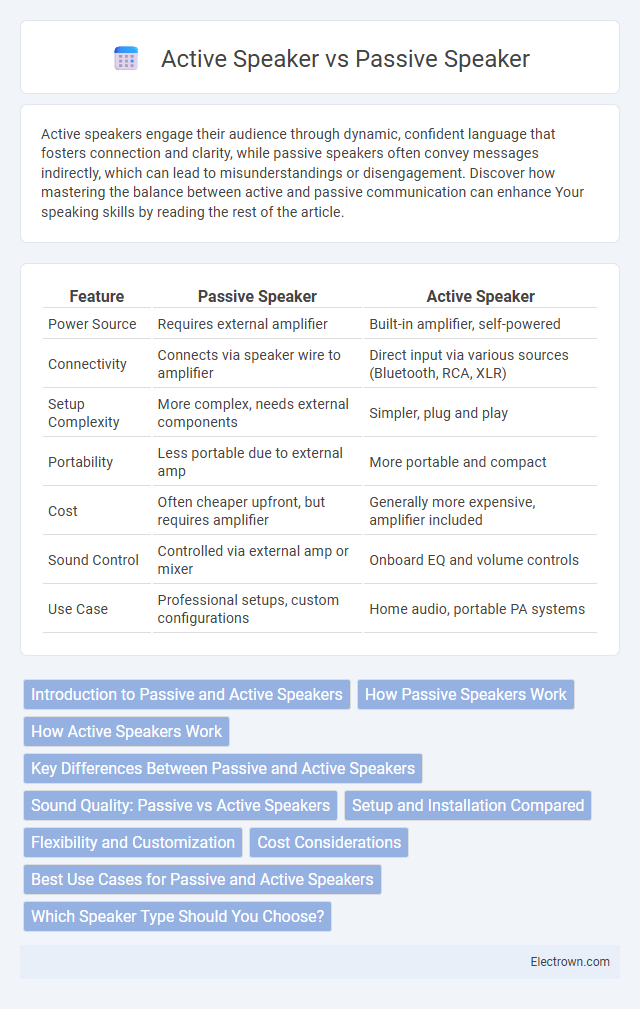
| Feature | Passive Speaker | Active Speaker |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Requires external amplifier | Built-in amplifier, self-powered |
| Connectivity | Connects via speaker wire to amplifier | Direct input via various sources (Bluetooth, RCA, XLR) |
| Setup Complexity | More complex, needs external components | Simpler, plug and play |
| Portability | Less portable due to external amp | More portable and compact |
| Cost | Often cheaper upfront, but requires amplifier | Generally more expensive, amplifier included |
| Sound Control | Controlled via external amp or mixer | Onboard EQ and volume controls |
| Use Case | Professional setups, custom configurations | Home audio, portable PA systems |
Introduction to Passive and Active Speakers
Passive speakers understand a language through listening and reading but rarely engage in speaking or writing, limiting their productive skills. Active speakers demonstrate proficiency by actively using the language in conversations, presentations, and writing tasks. This distinction highlights the importance of balancing receptive and productive language skills for effective communication.
How Passive Speakers Work
Passive speakers operate by utilizing built-in amplifiers, which take audio signals from an external source and convert them into sound without requiring an external amplifier. These speakers contain internal circuitry that amplifies the signal directly, simplifying setup and reducing additional equipment needs. This design allows passive speakers to provide consistent sound quality while being easier to integrate into various audio systems.
How Active Speakers Work
Active speakers contain built-in amplifiers that power the speaker drivers directly, ensuring consistent sound quality and reducing the need for external equipment. They convert electrical signals into sound waves by amplifying audio input internally, providing greater control over volume and tone. This design offers convenience and efficiency, making active speakers ideal for professional audio setups and home entertainment systems.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Speakers
Passive speakers require an external amplifier to power their sound output, relying on wired connections to transmit audio signals. Active speakers have built-in amplifiers, enabling direct connection to audio sources for a more compact and convenient setup. Passive models offer flexibility in amplifier choice and upgrading, while active speakers provide optimized performance and ease of installation.
Sound Quality: Passive vs Active Speakers
Active speakers contain built-in amplifiers that optimize sound quality by precisely matching power output to speaker components, resulting in clearer audio and reduced distortion. Passive speakers rely on external amplifiers, which can affect sound performance depending on the amplifier's quality and compatibility. Integrated amplification in active speakers offers superior control over frequency response and dynamic range, enhancing overall audio fidelity.
Setup and Installation Compared
Active speakers require a simpler setup because they have built-in amplifiers, meaning you only need to connect the audio source and power supply. Passive speakers need an external amplifier or receiver, adding complexity to the installation process and requiring additional cables and components. Your choice will impact the ease and speed of setup, especially if you prefer a straightforward installation experience.
Flexibility and Customization
Active speakers offer greater flexibility and customization through adjustable EQ settings, multiple input options, and the ability to integrate with external amplifiers or processors. Passive speakers rely on external amplifiers for sound shaping, limiting direct customization but allowing you to choose and upgrade components separately. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hands-on control or a simpler, plug-and-play setup.
Cost Considerations
Passive speakers typically cost less than active speakers because they require an external amplifier, allowing you to upgrade components separately. Active speakers integrate amplifiers within the speaker enclosure, leading to higher initial costs but simplified setup and optimized performance. When budgeting, consider whether you prefer the flexibility to customize your audio system or the convenience of an all-in-one solution.
Best Use Cases for Passive and Active Speakers
Passive speakers are ideal for home theater systems and professional audio setups where custom amplification and precise control over sound output are desired. Active speakers are best suited for portable sound systems, desktop audio, and situations requiring integrated amplification for ease of use and quick setup. Choosing between passive and active speakers depends on factors like room size, power source availability, and the need for audio customization.
Which Speaker Type Should You Choose?
Choosing the right speaker type depends on your listening habits and environment; active speakers have built-in amplifiers, making them ideal for easy setup and portability, while passive speakers require an external amplifier, offering more customization for audiophiles. If you prefer a simple, all-in-one solution with fewer cables, active speakers are the better choice for your needs. For users who want to fine-tune sound quality and have a dedicated amplification system, passive speakers provide greater flexibility and scalability.
passive vs active speaker Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com