Balanced outputs use two signal lines with opposite polarities to reduce noise and interference, delivering cleaner audio especially over long cable runs, while single-ended outputs rely on a single signal line referenced to ground, which can be more susceptible to noise but often simpler and cost-effective. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right audio connection for your setup; read on to explore the benefits and applications of balanced and single-ended outputs.
Table of Comparison
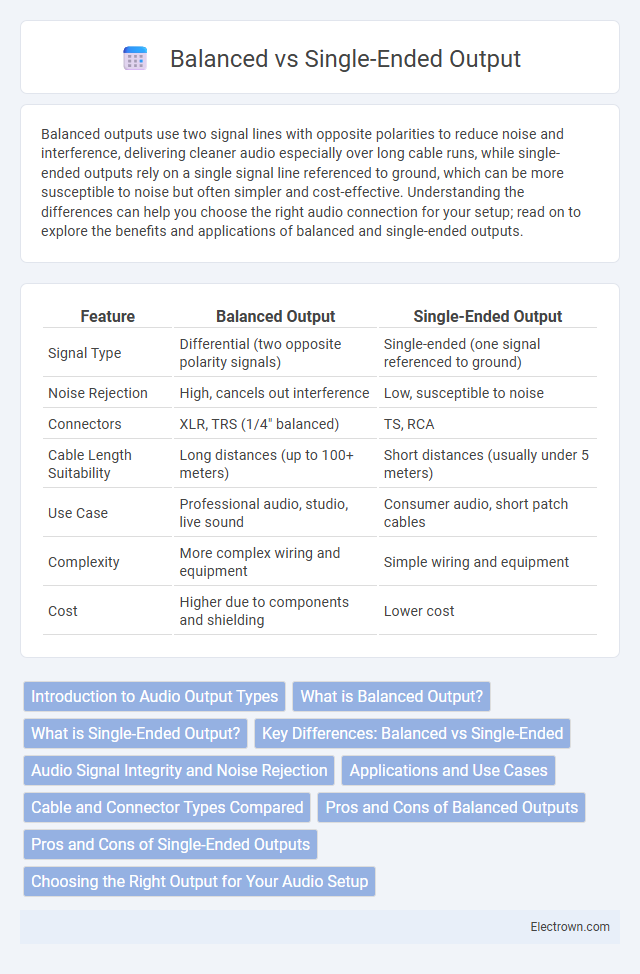
| Feature | Balanced Output | Single-Ended Output |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Differential (two opposite polarity signals) | Single-ended (one signal referenced to ground) |
| Noise Rejection | High, cancels out interference | Low, susceptible to noise |
| Connectors | XLR, TRS (1/4" balanced) | TS, RCA |
| Cable Length Suitability | Long distances (up to 100+ meters) | Short distances (usually under 5 meters) |
| Use Case | Professional audio, studio, live sound | Consumer audio, short patch cables |
| Complexity | More complex wiring and equipment | Simple wiring and equipment |
| Cost | Higher due to components and shielding | Lower cost |
Introduction to Audio Output Types
Balanced output uses two signal wires and a ground, reducing noise and interference for clearer audio, especially over long cable runs. Single-ended output relies on one signal wire and a ground, making it simpler but more susceptible to noise in complex setups. Understanding the difference ensures your audio equipment delivers optimal sound quality tailored to your environment.
What is Balanced Output?
Balanced output uses two signal wires and a ground to transmit audio, minimizing noise and interference over long cable runs by carrying equal and opposite signals. This method effectively cancels out electromagnetic interference, preserving audio quality in professional audio equipment and studio environments. Your choice of balanced output can significantly improve signal clarity and reduce hum compared to single-ended output.
What is Single-Ended Output?
Single-ended output transmits audio signals using one conductor and a ground, making it more susceptible to noise and interference compared to balanced output. This type of output is commonly found in consumer audio equipment and generally uses connectors such as RCA or TS (tip-sleeve) plugs. Understanding your single-ended output is crucial when connecting to other audio gear to ensure compatibility and optimal sound quality.
Key Differences: Balanced vs Single-Ended
Balanced outputs use two signal wires plus a ground, minimizing noise and interference through differential signaling, making them ideal for professional audio environments. Single-ended outputs rely on a single signal wire and ground, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness but are more susceptible to electromagnetic noise, suitable for short cable runs in consumer electronics. The choice depends on connectivity needs, noise rejection requirements, and the audio system's complexity.
Audio Signal Integrity and Noise Rejection
Balanced output significantly enhances audio signal integrity by transmitting two inverse signals that cancel out noise and interference, preserving clarity over long cable runs. Single-ended output, while simpler, is more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation, especially in noisy environments. Your audio setup benefits from balanced connections when optimal noise rejection and signal fidelity are critical for high-quality sound reproduction.
Applications and Use Cases
Balanced outputs are commonly used in professional audio environments, such as recording studios and live sound setups, where long cable runs require noise rejection and signal integrity. Single-ended outputs are typically found in consumer electronics, like home audio systems and headphones, where shorter cables reduce interference concerns. Your choice depends on the application's need for noise reduction, distance, and equipment compatibility.
Cable and Connector Types Compared
Balanced outputs typically use XLR or TRS cables that feature two signal wires plus a ground, providing better noise rejection over long cable runs ideal for professional audio setups. Single-ended outputs rely on TS or RCA connectors with a single signal wire and ground, making them more susceptible to interference and suited for shorter, consumer-grade connections. The choice between these cable and connector types significantly impacts signal integrity, especially in environments with electromagnetic interference.
Pros and Cons of Balanced Outputs
Balanced outputs offer superior noise rejection and reduced electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for professional audio environments and long cable runs. They maintain signal integrity by using two inverse signals, which enhances sound quality and minimizes hum and ground loop issues. However, balanced outputs demand more complex circuitry and cables, which can increase cost and size compared to simpler single-ended designs.
Pros and Cons of Single-Ended Outputs
Single-ended outputs offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for short cable runs and consumer audio devices. Their main drawbacks include higher susceptibility to noise and electromagnetic interference compared to balanced outputs, which can degrade audio quality over longer distances. Single-ended designs also typically provide lower signal-to-noise ratios, limiting their use in professional audio environments where pristine sound integrity is crucial.
Choosing the Right Output for Your Audio Setup
Balanced output provides superior noise rejection and interference reduction, making it ideal for professional audio environments and long cable runs. Single-ended output offers simplicity and compatibility with most consumer audio devices but is more susceptible to noise and signal degradation. Choosing the right output for your audio setup depends on the environment and equipment, ensuring optimal sound quality and signal integrity tailored to Your needs.
balanced vs single-ended output Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com